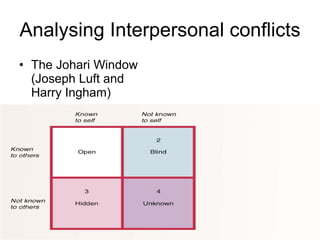
Conflict can occur at three levels: individual, interpersonal, and group. At the individual level, intra-individual conflict arises from competing needs, roles, and barriers between drives and goals. Interpersonal conflict stems from personal differences, lack of information, and environmental stress between parties. Analyzing conflicts using the Johari Window model can increase self-awareness and trust. Resolving conflicts may involve competing, collaborating, avoiding, accommodating, or compromising to satisfy interests or concerns of parties in conflict.