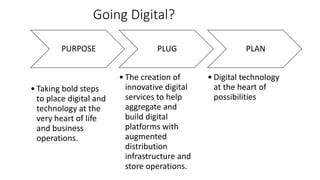
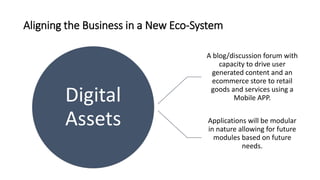
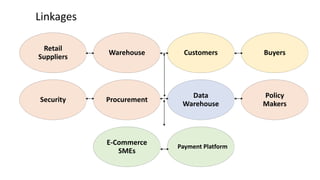
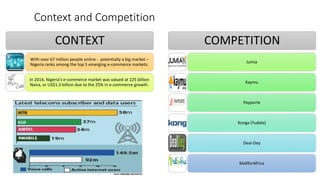
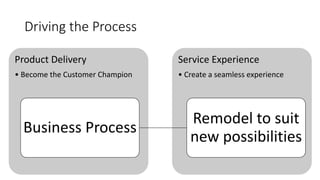
This document discusses digital transformation and how going digital changes business models. It covers how businesses are moving from analogue to digital models across various industries like publishing, commerce, banking, and news/film/music.
Some key points discussed include how the creation and aggregation of digital platforms and services can help businesses reinvent themselves, how understanding customer data and behavior is important for digital transformation, and how integrating digital technologies can accelerate this process for businesses. Case studies of digital businesses in industries like e-commerce, digital banking, and online news are also provided.