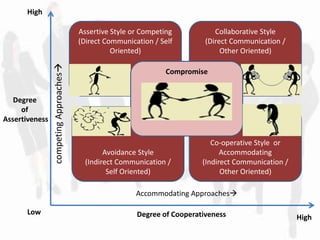
This document discusses conflict management and resolution. It defines conflict as an incompatibility of ideas between parties. There are five styles of handling conflict - competing, collaborating, compromising, avoiding, and accommodating. The goal of collaboration is to add value rather than subtract it by considering all perspectives, while compromise involves give-and-take. Causes of conflicts include poorly defined goals, divergent values, and lack of trust or cooperation. Conflicts can result in stress, absenteeism, and decreased productivity if poorly managed but can stimulate competition if well managed.