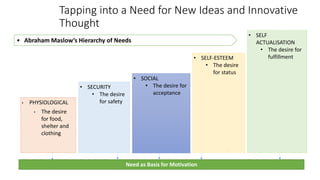
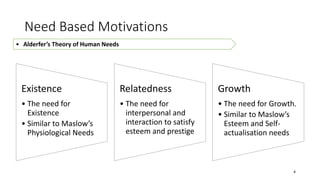
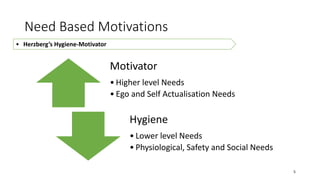
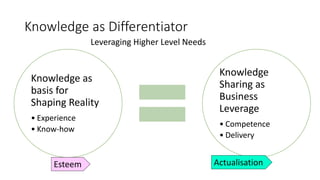
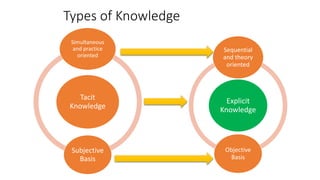
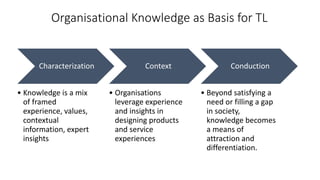
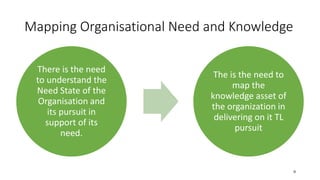
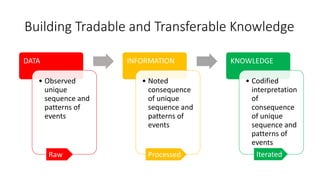
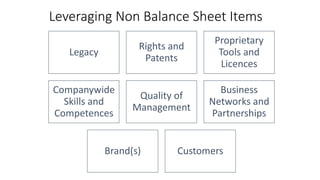
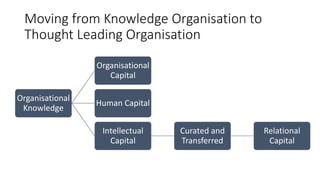
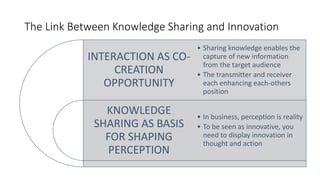
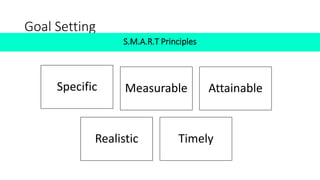
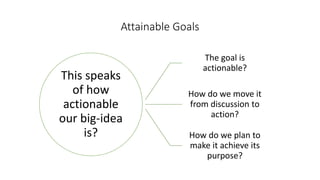
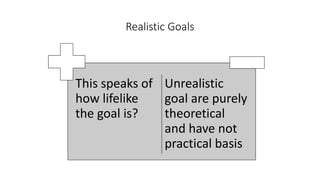
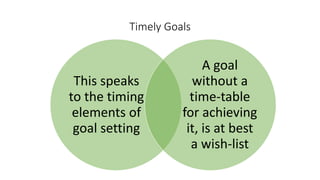
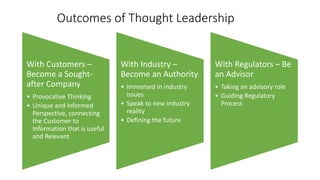
The document discusses establishing thought leadership through goal setting. It first covers understanding organizational needs and knowledge based on theories like Maslow's hierarchy of needs. It then discusses mapping the organization's needs and knowledge assets and developing tradable and transferable knowledge. The document outlines SMART principles for setting specific, measurable, attainable, realistic and timely thought leadership goals that leverage the organization's knowledge resources and produce outcomes with customers, industry and regulators.