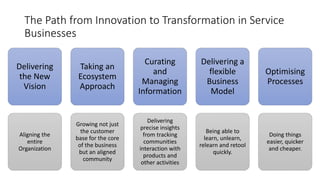
The document discusses the distinction between creativity and innovation, emphasizing that creativity involves intuitive decision-making while innovation pertains to creating new and valuable solutions in response to changing market demands. It outlines the stages of the creative process and details the importance of innovation in addressing rising needs and competition, along with its various forms such as product, process, and marketing innovations. Lastly, it highlights the factors driving innovation and the necessity for organizations to adapt and transform in a rapidly evolving environment.