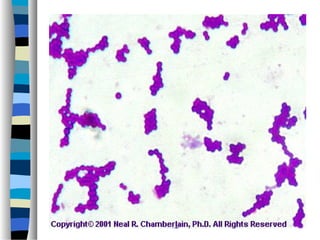
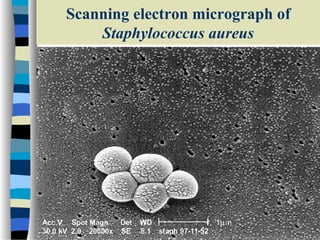
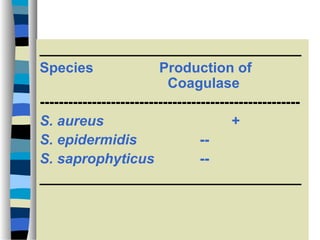
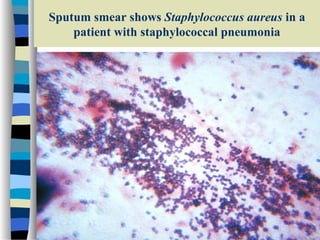
This document discusses Staphylococcus, including S. aureus. It notes that Staphylococcus is a facultative anaerobic, gram-positive coccus that forms grape-like clusters. It distinguishes between coagulase-positive and coagulase-negative species. S. aureus is described as the most virulent species, producing toxins and enzymes that can cause infections like impetigo, pneumonia, toxic shock syndrome, and food poisoning. Laboratory diagnosis and treatments like antibiotics are also summarized.