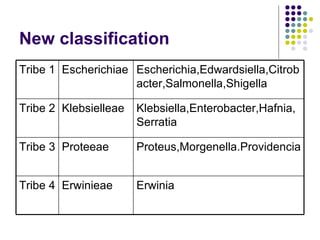
The document discusses various species of Enterobacteriaceae including E. coli, Salmonella, Shigella, Klebsiella, and Proteus. It covers their classification, characteristics, pathogenicity, mechanisms of infection, clinical presentations including urinary tract infections and diarrheal diseases, and methods for identification and diagnosis in clinical microbiology laboratories.