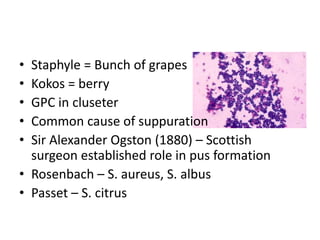
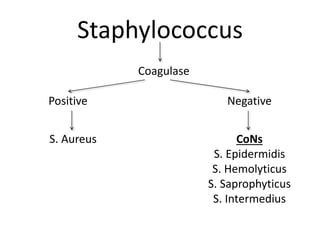
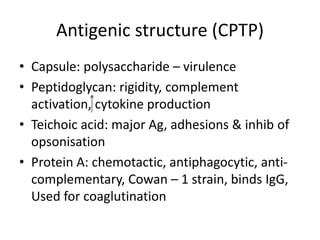
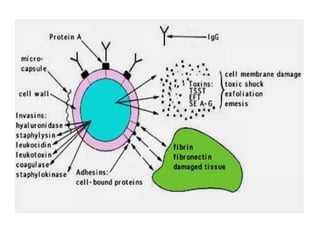
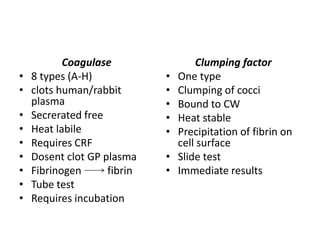
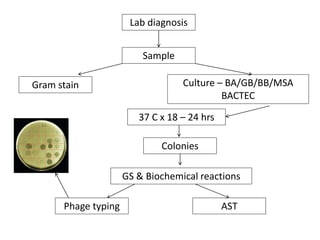
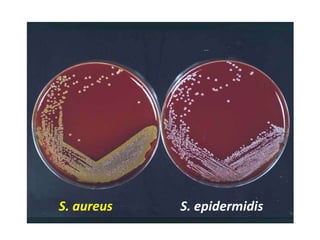
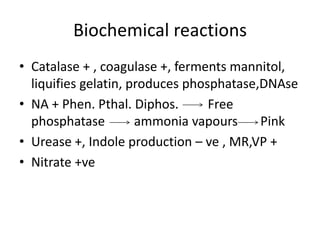
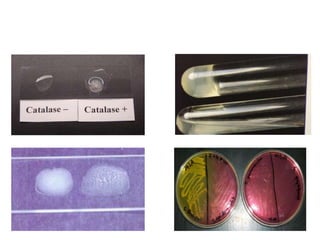
Staphylococcus is a genus of gram-positive cocci that commonly causes infections in humans. Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most important pathogenic species, able to produce several toxins and enzymes that contribute to its virulence. These include hemolysins, leukocidins, enterotoxins, toxic shock syndrome toxin, and exfoliative toxins. S. aureus can cause a variety of infections through cutaneous, respiratory, or deep tissue routes. Laboratory identification involves gram stain morphology, culture characteristics such as catalase and coagulase production, and biochemical testing. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus is an important antibiotic resistant variant.