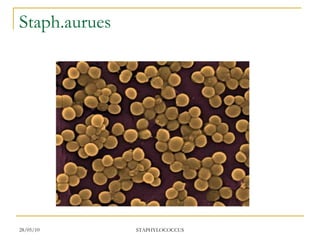
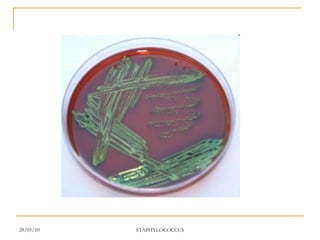
Staphylococcus aureus is a common cause of skin infections that forms clusters resembling bunches of grapes under the microscope. It is resistant to many antibiotics but can be treated with penicillin, methicillin, or vancomycin. S. aureus produces several virulence factors like toxins and enzymes that allow it to infect humans and cause diseases ranging from minor skin infections to life-threatening conditions like toxic shock syndrome. Laboratory tests help identify S. aureus and determine appropriate antibiotic treatment.