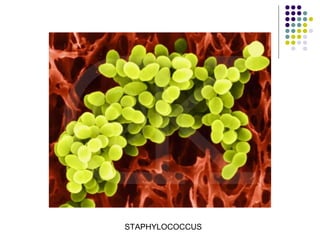
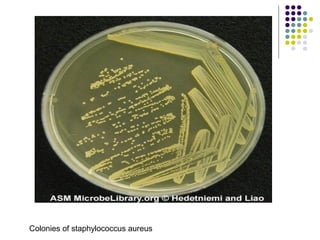
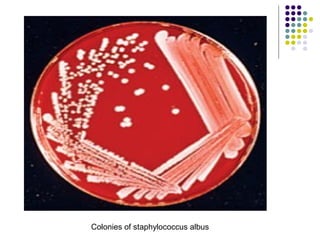
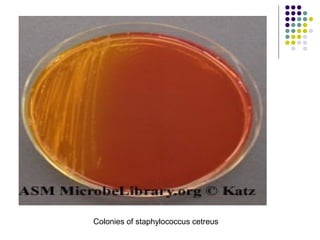
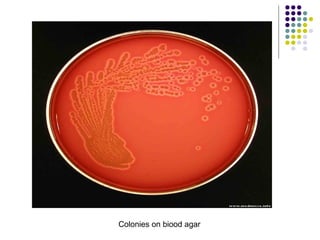
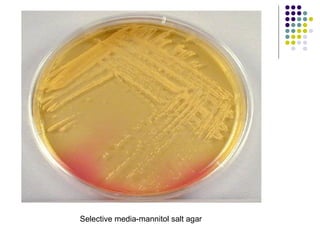
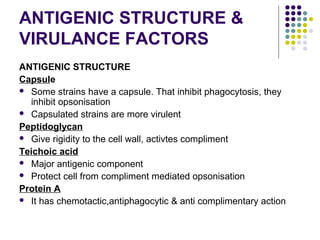
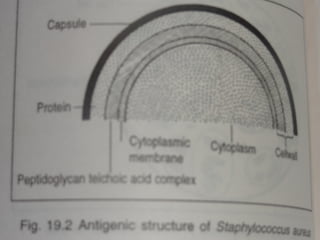
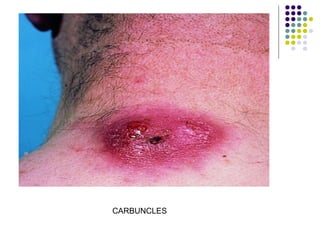
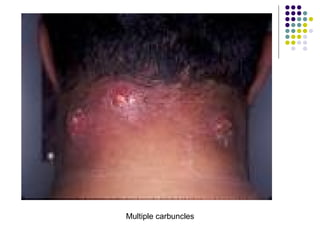
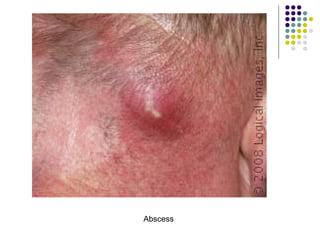
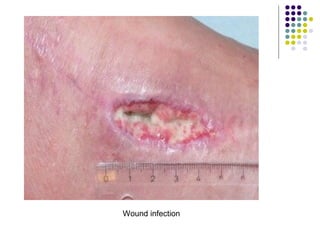
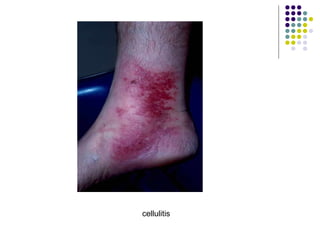
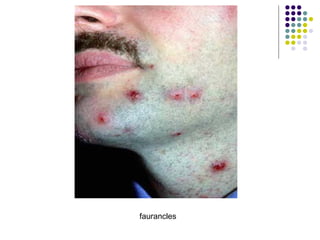
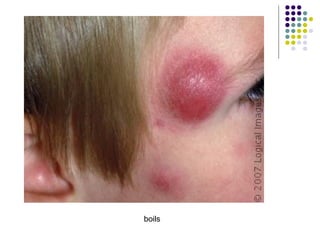
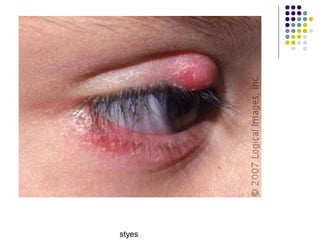
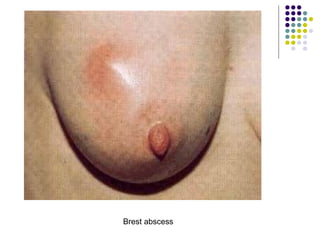
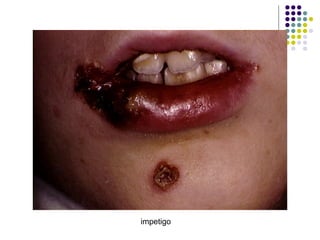
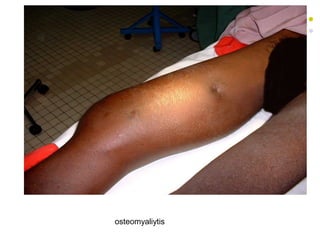
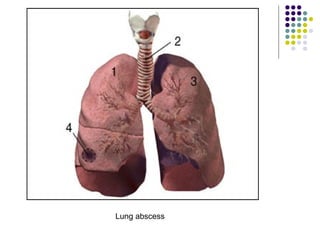
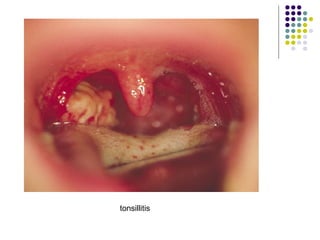
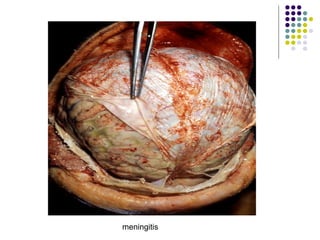
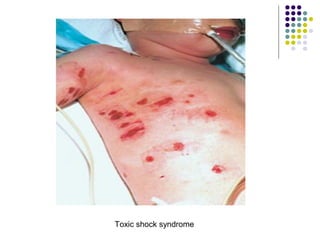
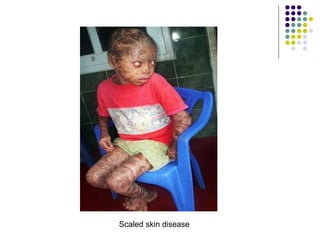
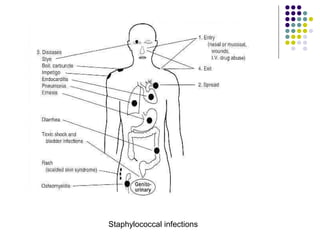
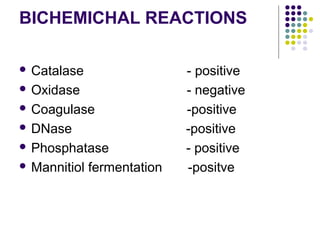
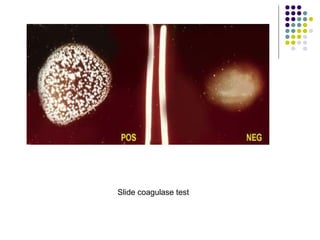
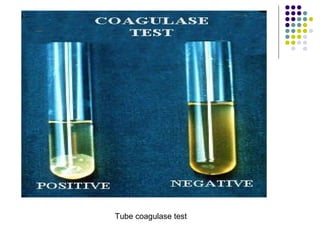
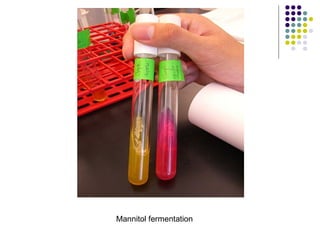
Staphylococcus is a common cause of skin infections in humans. Staphylococcus aureus is an important pathogenic species. It is gram-positive, catalase-positive, and produces coagulase. S. aureus causes a variety of infections, including skin and soft tissue infections like boils and abscesses. It can also cause pneumonia, osteomyelitis, toxic shock syndrome, and food poisoning. Laboratory diagnosis involves culturing specimens on blood agar and performing tests like the coagulase test and mannitol fermentation. Treatment involves antibiotics like penicillin, cloxacillin, or vancomycin for resistant strains.