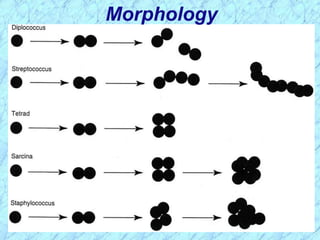
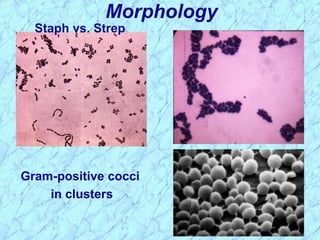
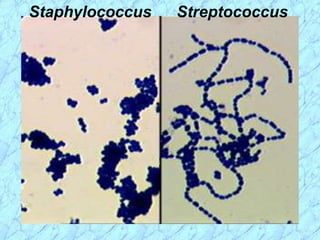
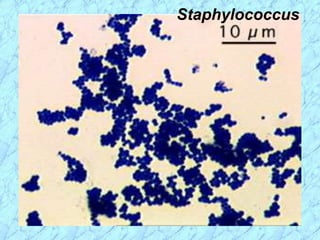
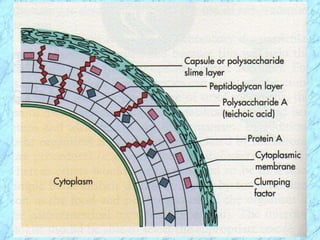
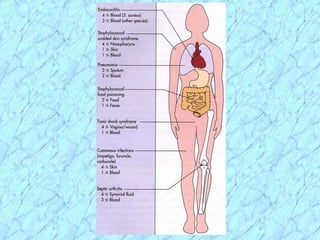
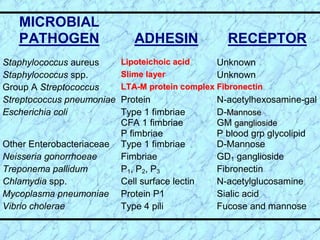
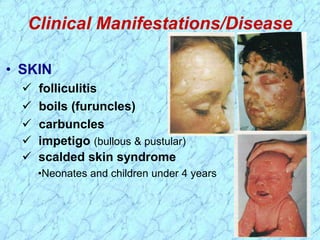
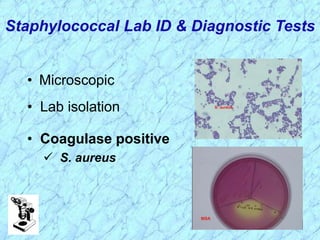
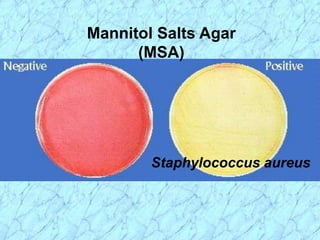
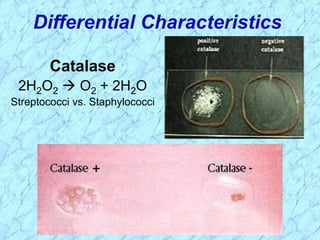
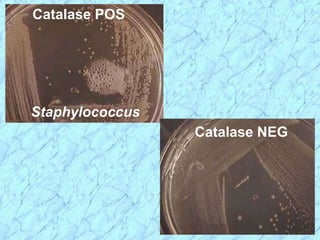
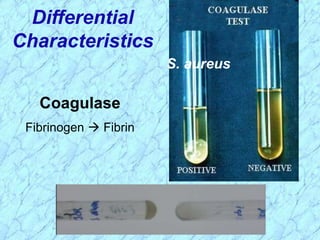
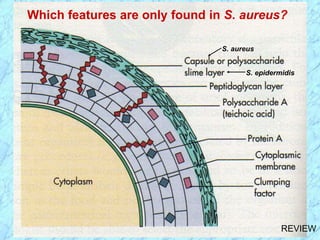
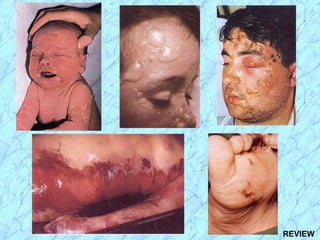
This document discusses Staphylococcus bacteria, including their classification, morphology, virulence factors, pathogenesis, and clinical manifestations. It focuses on S. aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci like S. epidermidis. Key points include: S. aureus is distinguished from other staphylococci by being coagulase-positive; virulence factors include exotoxins and cell-associated components like capsules; infections range from minor skin infections to serious conditions like pneumonia, toxic shock syndrome, and endocarditis. Treatment involves antibiotics like penicillins, cephalosporins, and clindamycin.