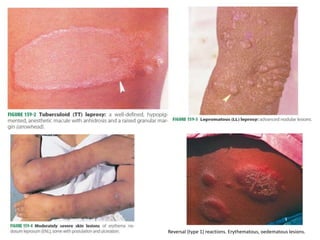
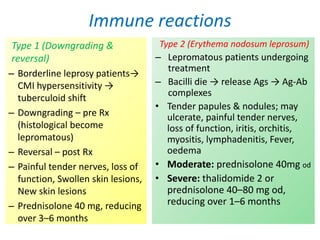
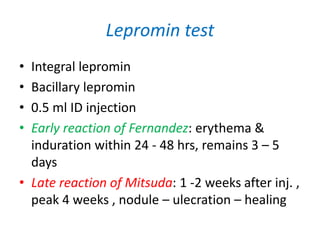
Leprosy is a chronic infection caused by Mycobacterium leprae that primarily affects the skin and peripheral nerves. It was first identified and isolated in 1873 by Gerhard Hansen in Norway. While leprosy has affected humans for thousands of years, it remains endemic in some developing countries today. Treatment involves multidrug therapy with rifampicin, dapsone, and clofazimine over the course of months to years depending on the type of leprosy.