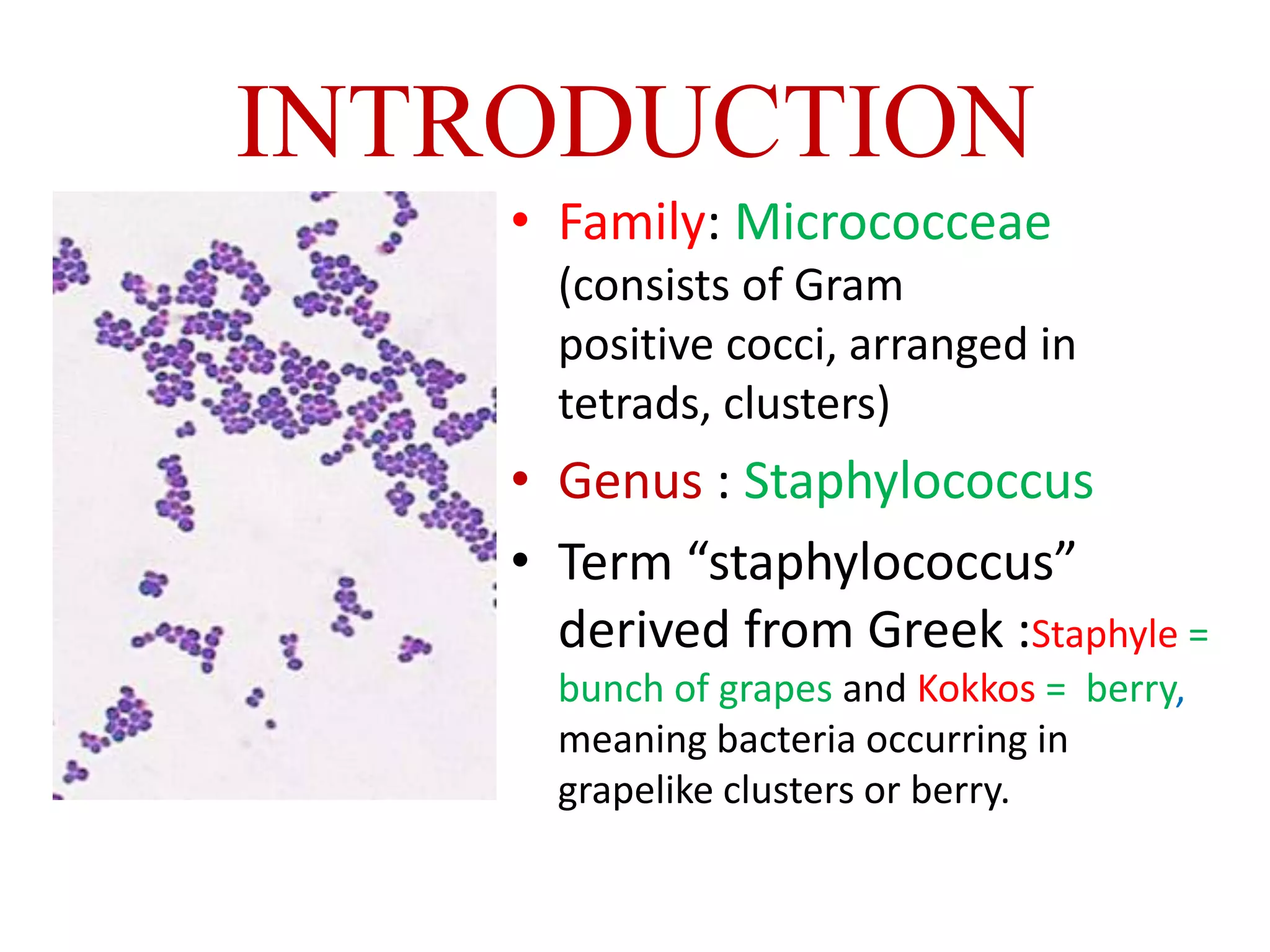
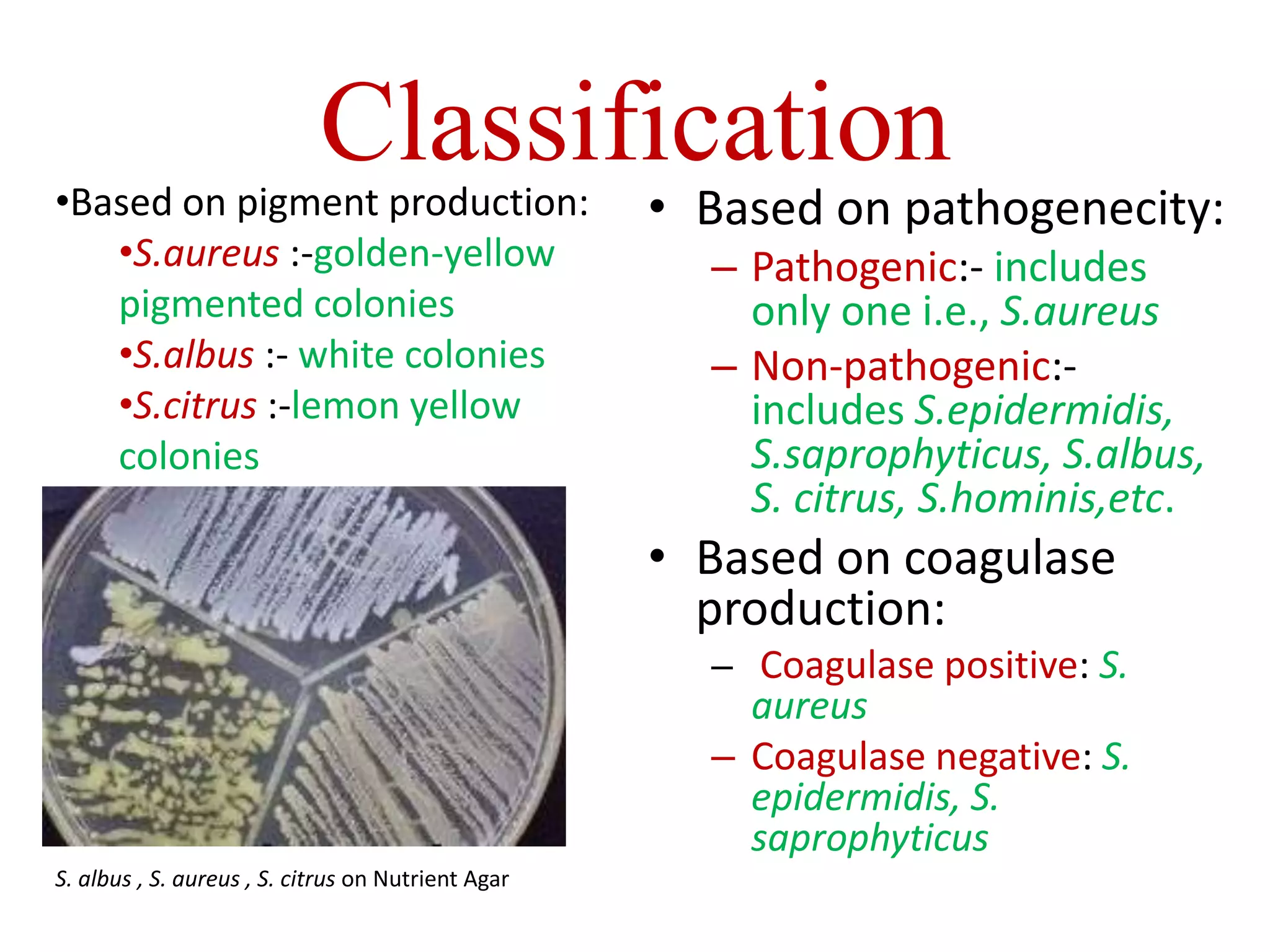
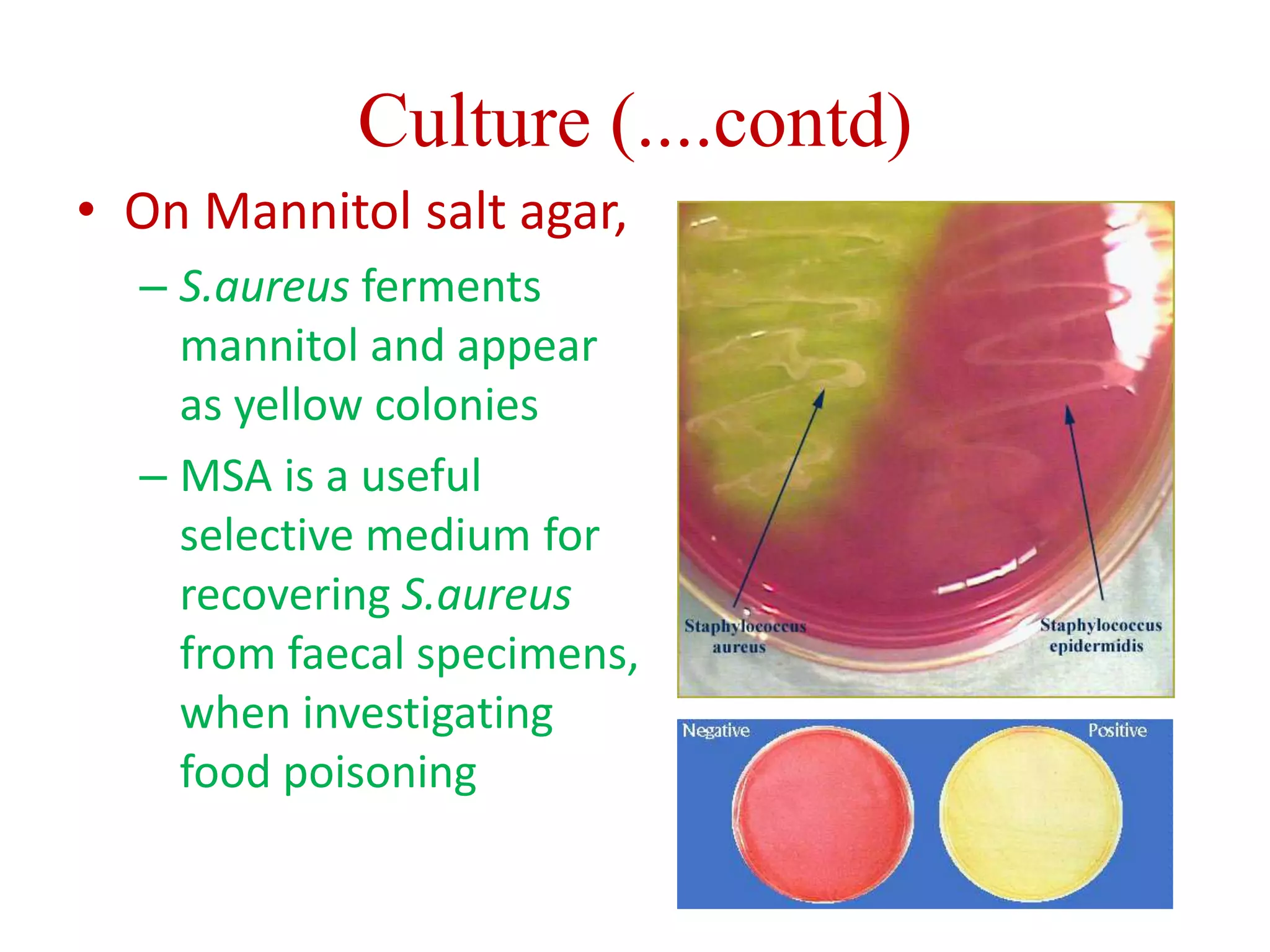
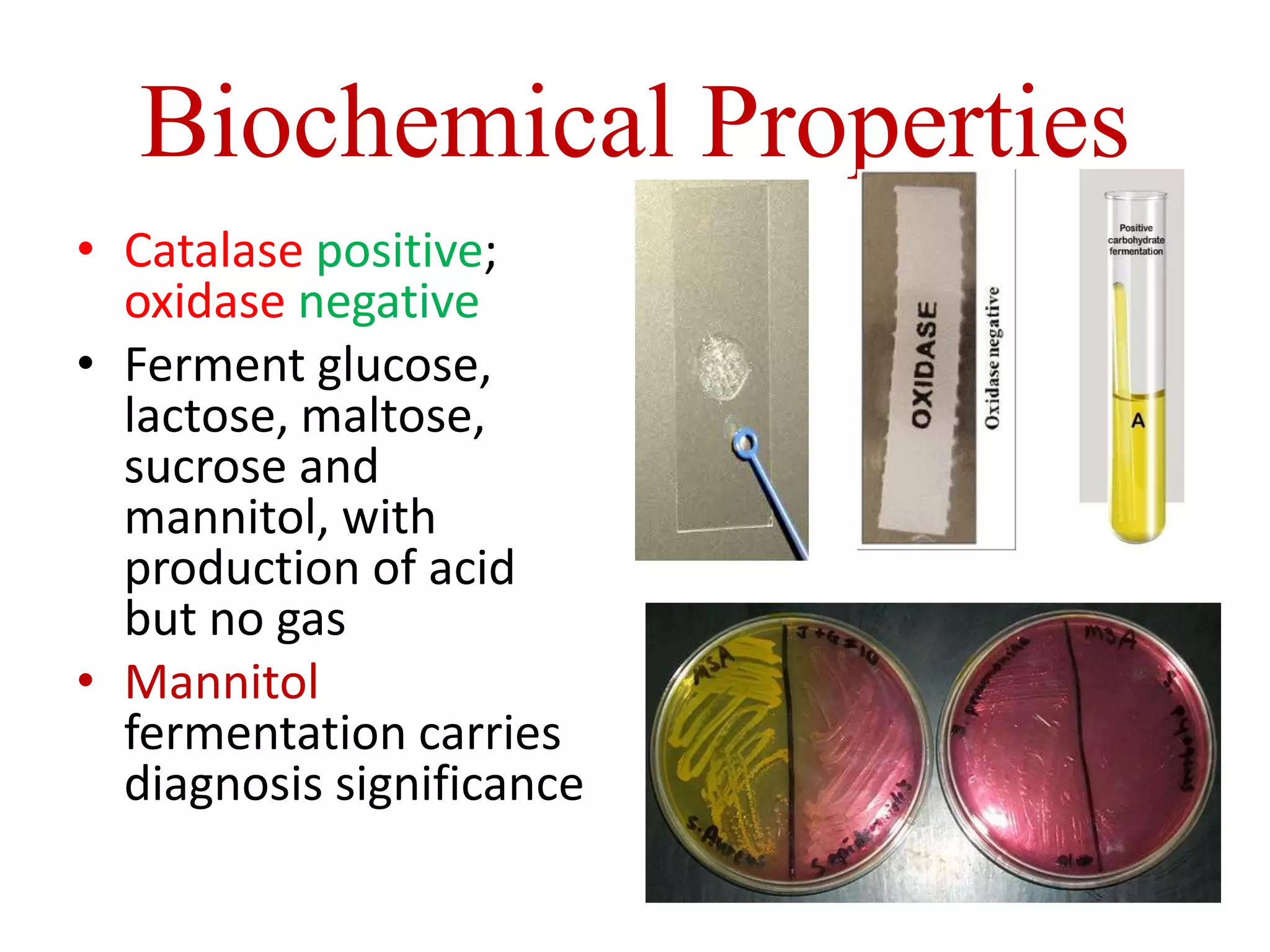
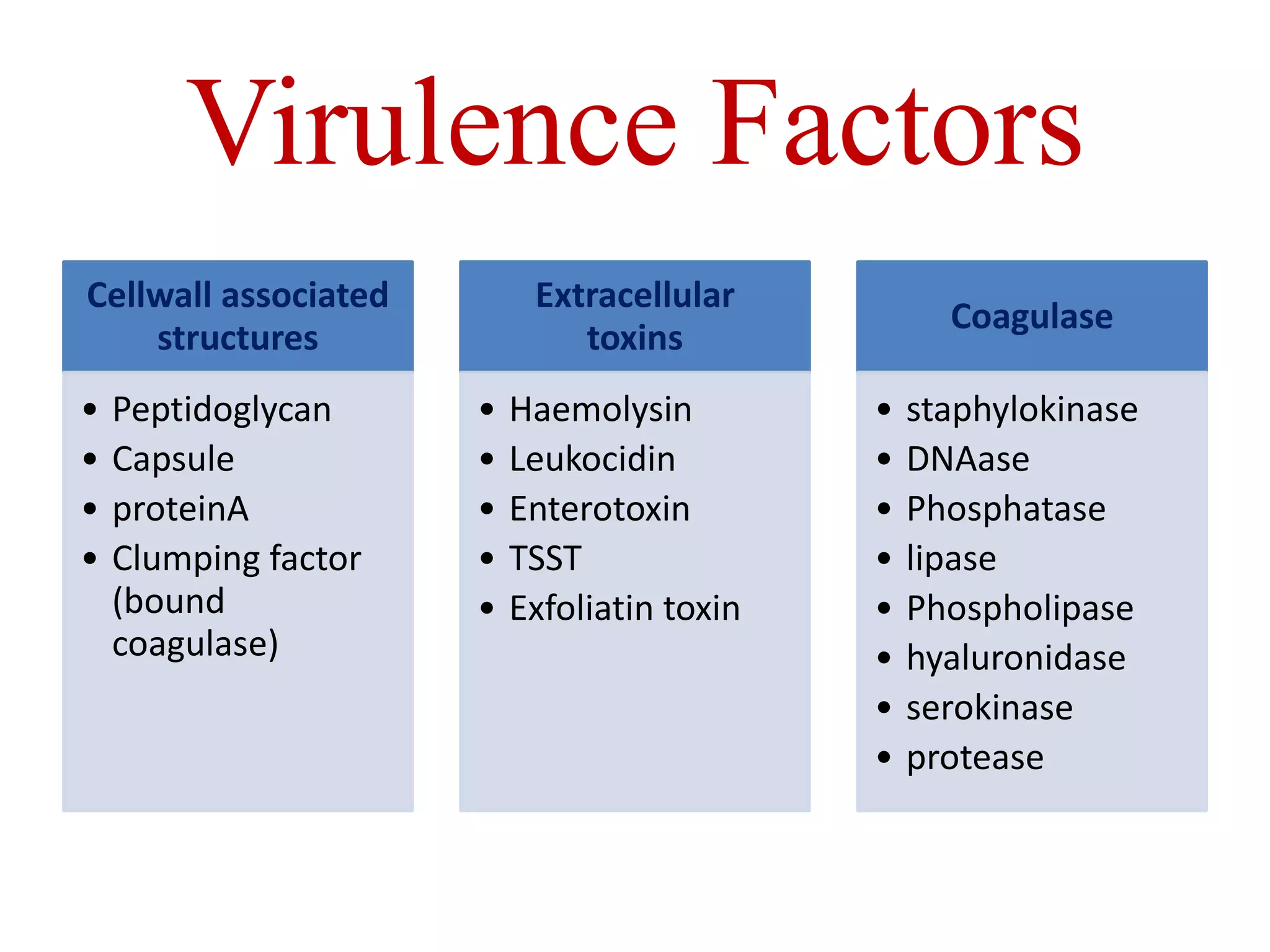
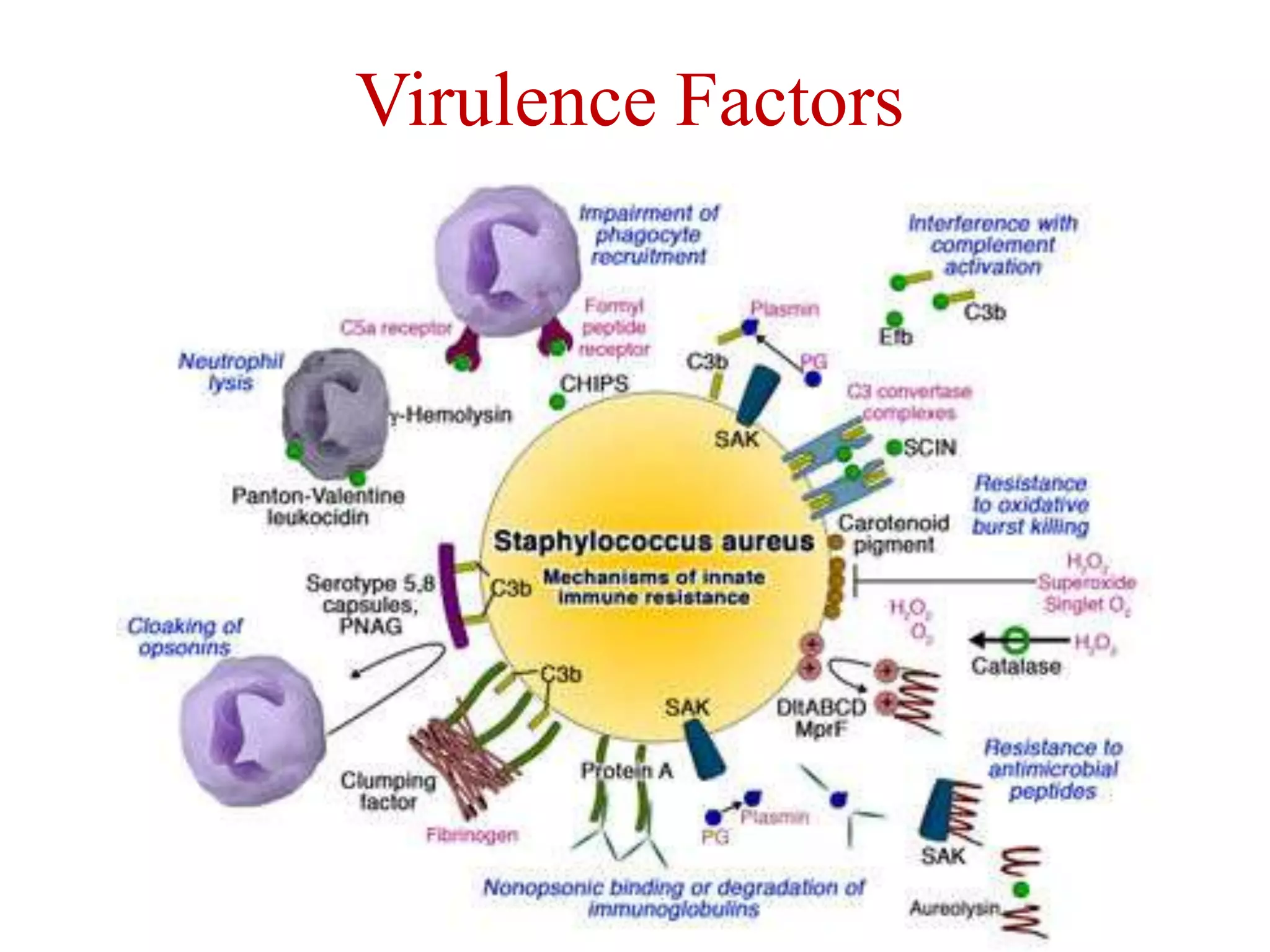
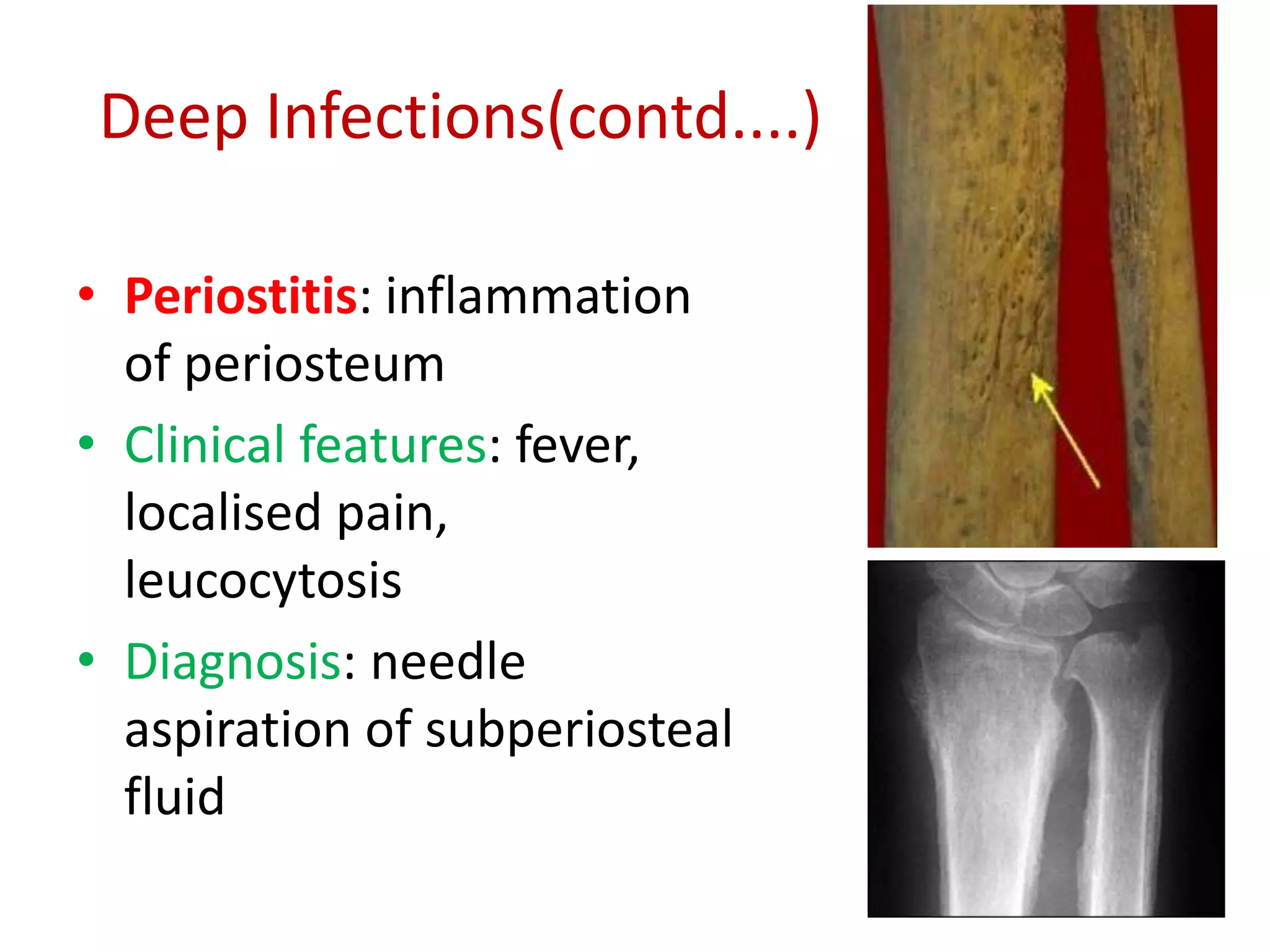
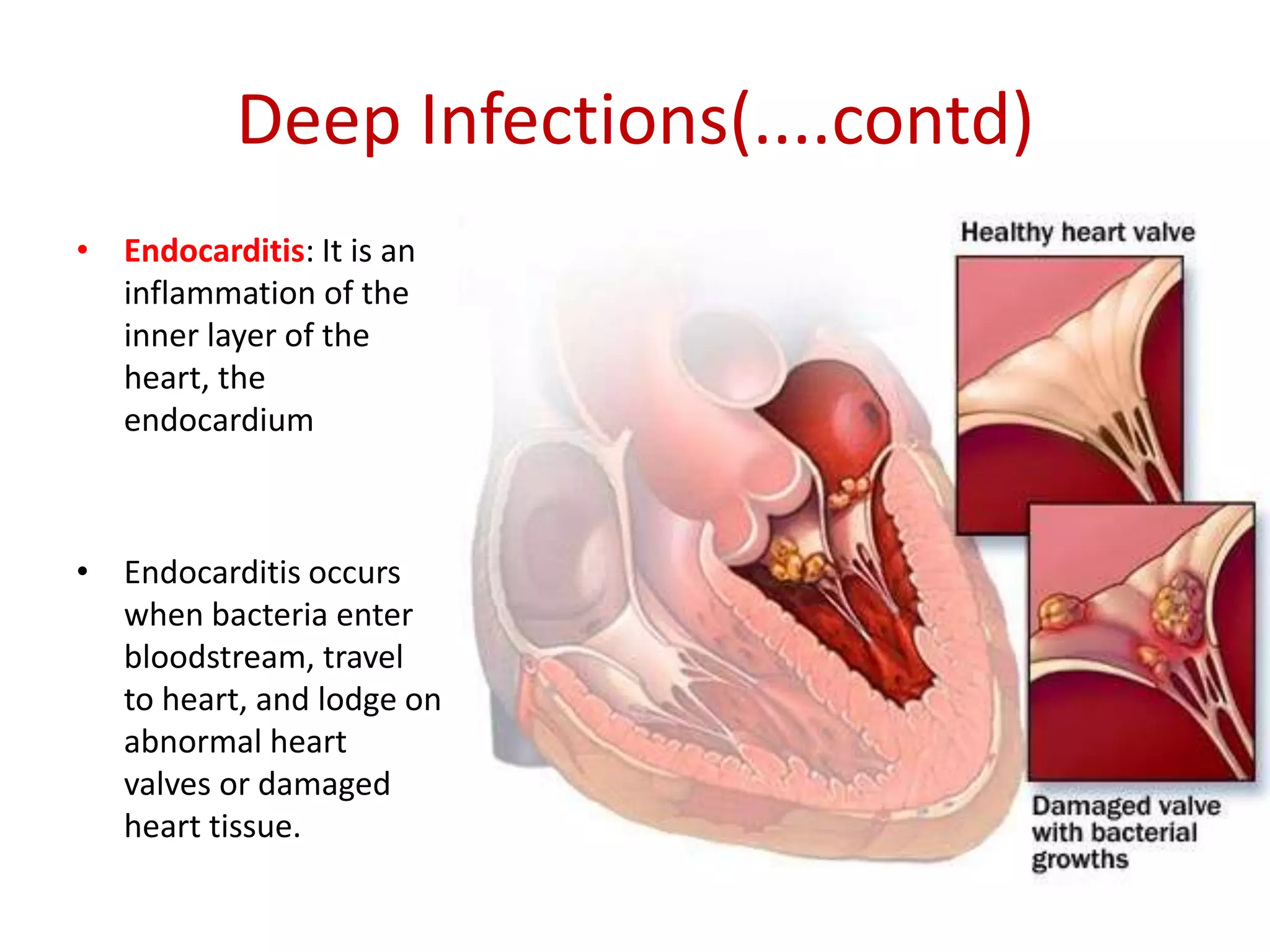
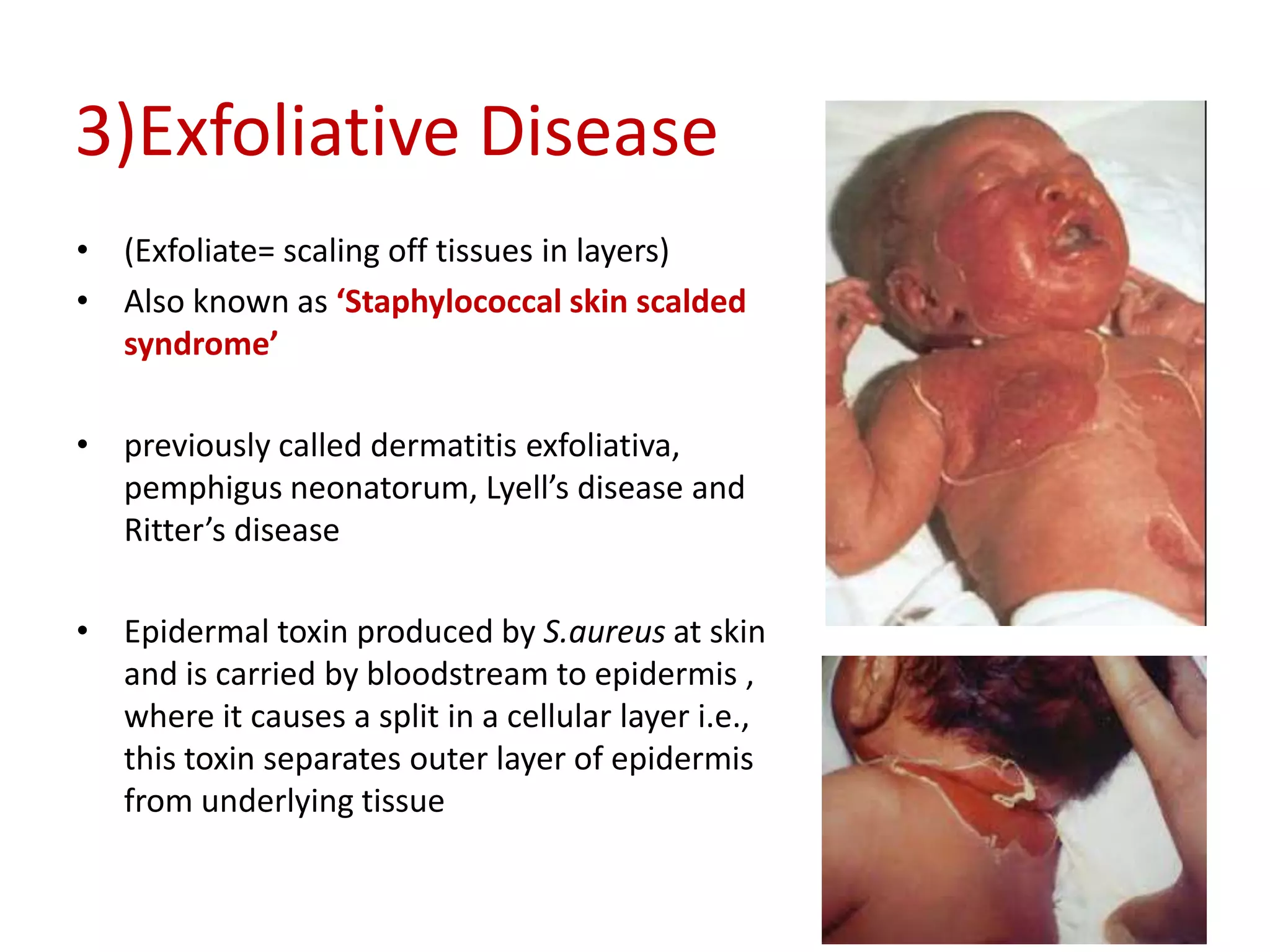
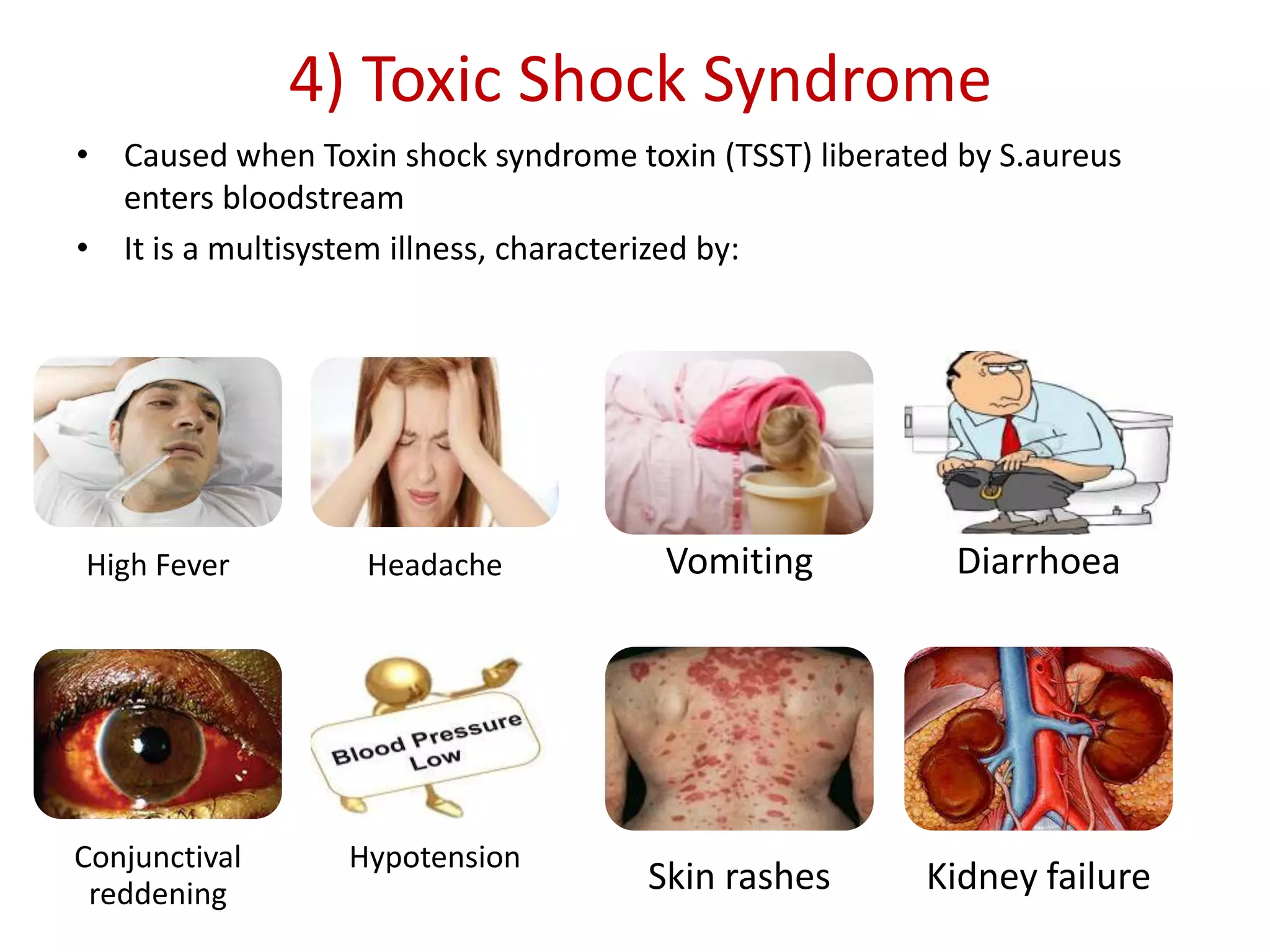
Staphylococci are spherical bacteria that occur in grape-like clusters. Staphylococcus aureus is an important human pathogen that can cause a variety of infections, from minor skin infections to life-threatening conditions like toxic shock syndrome and endocarditis. S. aureus produces several virulence factors like toxins and enzymes that damage tissues and evade the immune system. Laboratory diagnosis involves culture, microscopy, and tests like coagulase to identify S. aureus. Antibiotics are used to treat infections, and prevention focuses on hygiene and safe food handling. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus is an antibiotic resistant form that is more difficult to treat.










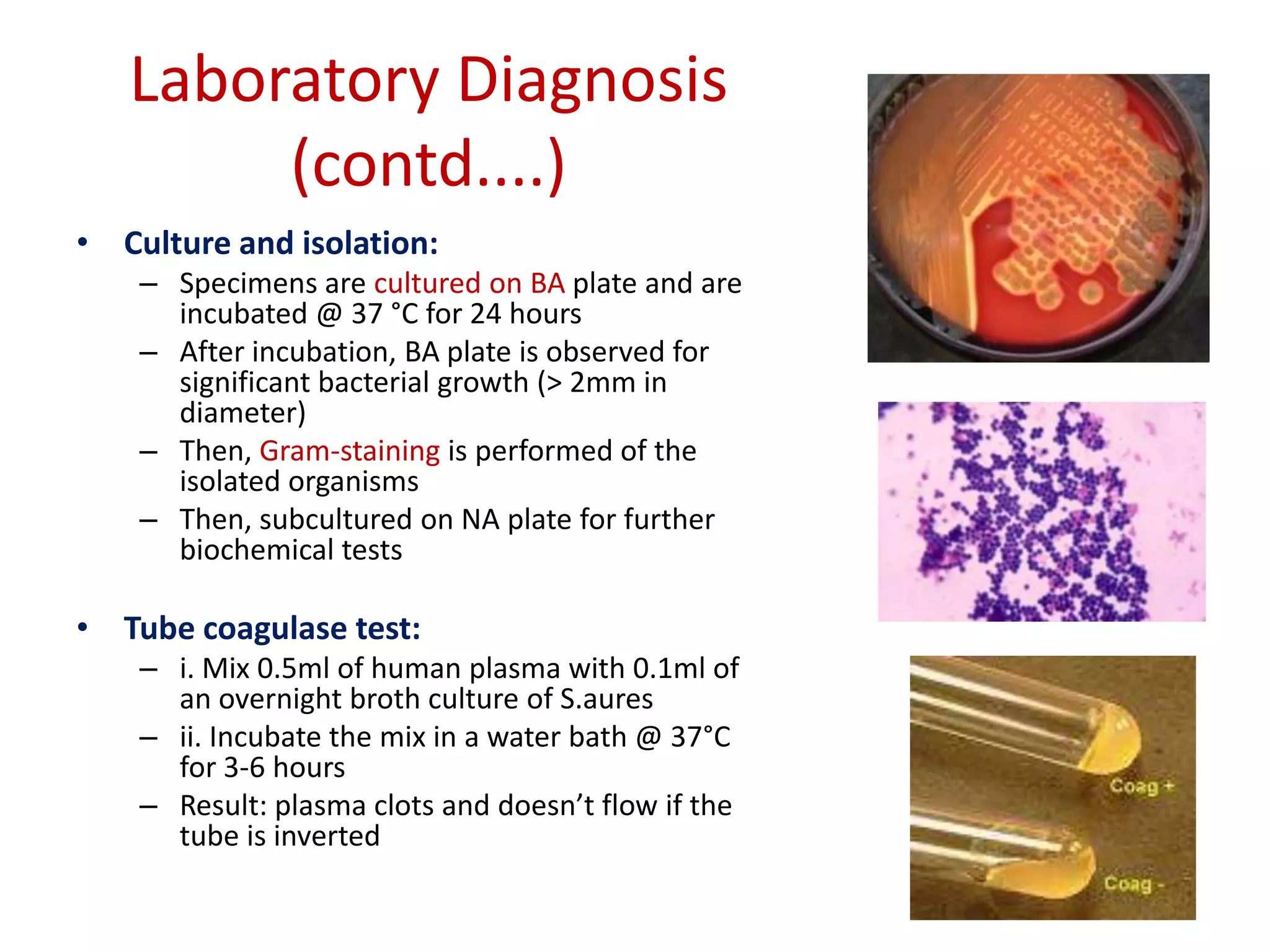
![Laboratory Diagnosis (contd....)
B. Bacteriological
Investigation:
• Specimens:
– Pus: from wound or
abscess or burns]
– Nasal Swab: from
suspected carrier
– Food: to diagnose
staphylococcal intoxication
– Blood: to diagnose
endocarditis and
bacteremia
– Sputum: to diagnose lower
respiratory tract infection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staphylococcus-131009035940-phpapp01/75/Staphylococcus-32-2048.jpg)