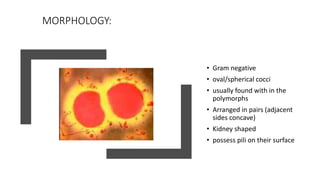
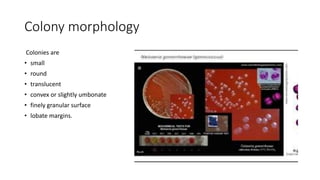
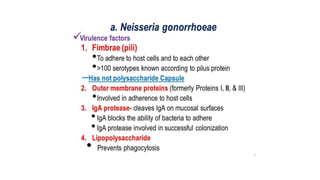
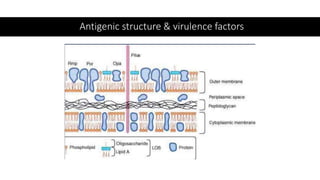
Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the causative agent of gonorrhea, first identified in 1879, characterized as gram-negative cocci that require specific culture media for growth. The bacteria infects mucosal surfaces, leading to conditions like urethritis and pelvic inflammatory disease, with different manifestations in men and women. Treatment has evolved due to antibiotic resistance, with ceftriaxone or ciprofloxacin being current options, while prevention focuses on early detection and education.