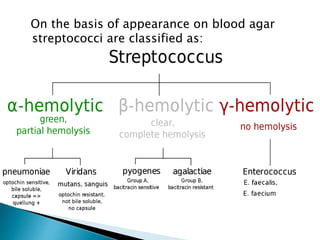
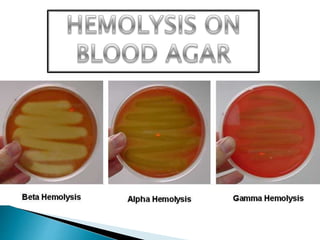
This document discusses the classification and identification of streptococci bacteria. It describes their morphology, culture characteristics, biochemical reactions, Lancefield grouping, and clinical significance. Key streptococci groups discussed include Group A (Streptococcus pyogenes), Group B (Streptococcus agalactiae), Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Enterococcus species. Identification is based on colony appearance on blood agar, Gram staining, and biochemical tests like catalase and bile solubility.