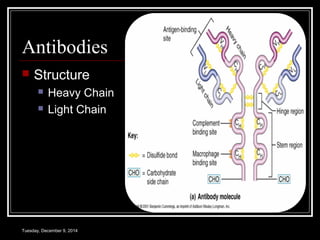
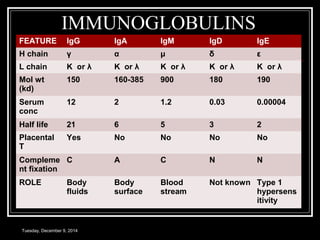
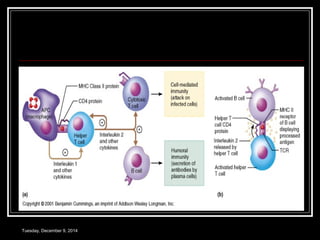
The document discusses the immune system and immunity. It provides an overview of the key components of the immune system including the architecture, cells, tissues, antigens, antibodies, immune responses, and immune mechanisms. The objectives are to understand the structure of the immune system, the concepts of immunity, antigens and antibodies, how the immune response develops, and other immune mechanisms.