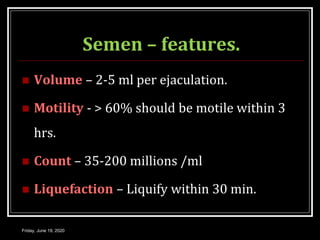
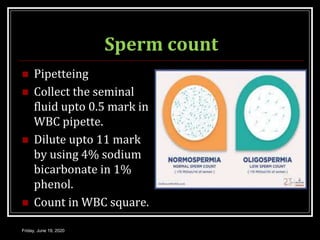
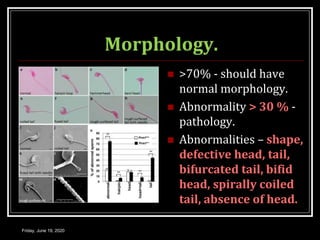
This document discusses semen analysis, including its importance in evaluating male fertility and after vasectomy. It outlines normal values for semen volume, motility, count, liquefaction, pH, and fructose. The procedure for semen analysis is described, which involves examining a freshly collected semen sample under a microscope after 30 minutes to assess various parameters. Precautions like abstaining for 2 days prior are noted. The roles of seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral glands in contributing secretions and nutrients to semen are briefly covered.