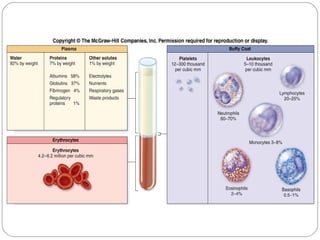
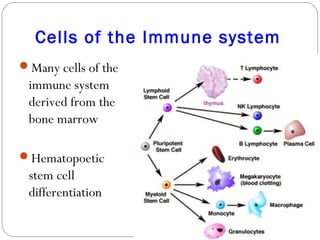
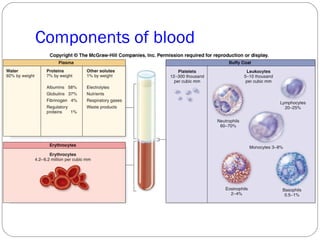
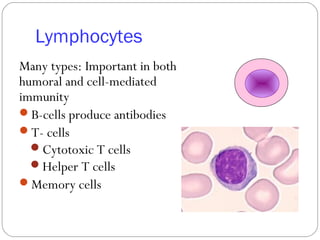
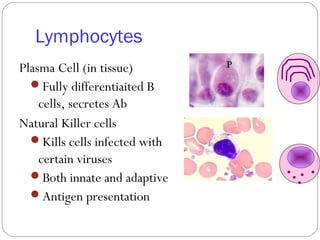
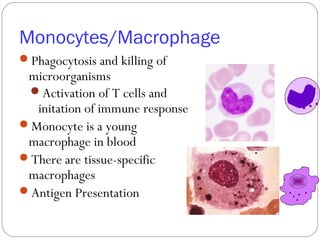
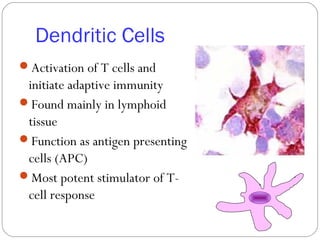
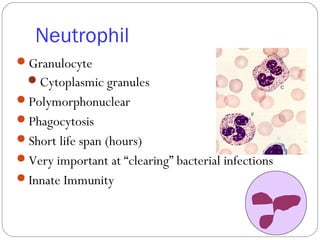
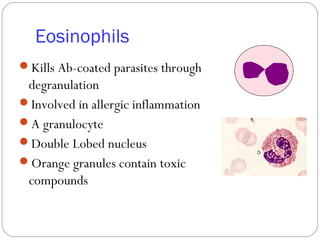
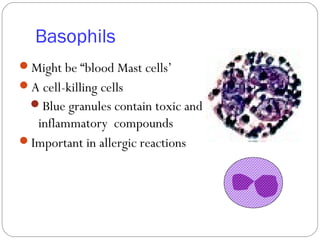
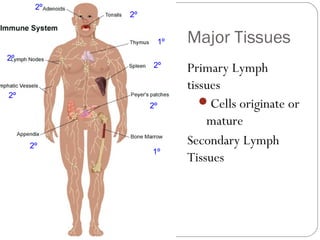
Immunology is the study of the physiological mechanisms that defend the body against pathogens like bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. The immune system uses innate and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity acts from the start of an infection non-specifically, while adaptive immunity develops antigen-specific B and T lymphocytes that provide immunological memory. Key cells involved include lymphocytes, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and granulocytes like neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. Antibodies, cytokines and cellular responses work together to recognize and eliminate invading pathogens.