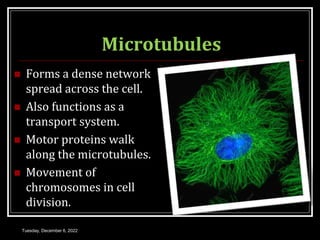
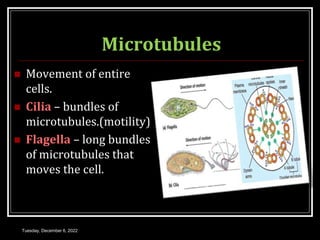
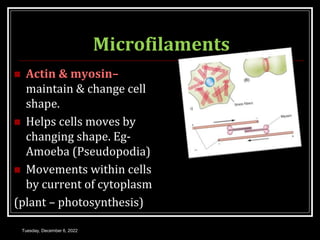
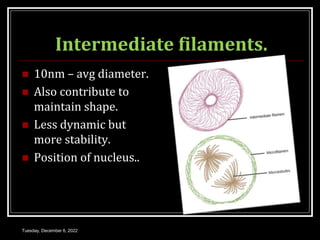
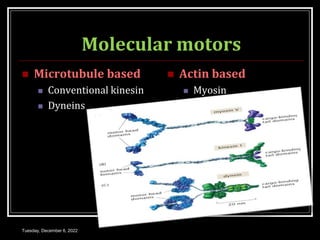
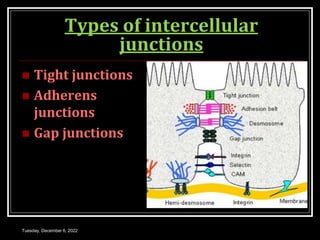
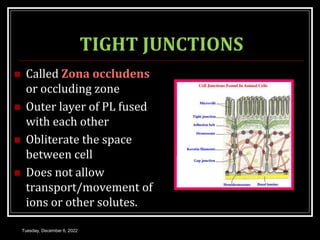
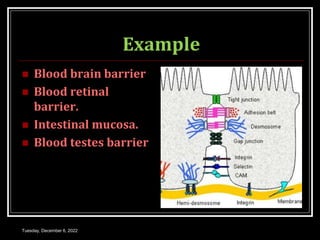
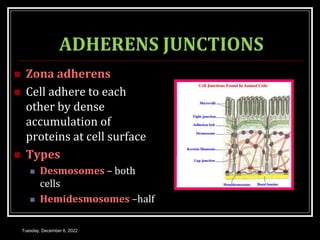
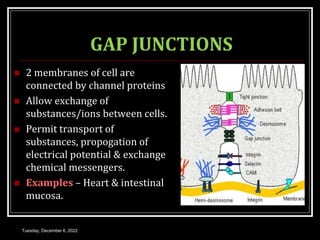
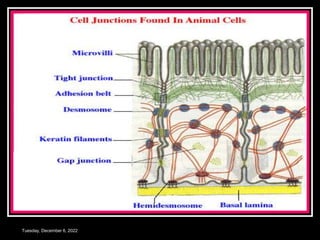
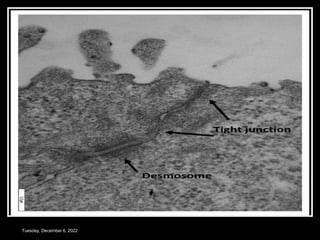
This document outlines a class on cell junctions and intercellular communication. The objectives are to understand the cytoskeleton, molecular motors, intercellular communication, types of intercellular communication, and cell adhesion molecules. The cytoskeleton is made up of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments and provides shape, movement, and anchorage for cells. Intercellular communication allows for signaling between cells via tight junctions, adherens junctions, and gap junctions. Cell adhesion molecules like cadherins, selectins, and integrins mediate adhesion between cells.