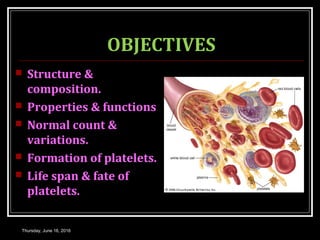
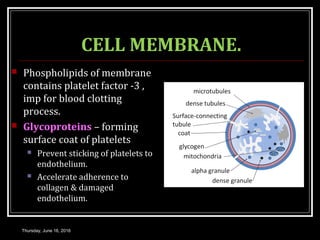
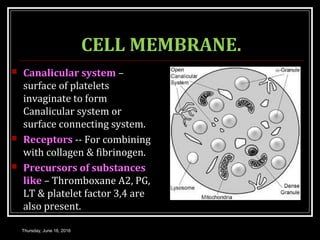
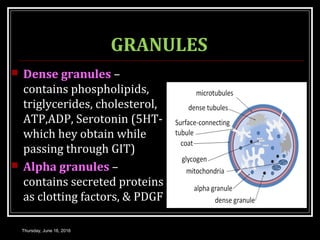
This document discusses the structure, composition, functions, formation and lifespan of platelets. It provides details on platelets, including that they are the smallest blood cells, lack a nucleus, and function in hemostasis through adhesion, aggregation and clot formation. Platelets are formed from megakaryocytes in the bone marrow, have a lifespan of 8-12 days, and are destroyed by macrophages in the spleen.