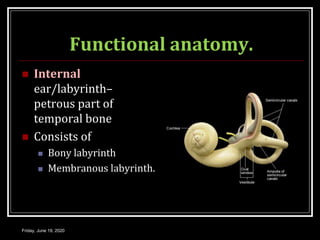
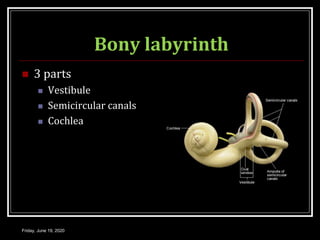
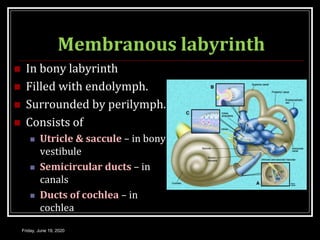
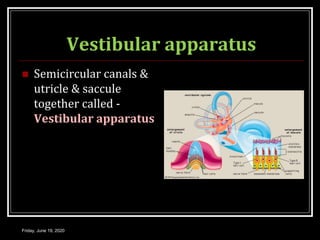
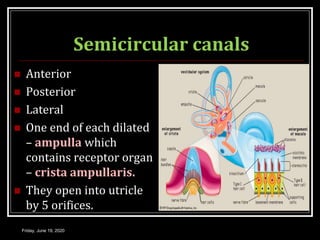
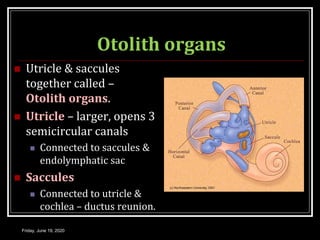
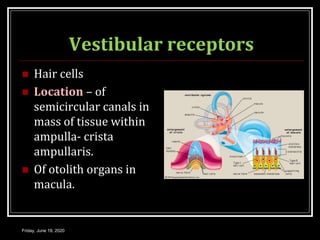
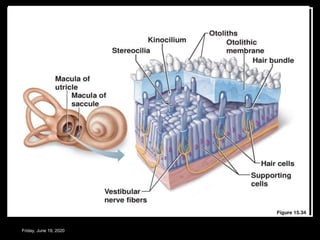
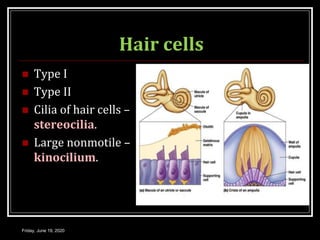
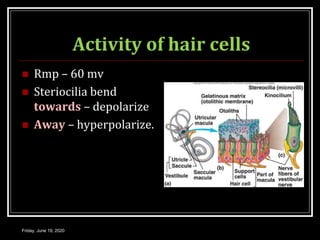
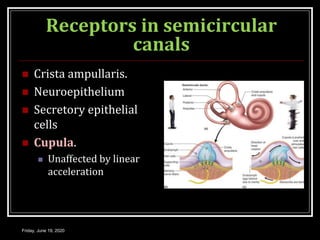
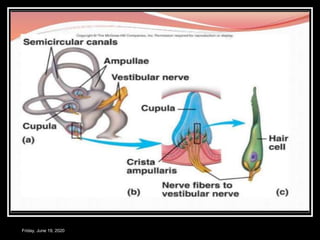
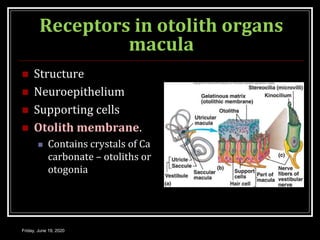
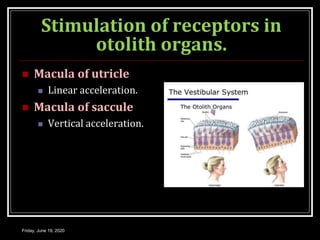
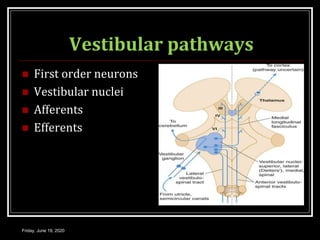
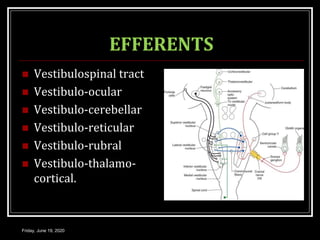
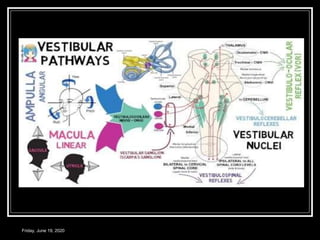
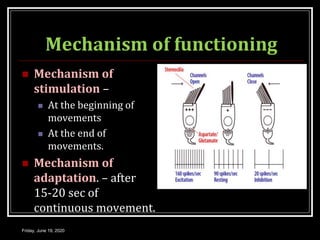
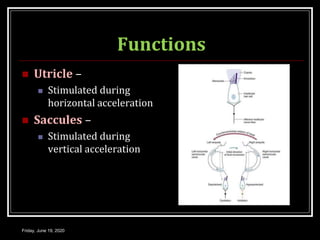
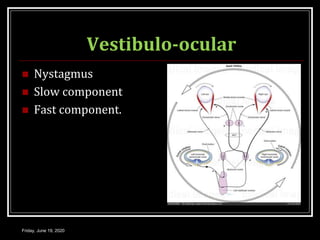
The document discusses the anatomy and functions of the vestibular apparatus. It describes the vestibular apparatus as consisting of the semicircular canals, utricle, and saccule located in the inner ear. These contain hair cells that act as receptors and detect head movement and acceleration. When stimulated, the hair cells trigger vestibular pathways that connect to the brainstem and mediate reflexes for eye and body movements to maintain equilibrium and posture. The vestibular apparatus plays an important role in functions such as balance, spatial orientation, and eye movement coordination.