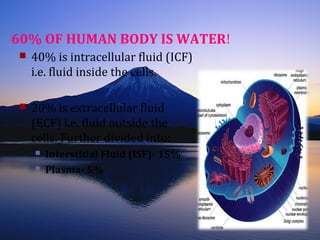
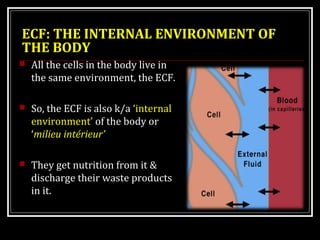
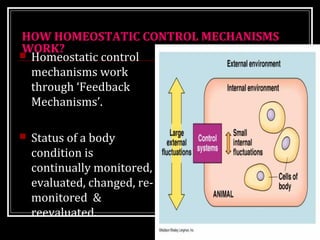
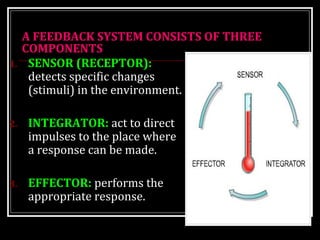
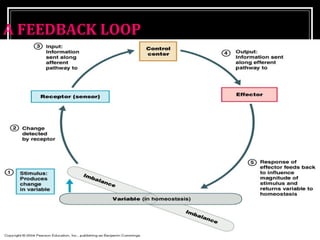
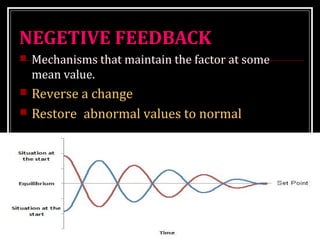
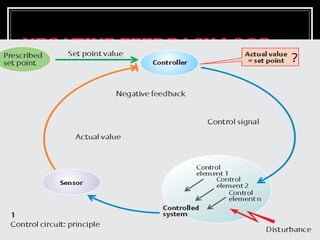
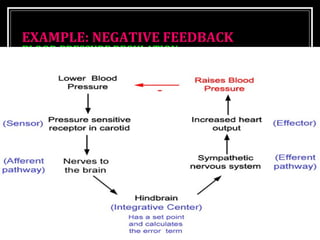
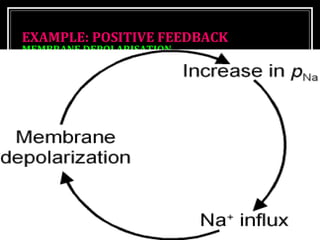
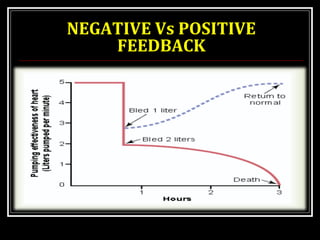
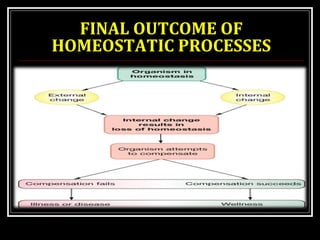
This document discusses homeostasis, which refers to the maintenance of stable internal conditions in the body despite changes in the external environment. It describes how unicellular organisms evolved internal environments as multicellular organisms developed. The human body maintains homeostasis through various organ systems that cooperate via feedback mechanisms to keep conditions like temperature, pH, electrolyte levels, and oxygen/carbon dioxide levels within normal ranges. Homeostatic control mechanisms can involve negative or positive feedback loops to restore the body's normal state when disturbed.