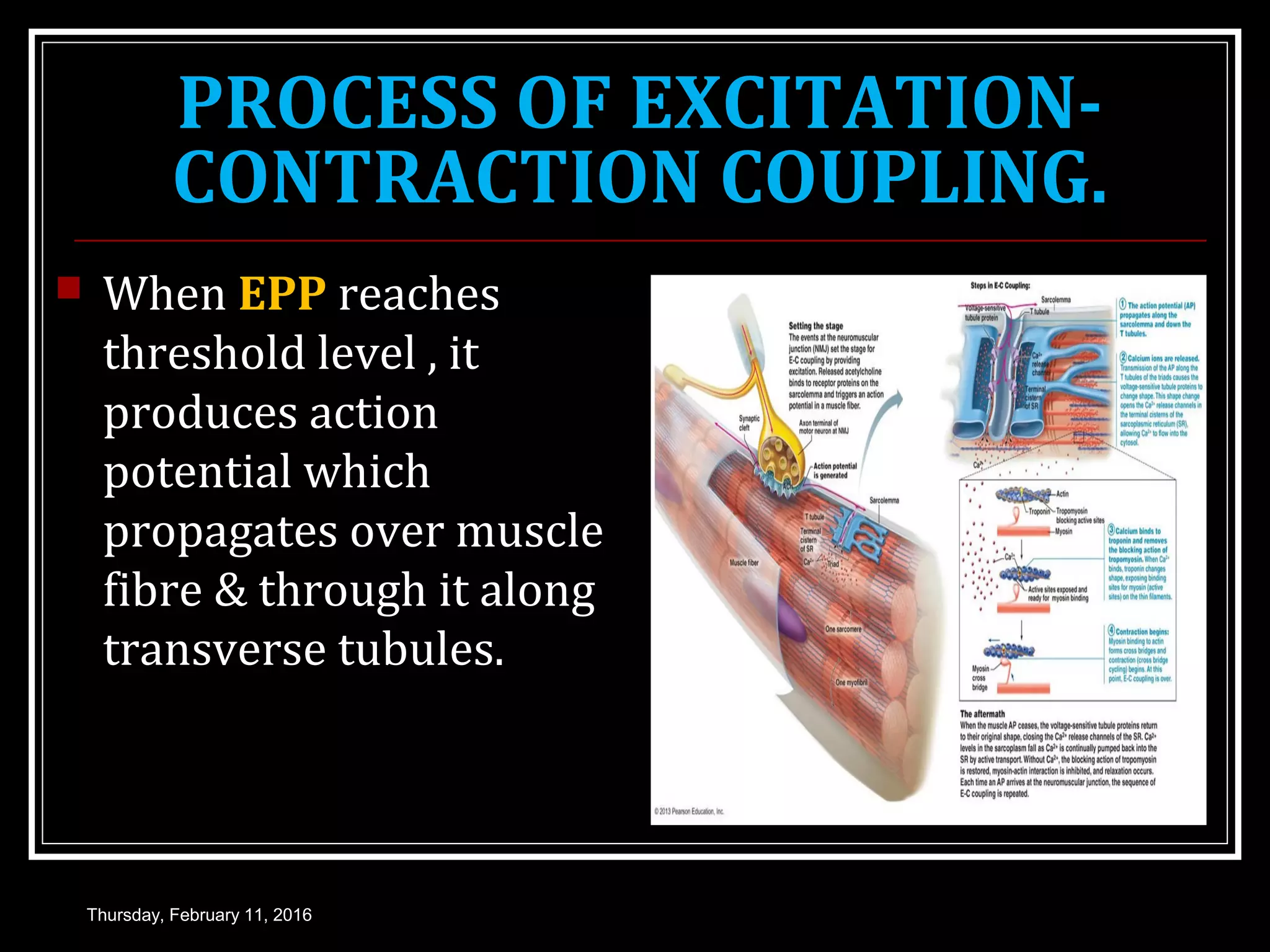
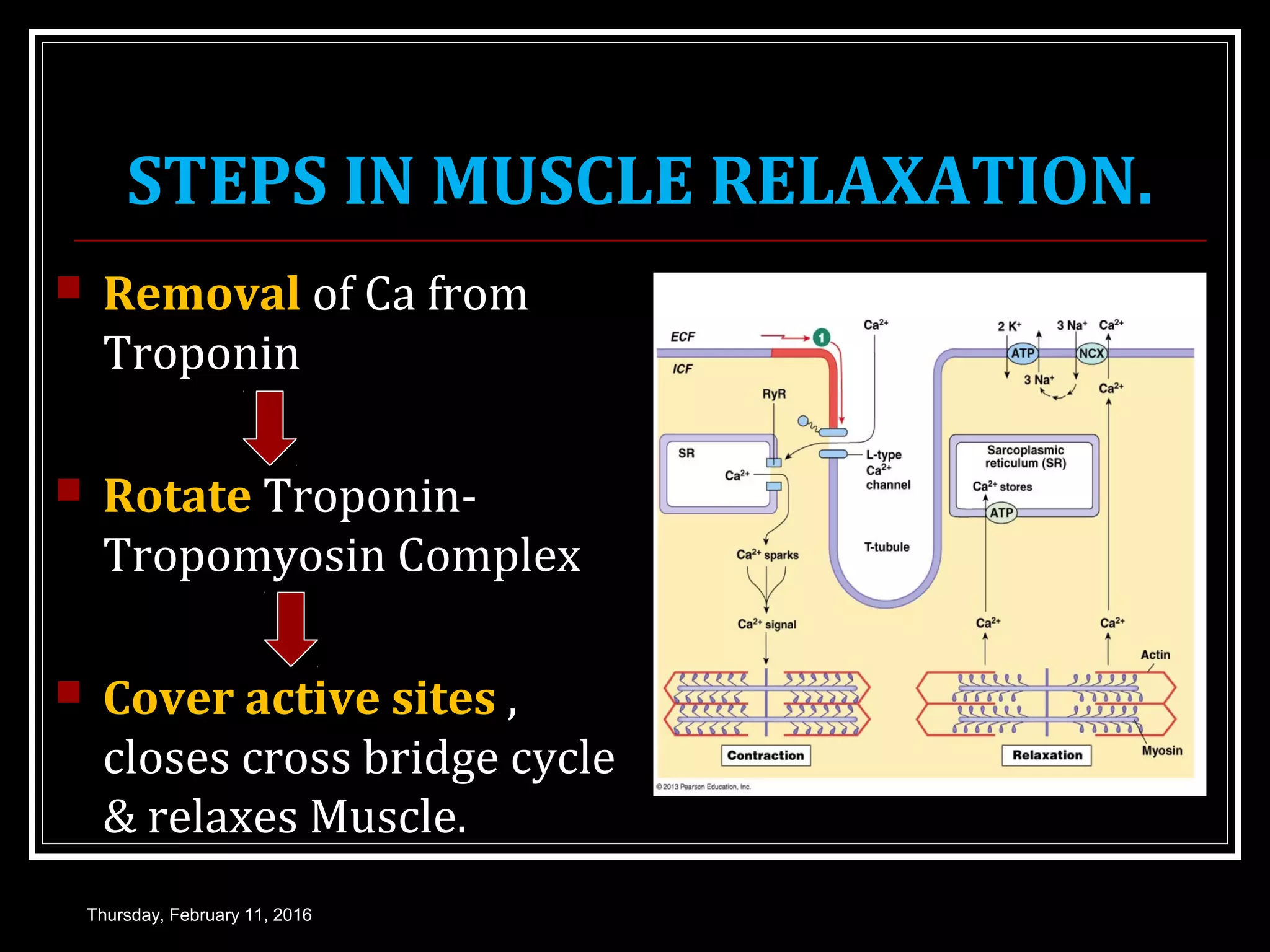
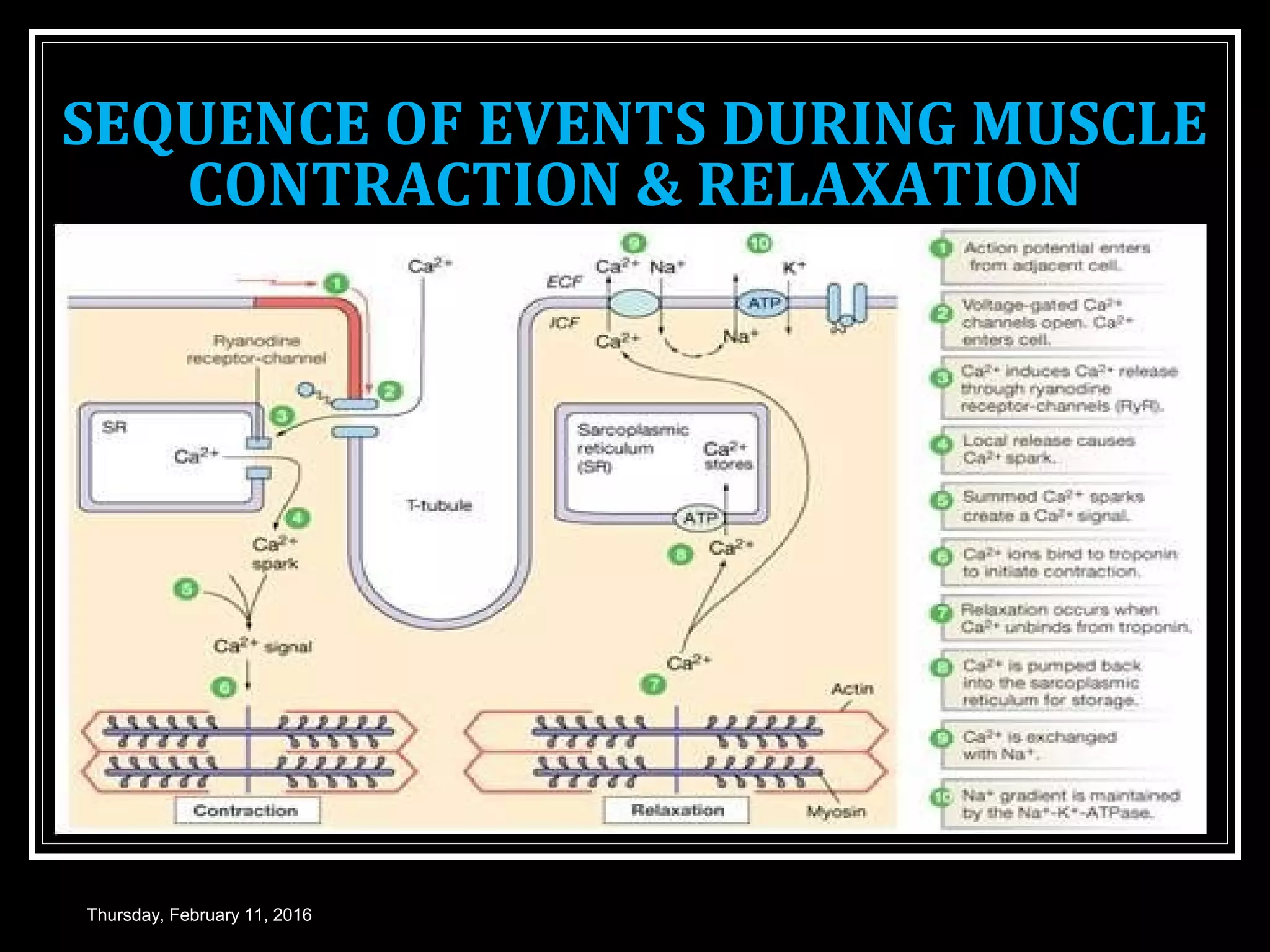
The document discusses skeletal muscle contraction and is presented by Dr. Nilesh Kate. It covers the process of muscle excitation through the generation of an action potential. It then explains excitation-contraction coupling, where the action potential triggers the release of calcium ions, which allows for the linking of excitation and contraction. The process of muscle contraction is described through cross-bridge cycling and the sliding filament theory. Both isotonic and isometric muscle contractions are defined. Key events during muscle contraction and relaxation are outlined, including the roles of calcium ions and ATP.