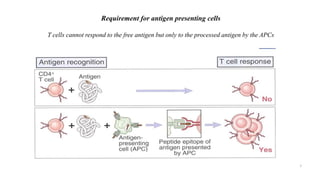
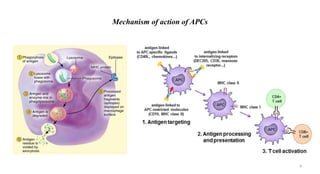
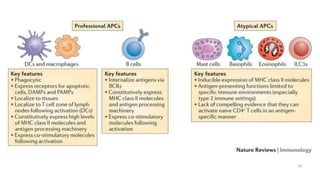
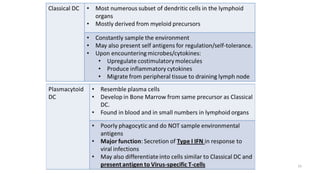
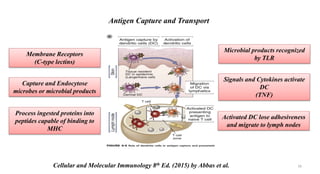
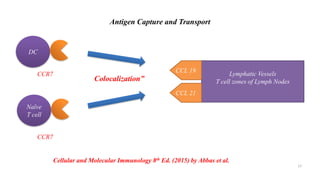
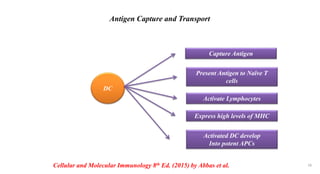
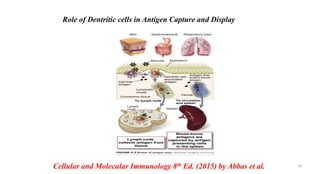
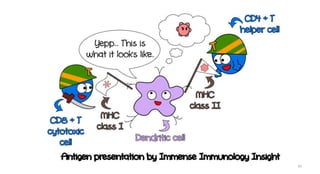
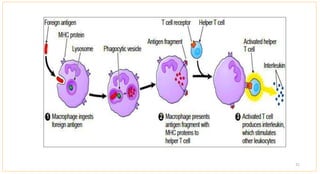
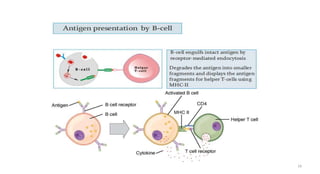
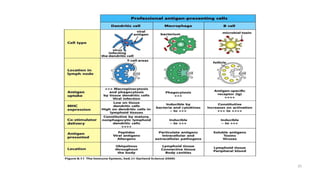
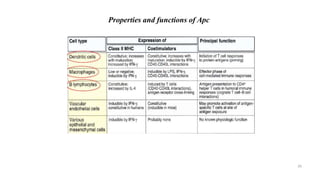
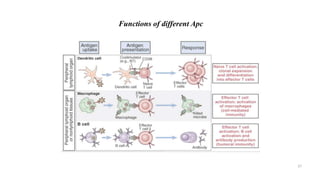
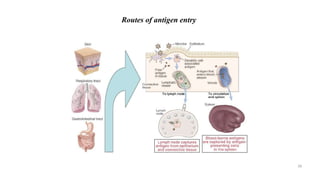
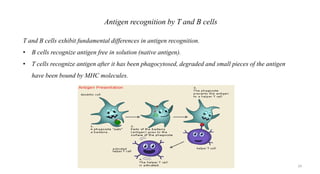
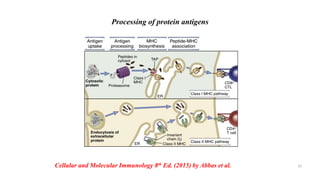
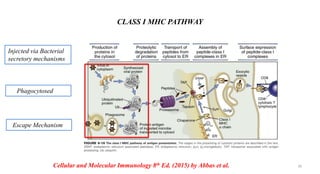
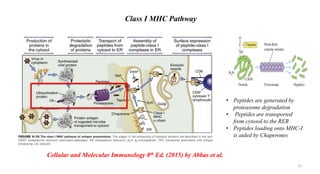
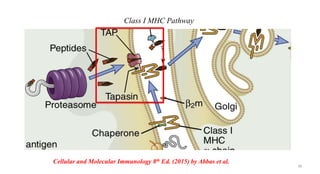
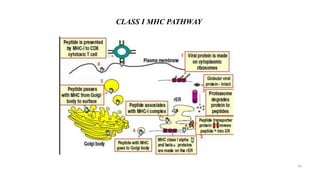
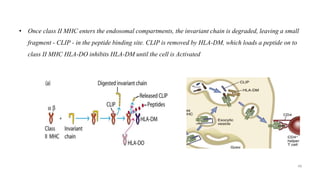
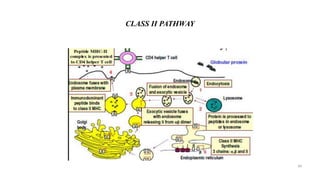
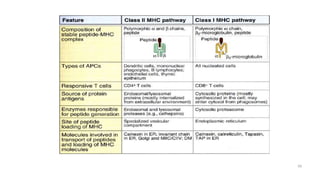
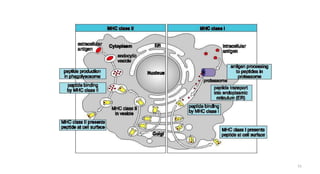
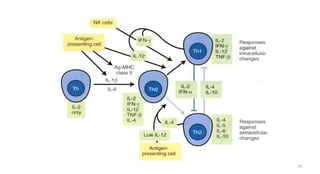
1) Antigen presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells present antigen peptides on their surfaces to activate T cells.
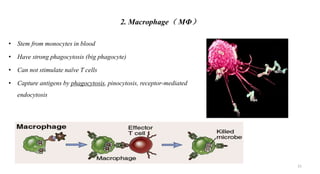
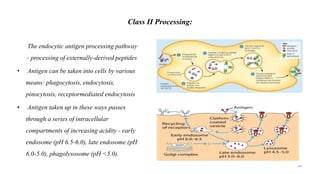
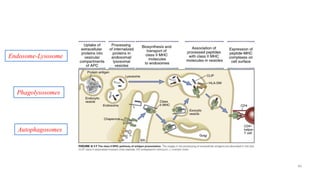
2) APCs capture antigens through phagocytosis, pinocytosis, or receptor-mediated endocytosis and process the antigens into peptides.
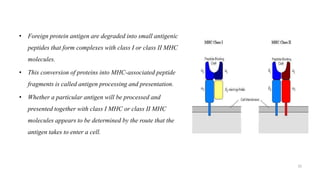
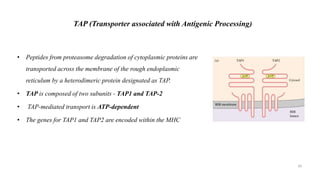
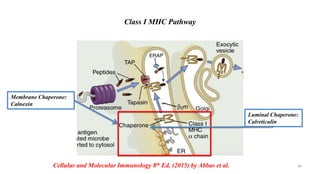
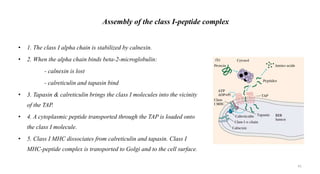
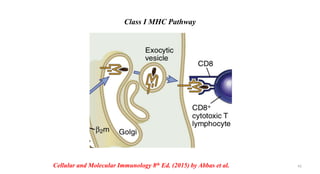
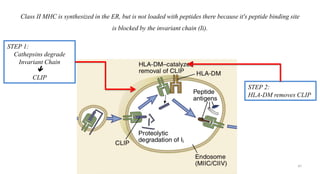
3) The peptides are then presented on either MHC class I or MHC class II molecules for recognition by CD8+ or CD4+ T cells respectively, initiating an adaptive immune response.