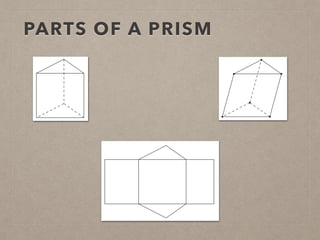
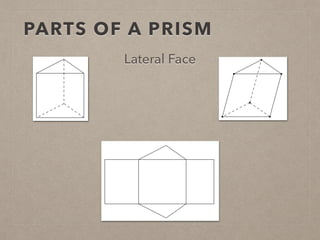
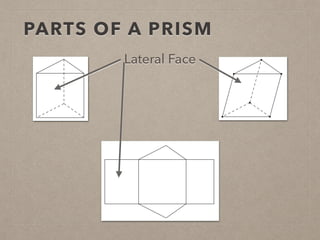
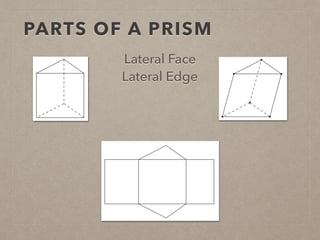
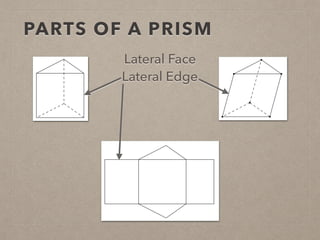
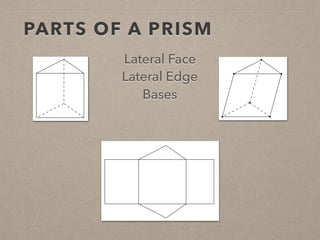
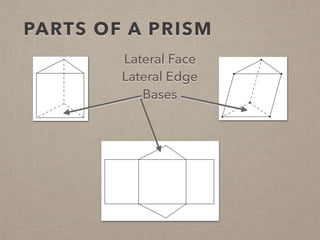
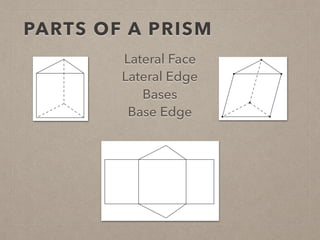
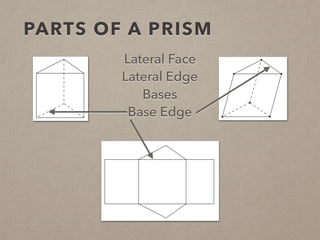
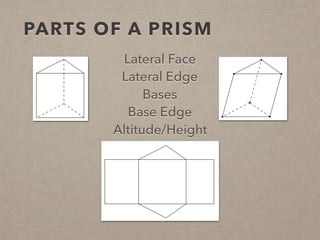
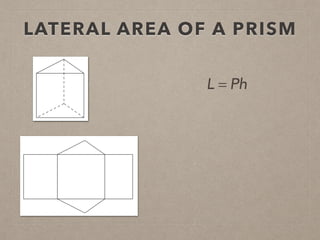
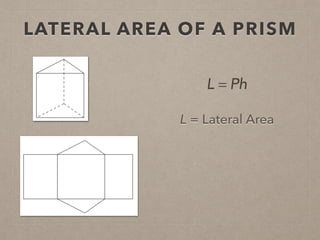
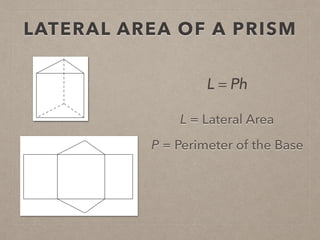
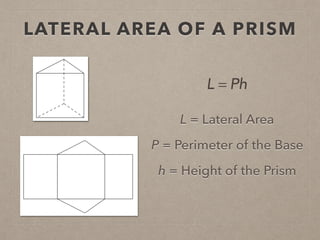
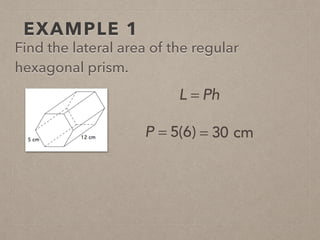
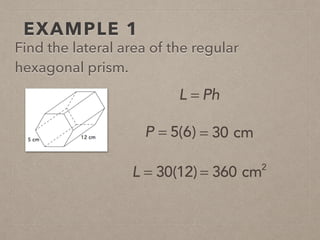
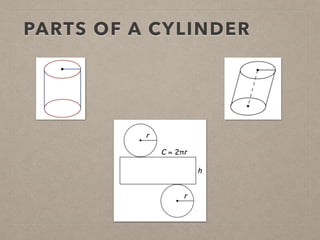
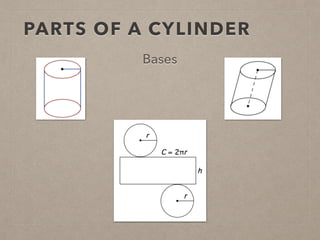
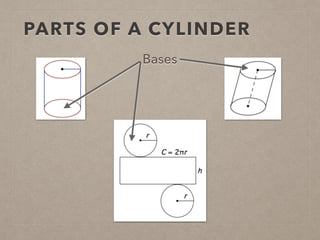
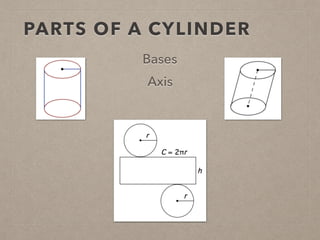
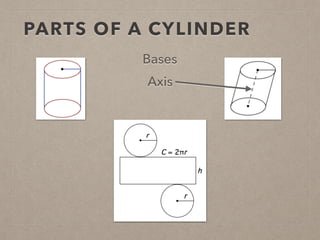
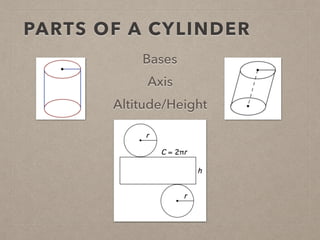
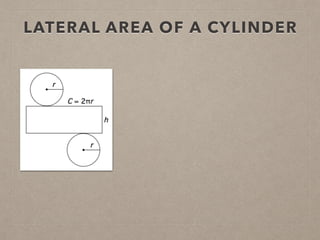
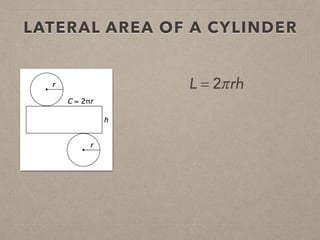
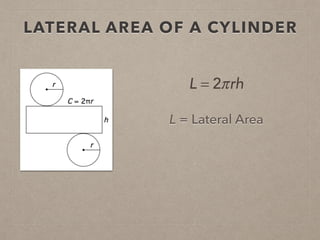
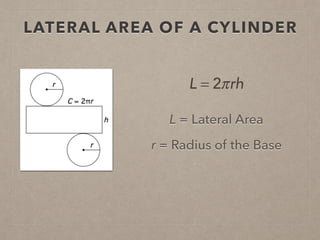
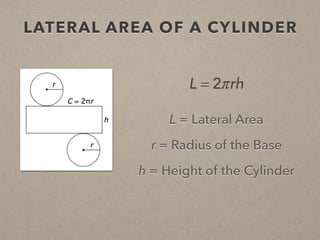
This document provides information on calculating the surface areas of prisms and cylinders. It defines key terms like lateral face, base edge, and altitude. It explains that the lateral area of a prism is calculated as P*h, where P is the perimeter of the base and h is the height. The surface area of a prism is the lateral area plus twice the area of the base. For cylinders, the lateral area is 2πrh, where r is the radius and h is the height. The surface area of a cylinder is the lateral area plus twice the area of the circular base. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating lateral and surface areas.