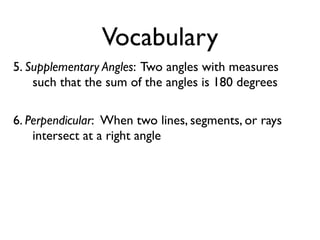
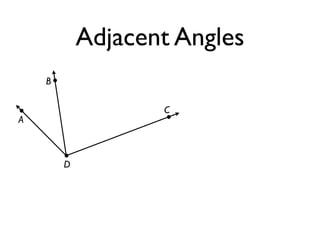
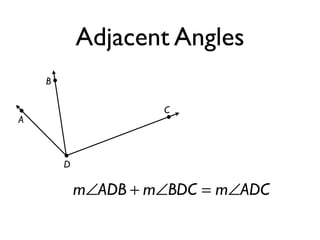
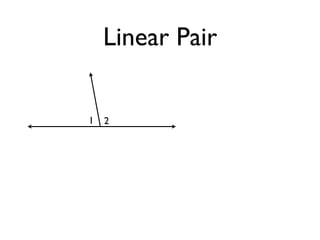
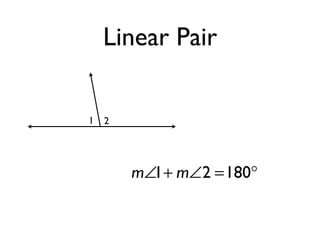
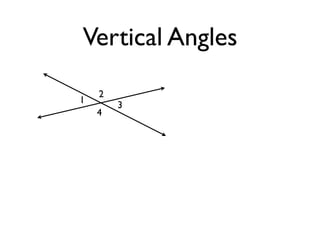
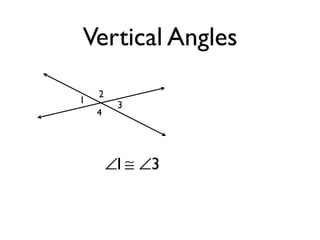
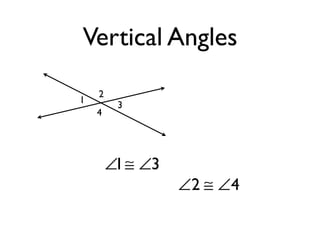
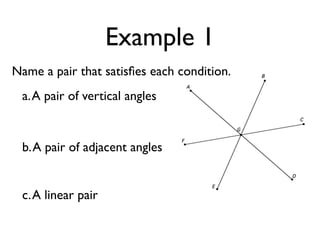
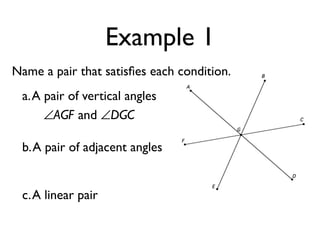
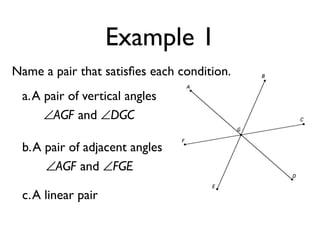
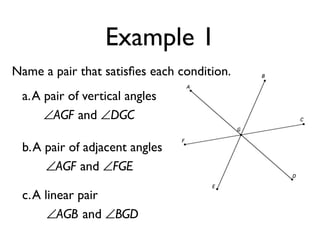
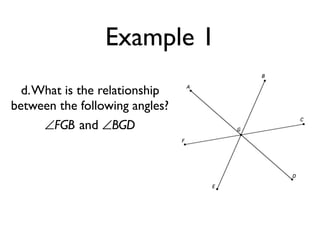
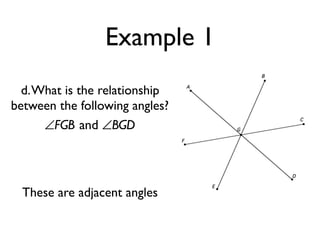
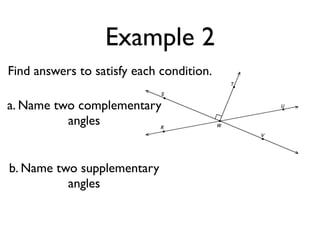
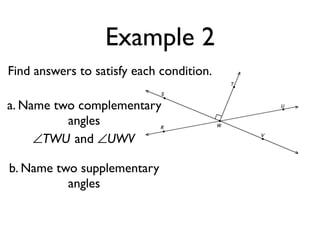
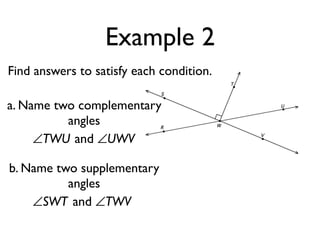
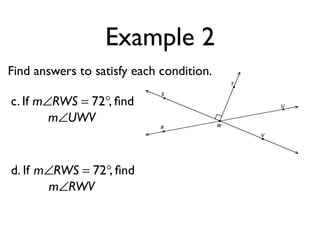
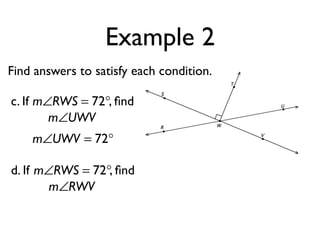
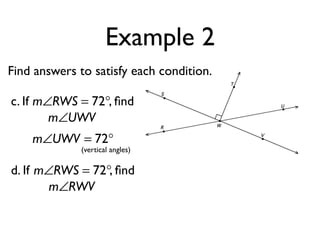
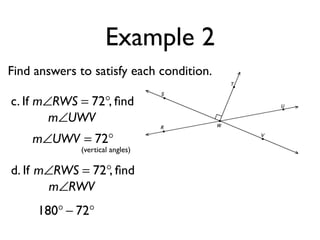
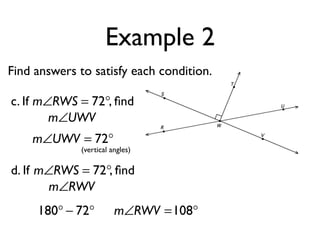
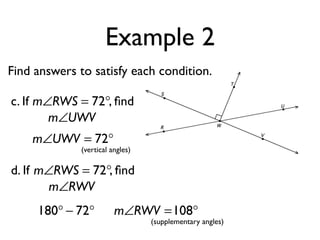
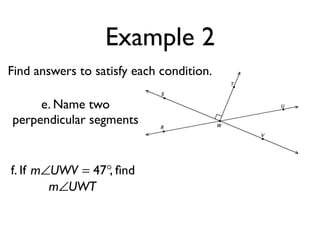
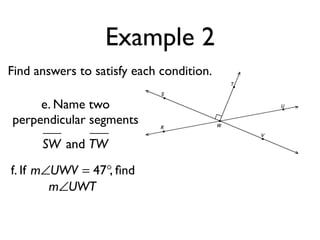
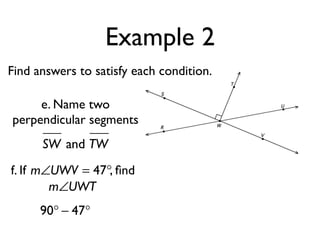
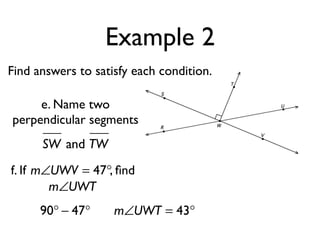
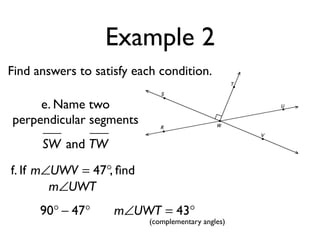
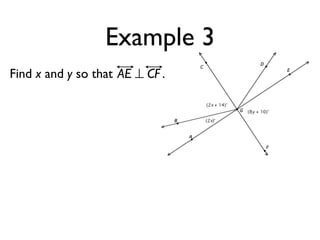
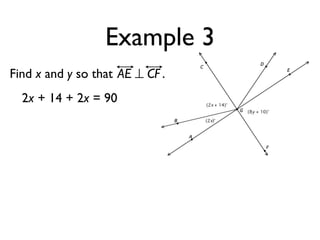
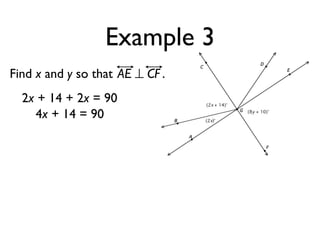
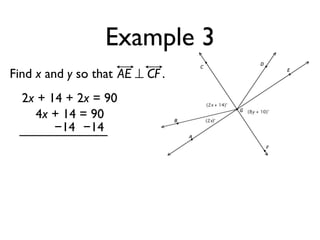
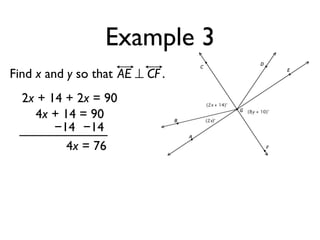
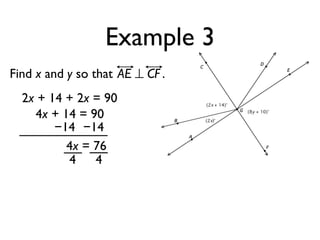
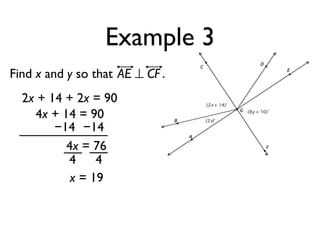
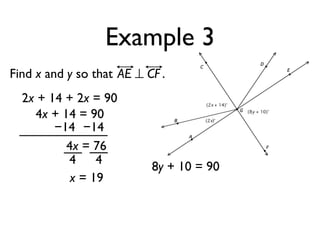
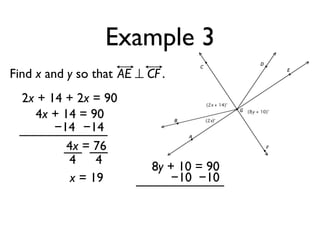
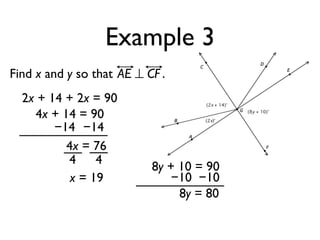
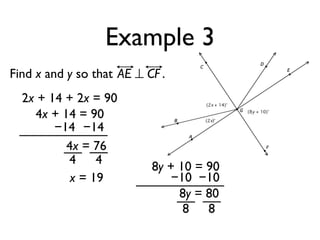
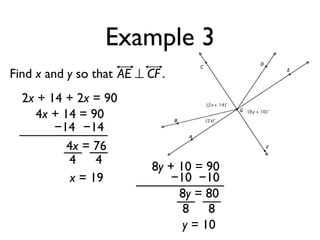
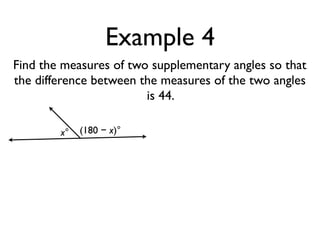
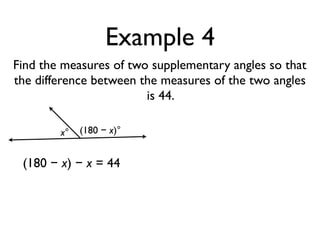
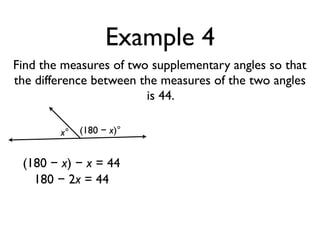
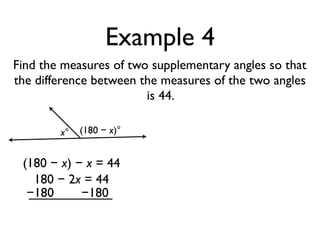
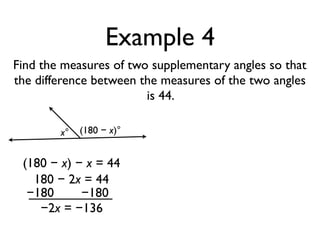
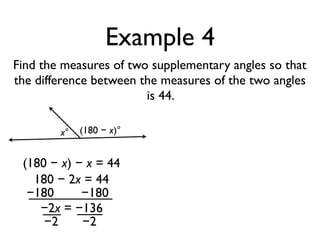
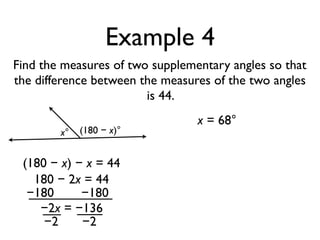
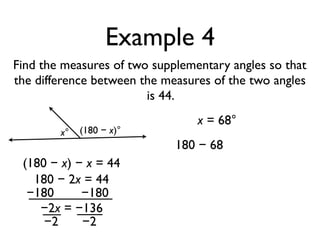
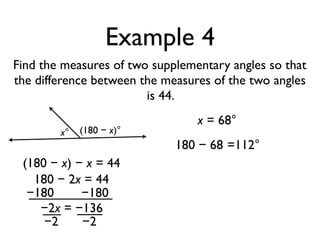
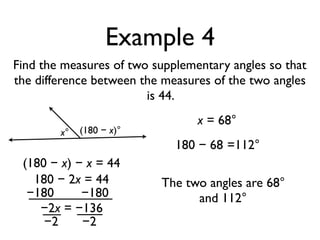
The document defines and provides examples of angle relationships including adjacent angles, linear pairs, vertical angles, complementary angles, and supplementary angles. It defines each term and provides examples of identifying angle pairs that satisfy each relationship. It also includes examples of using properties of these angle relationships to solve problems, such as finding missing angle measures.