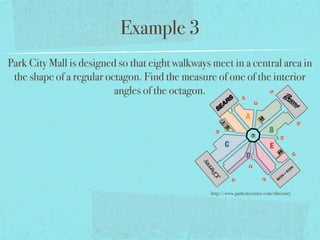
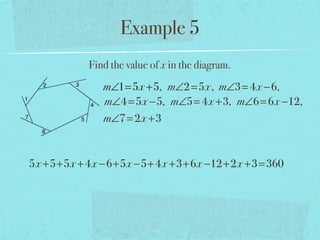
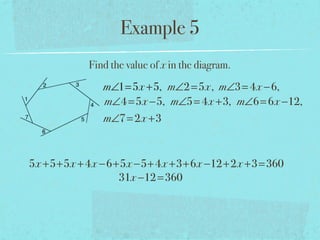
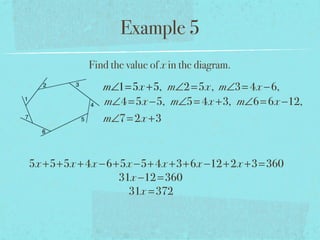
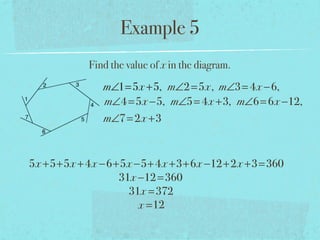
The document summarizes key concepts about polygons, including:
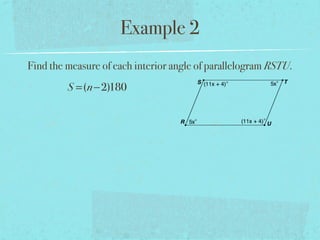
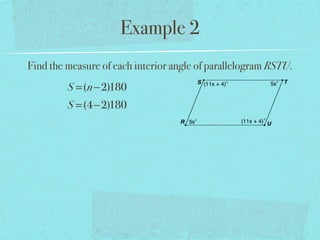
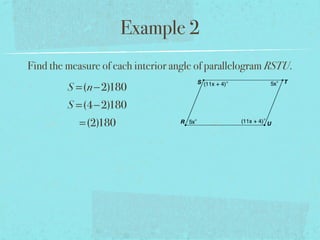
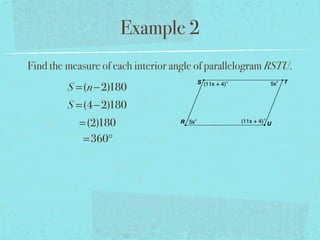
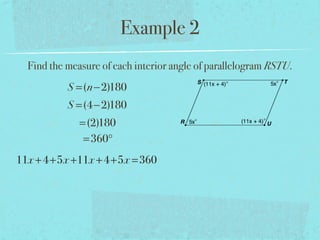
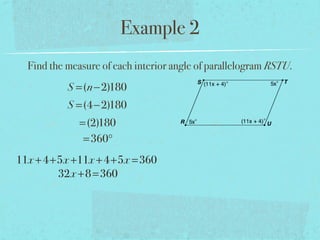
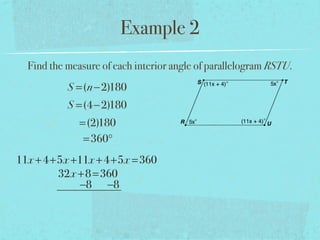
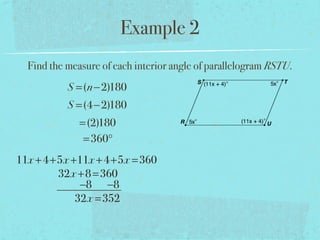
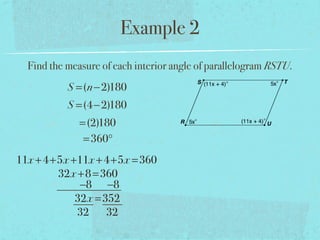
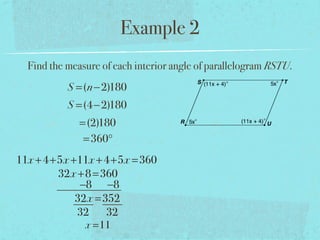
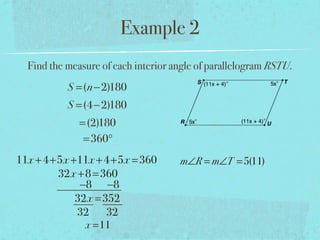
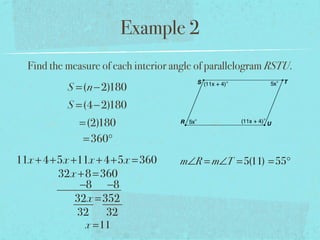
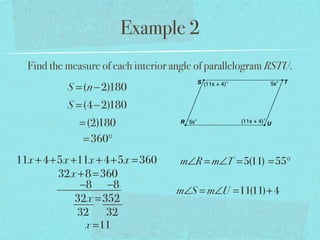
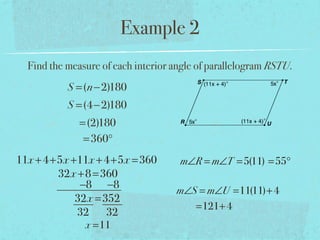
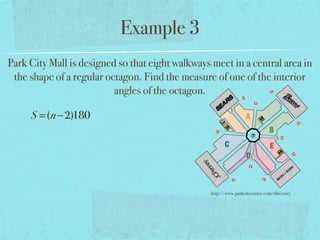
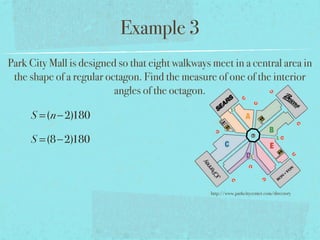
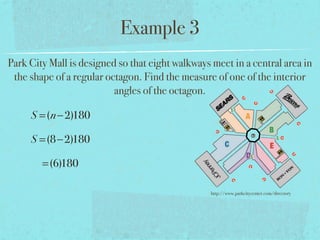
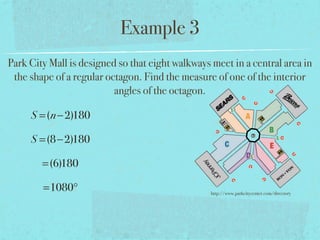
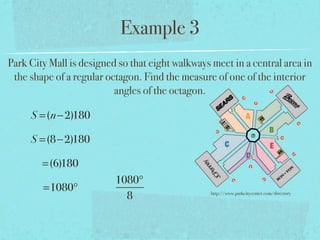
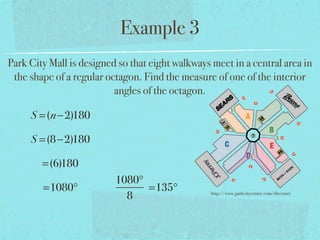
- The sum of the interior angles of a polygon with n sides is (n-2)180 degrees.
- The sum of the exterior angles of a polygon is 360 degrees.
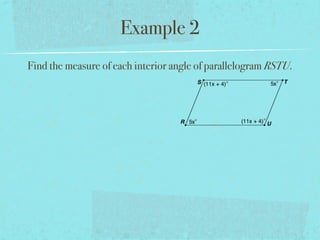
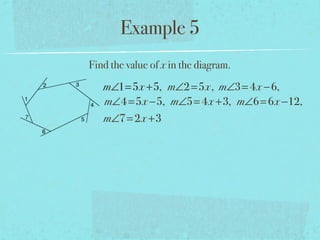
- Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating sums of interior/exterior angles and finding missing angle measures using angle sums.
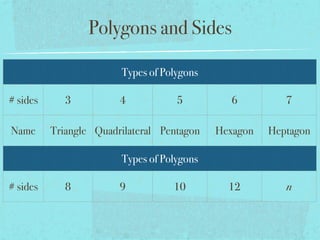
- Regular polygons are defined by their number of sides.