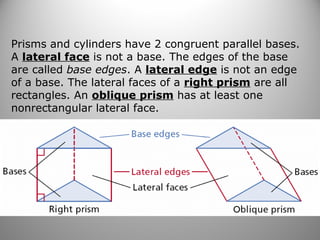
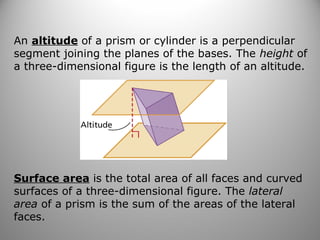
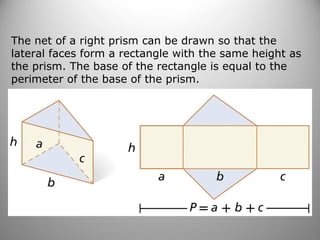
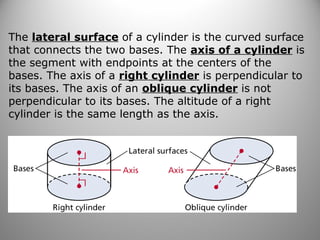
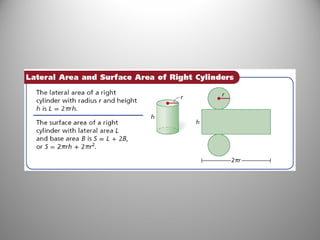
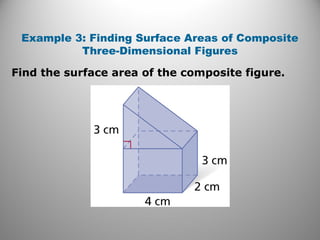
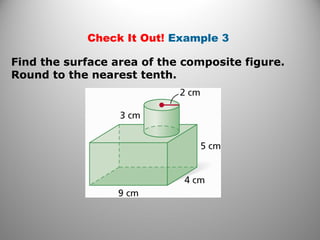
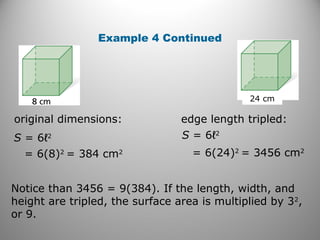
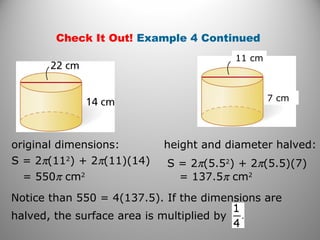
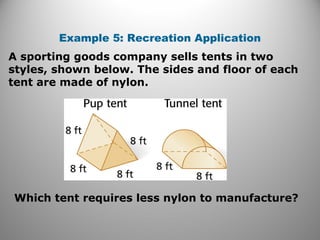
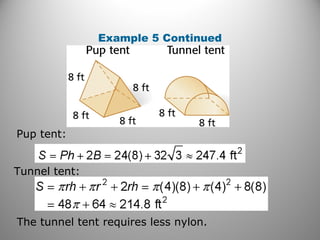
This document provides instruction on calculating the surface areas of prisms and cylinders. It defines key terms like lateral face, altitude, and axis. It presents formulas for calculating the surface area of right rectangular prisms and right cylinders. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating surface areas of various prisms and cylinders. The document also addresses how surface areas change with modifications to dimensions and provides a word problem comparing the surface areas of different shapes.