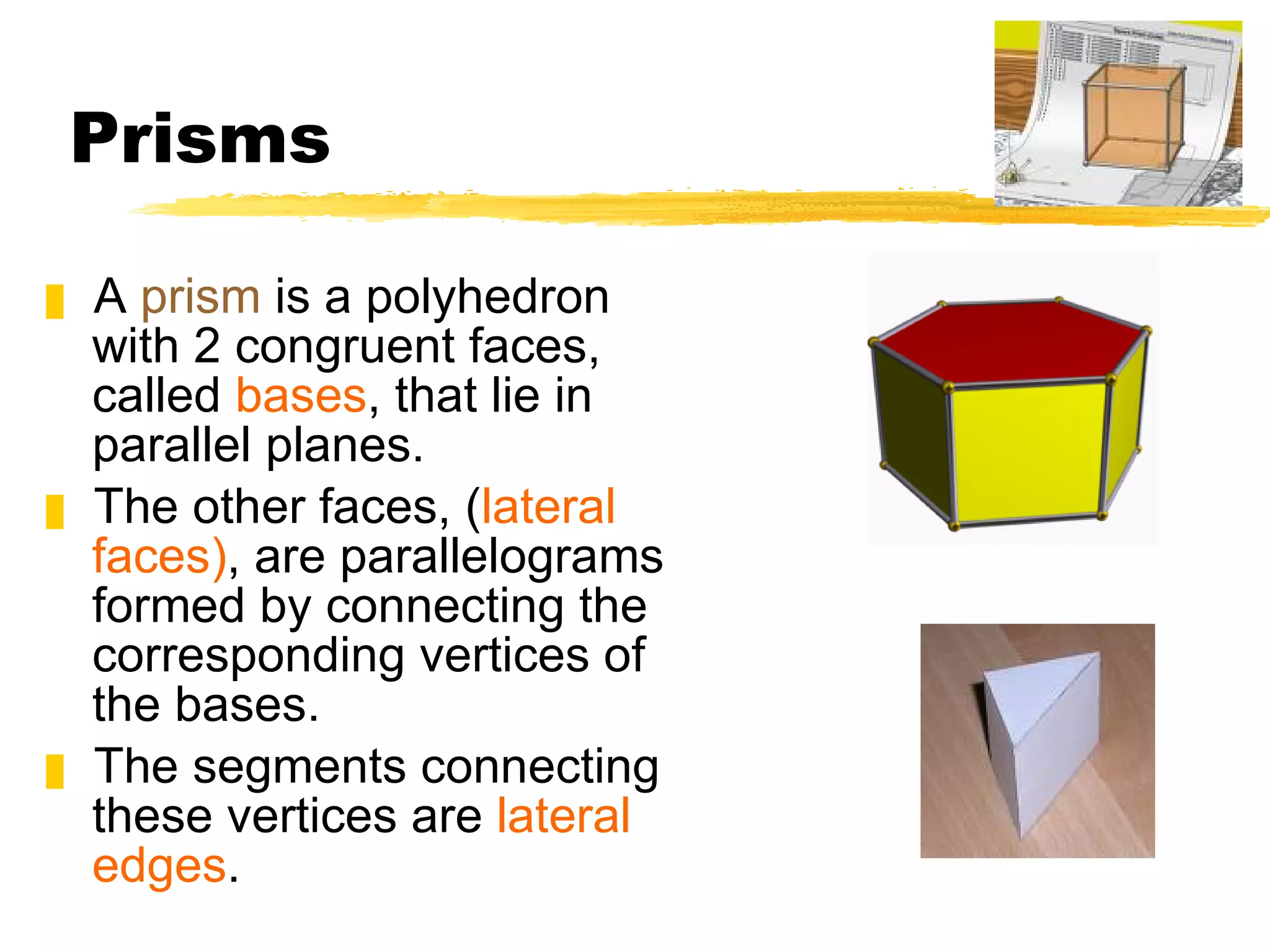
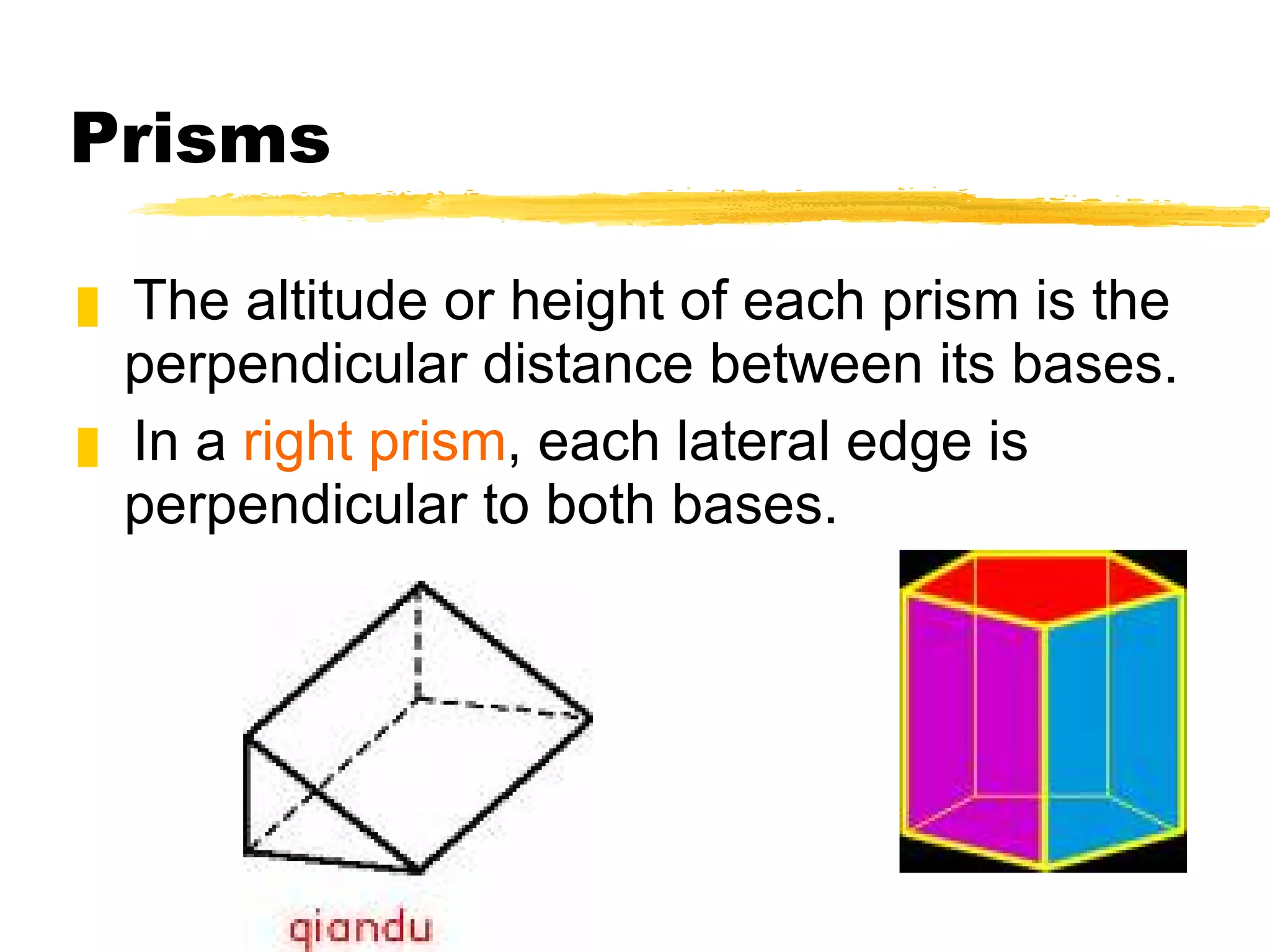
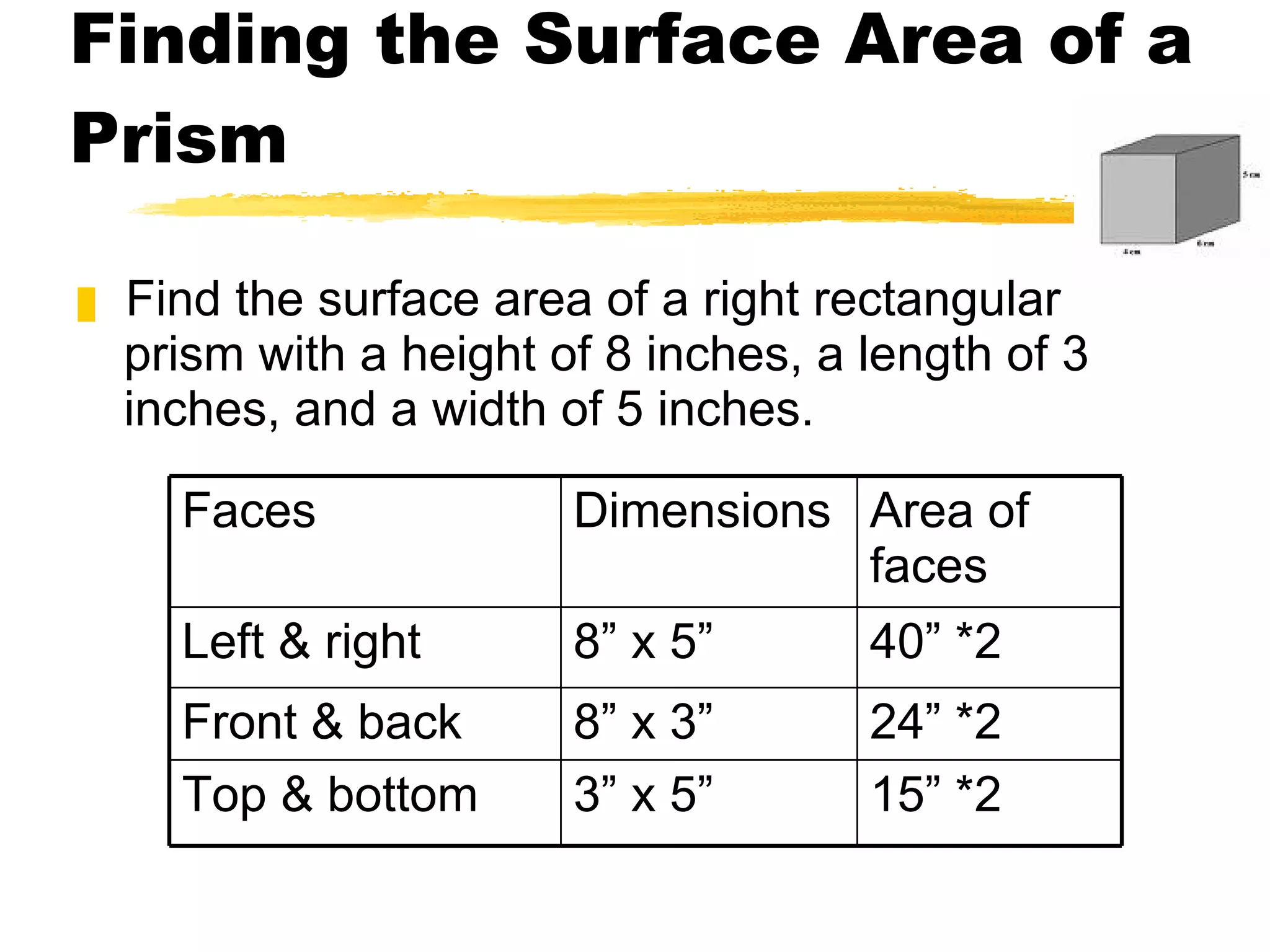
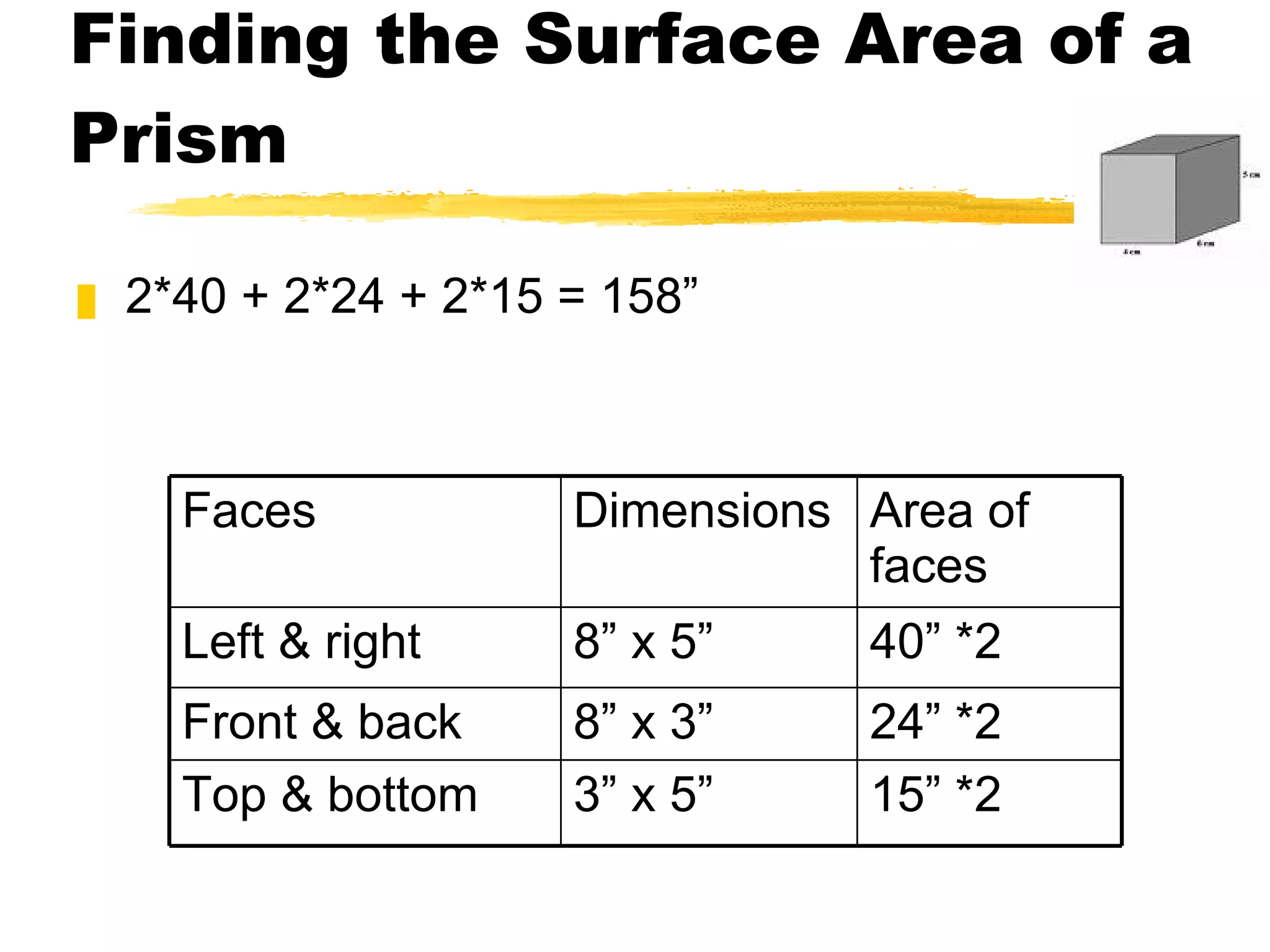
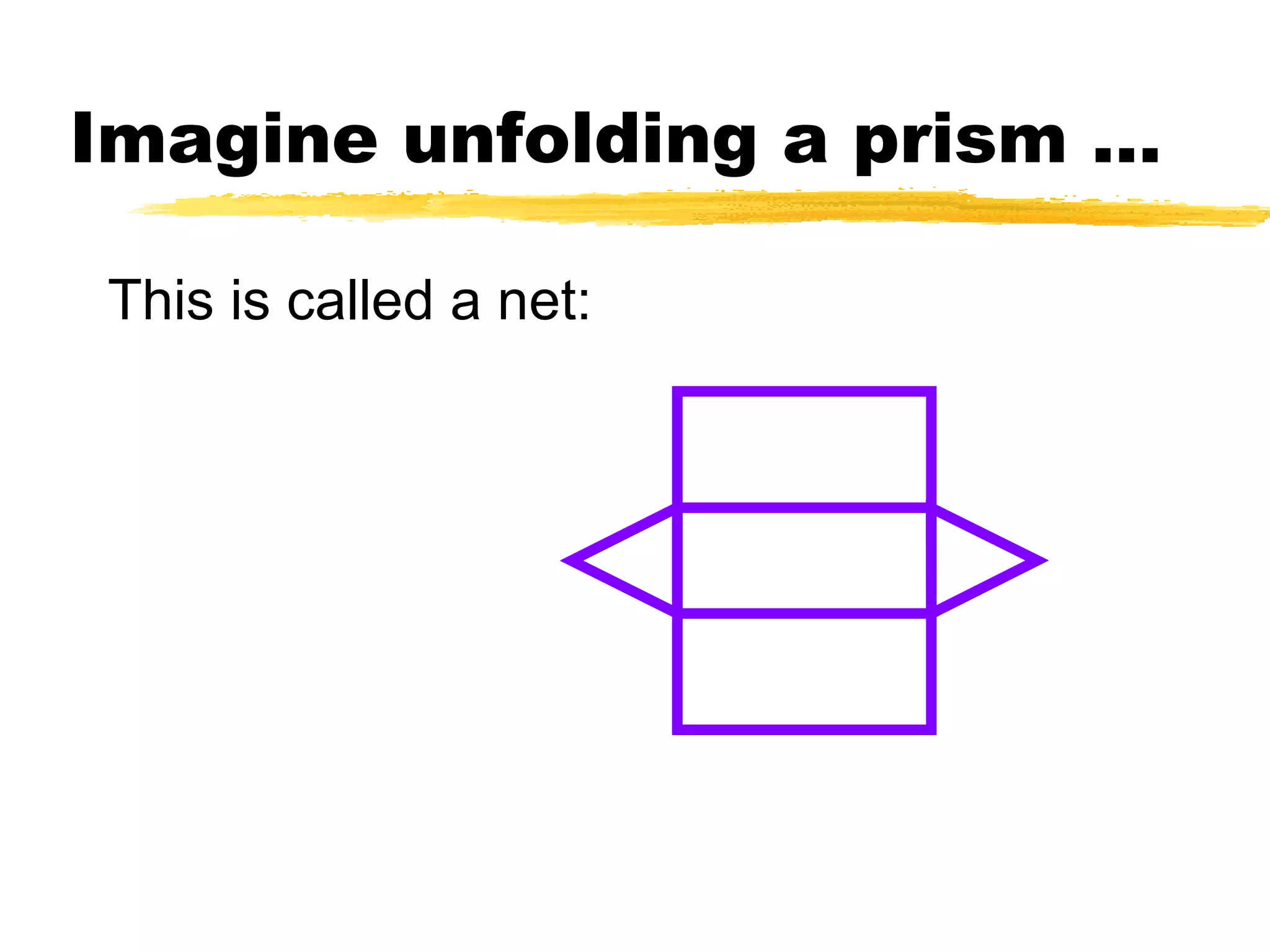
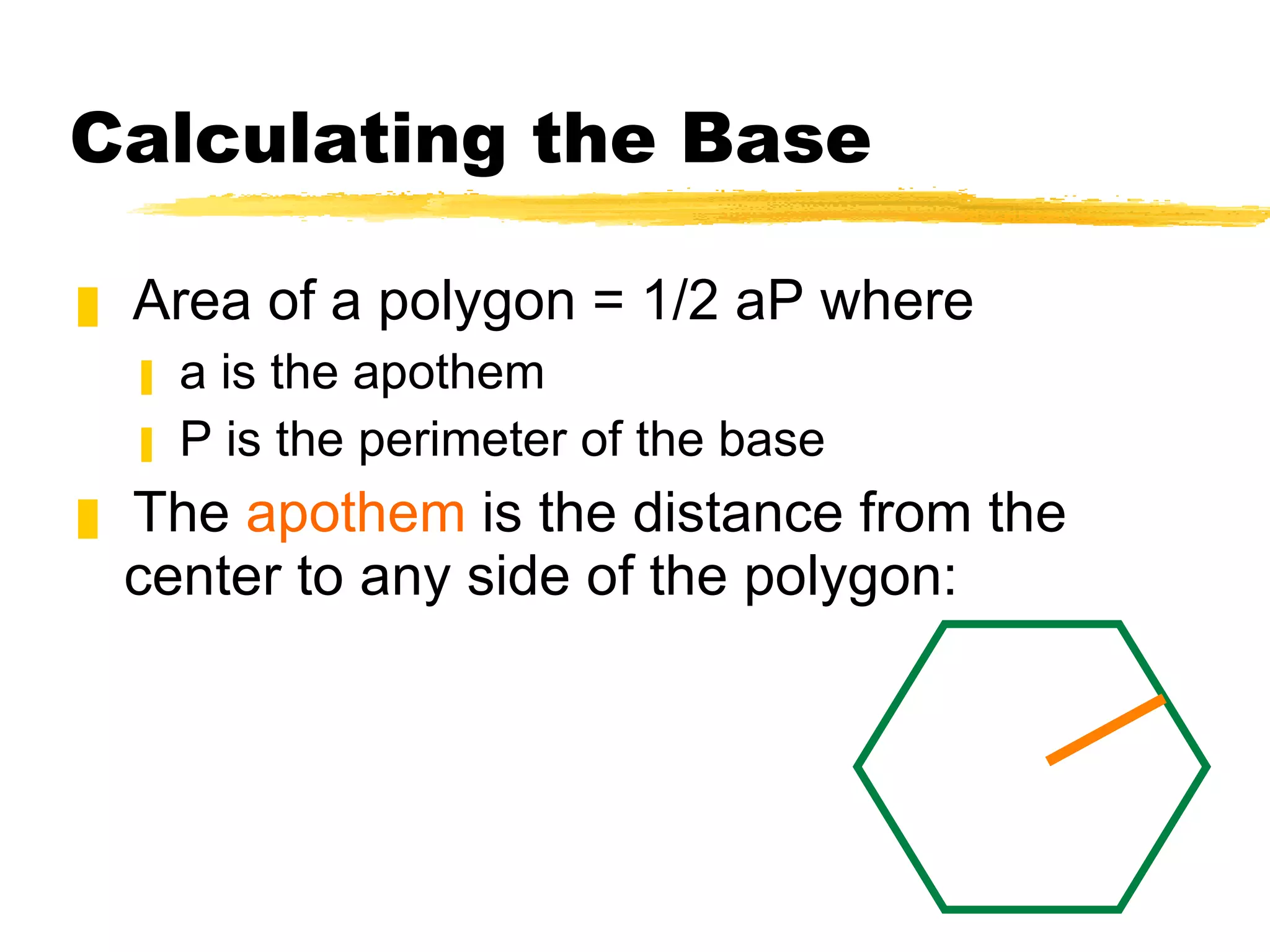
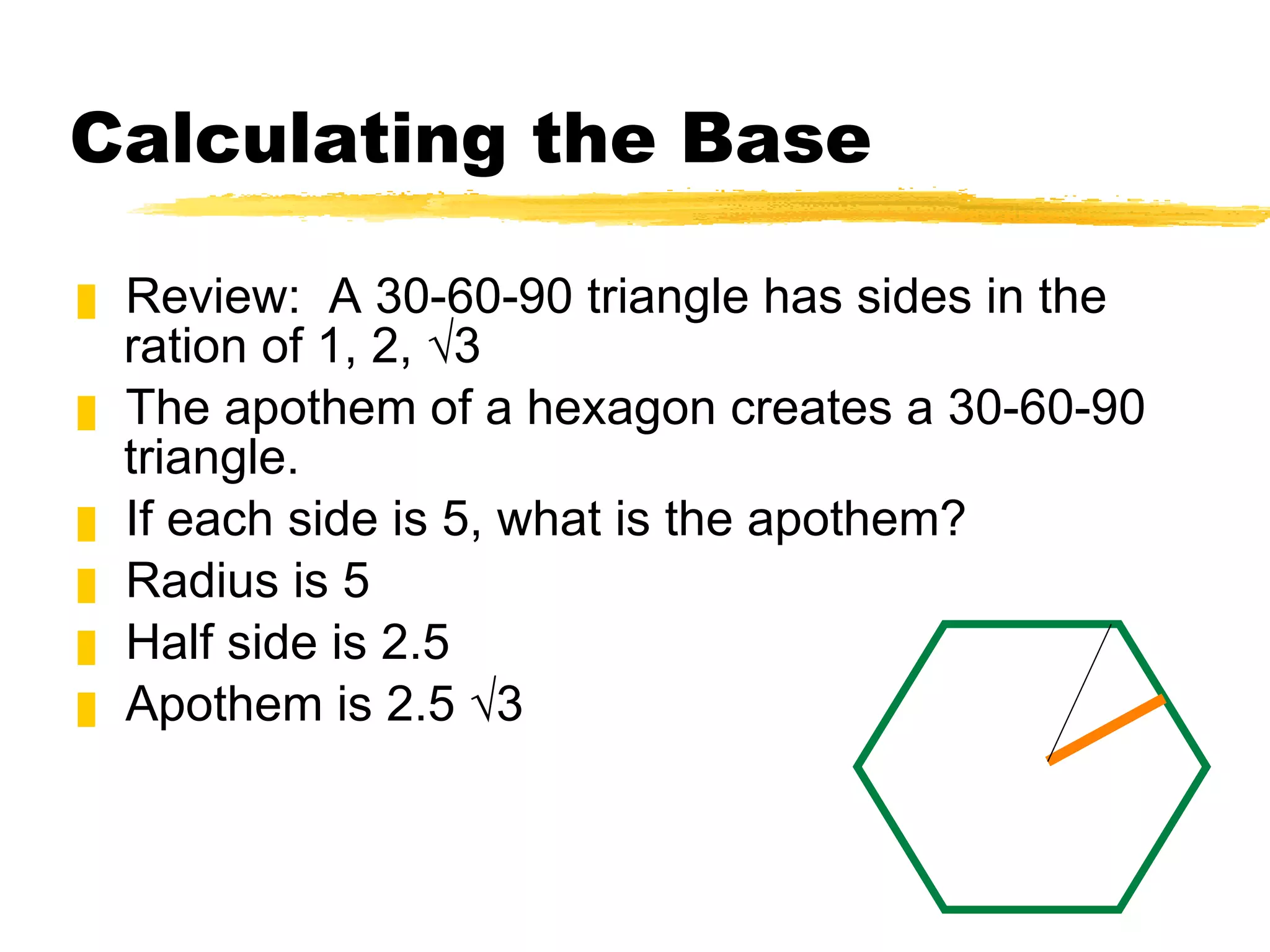
The document summarizes different types of geometric solids and how to calculate their surface areas. It discusses prisms, cylinders, pyramids, cones, and spheres. For each solid, it defines key terms like base, height, lateral face, radius, and provides the surface area formulas. Examples are included to demonstrate calculating the surface area of different solids.