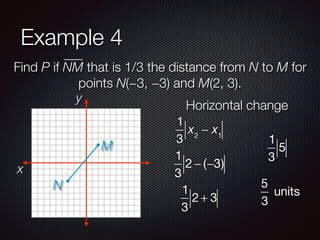
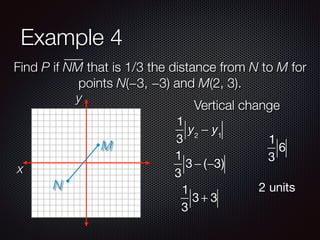
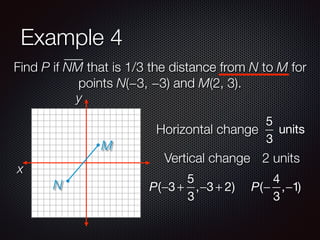
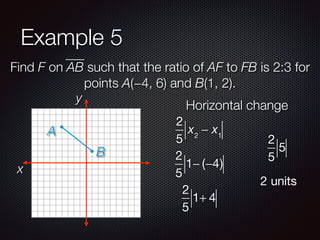
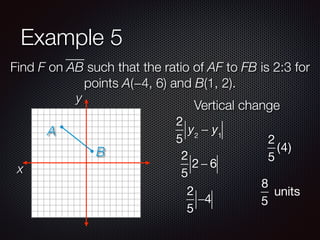
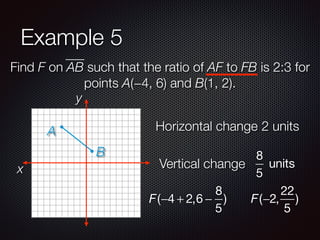
This document discusses finding points and midpoints on line segments. It defines midpoint as the point halfway between two endpoints and provides the formula to calculate it. Several examples are given to demonstrate how to find the midpoint of a segment, locate a point at a fractional distance from one endpoint, and find a point where the ratio of distances from the endpoints is a given ratio. The key concepts covered are calculating midpoints using averages of x- and y-coordinates, and setting up and solving equations to locate interior points using fractional or ratio distances along a segment.