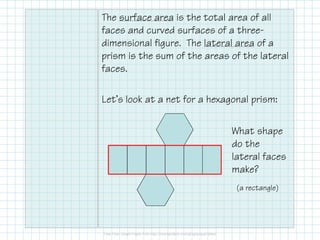
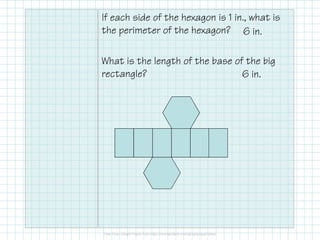
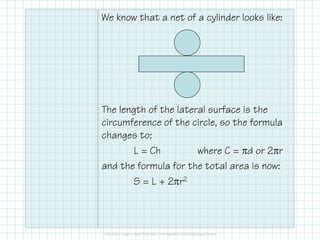
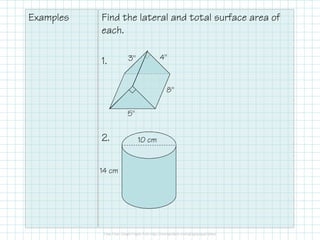
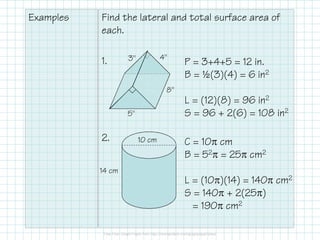
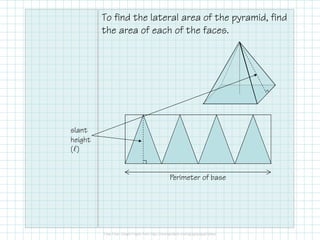
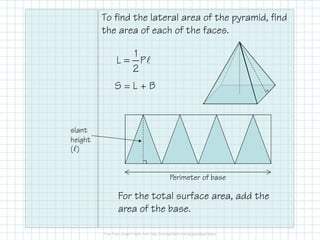
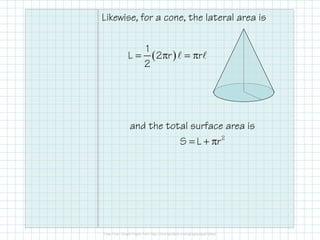
This document discusses how to calculate the surface area of various 3D shapes like prisms, cylinders, pyramids and cones. It provides formulas to find the lateral area and total surface area of each shape. For prisms and cylinders, the lateral area is calculated using the perimeter/circumference and height, while the total area adds the lateral area and both bases. Pyramids and cones use similar formulas involving the perimeter/circumference, slant or lateral height, and the base area. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating the lateral and total surface areas of different shapes.


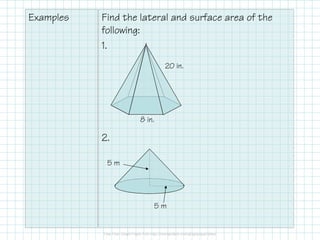

2
=
2
480 in=
2
S 480 96 3 in= +
2
646.3 in≈
5 2 m L (5)(5 2)= π
2
25 2 m= π
2
S 25 2 25 m= π + π
2
189.6 m≈](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-170511140650/85/5-13-4-Surface-Area-12-320.jpg)