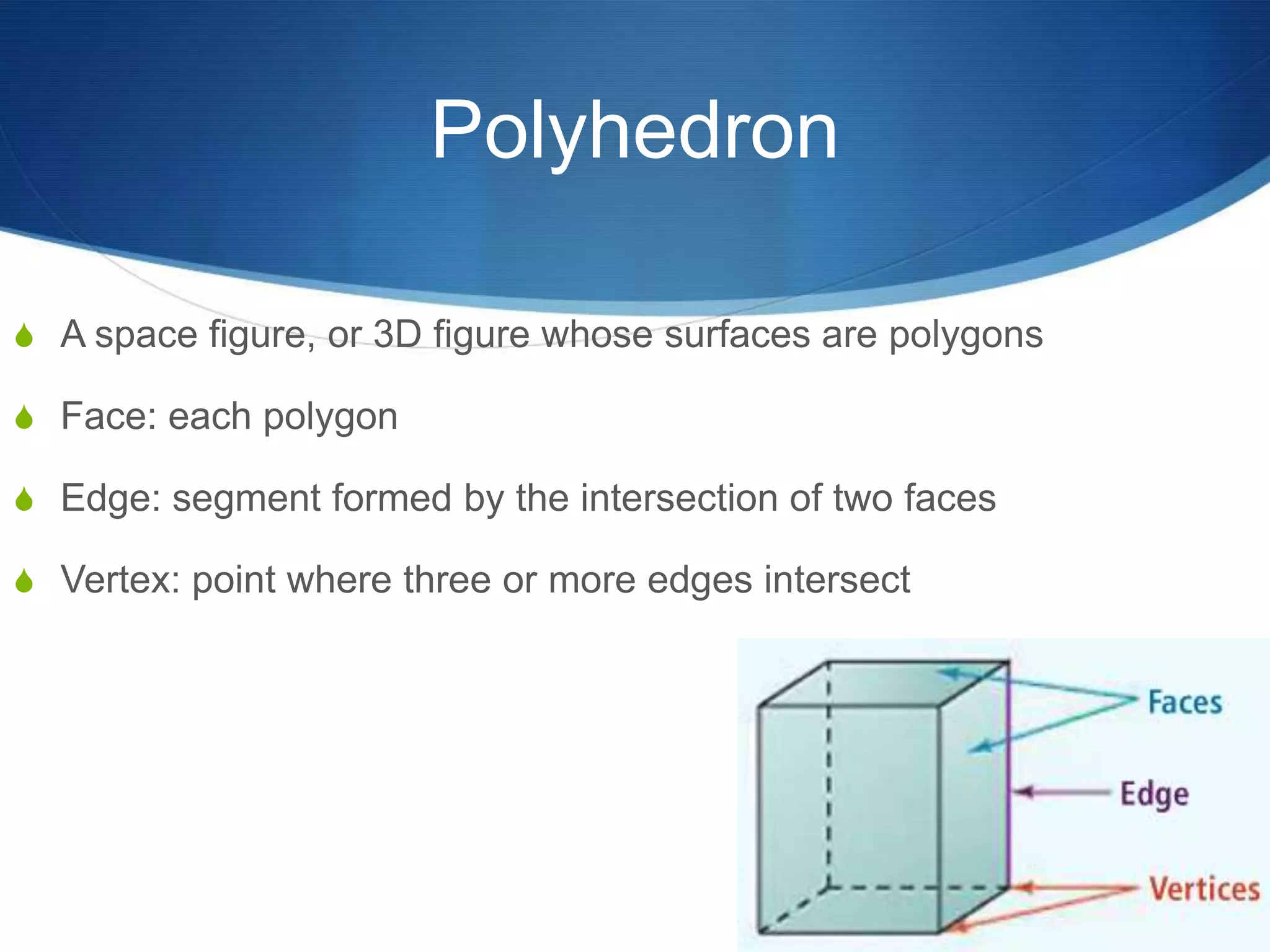
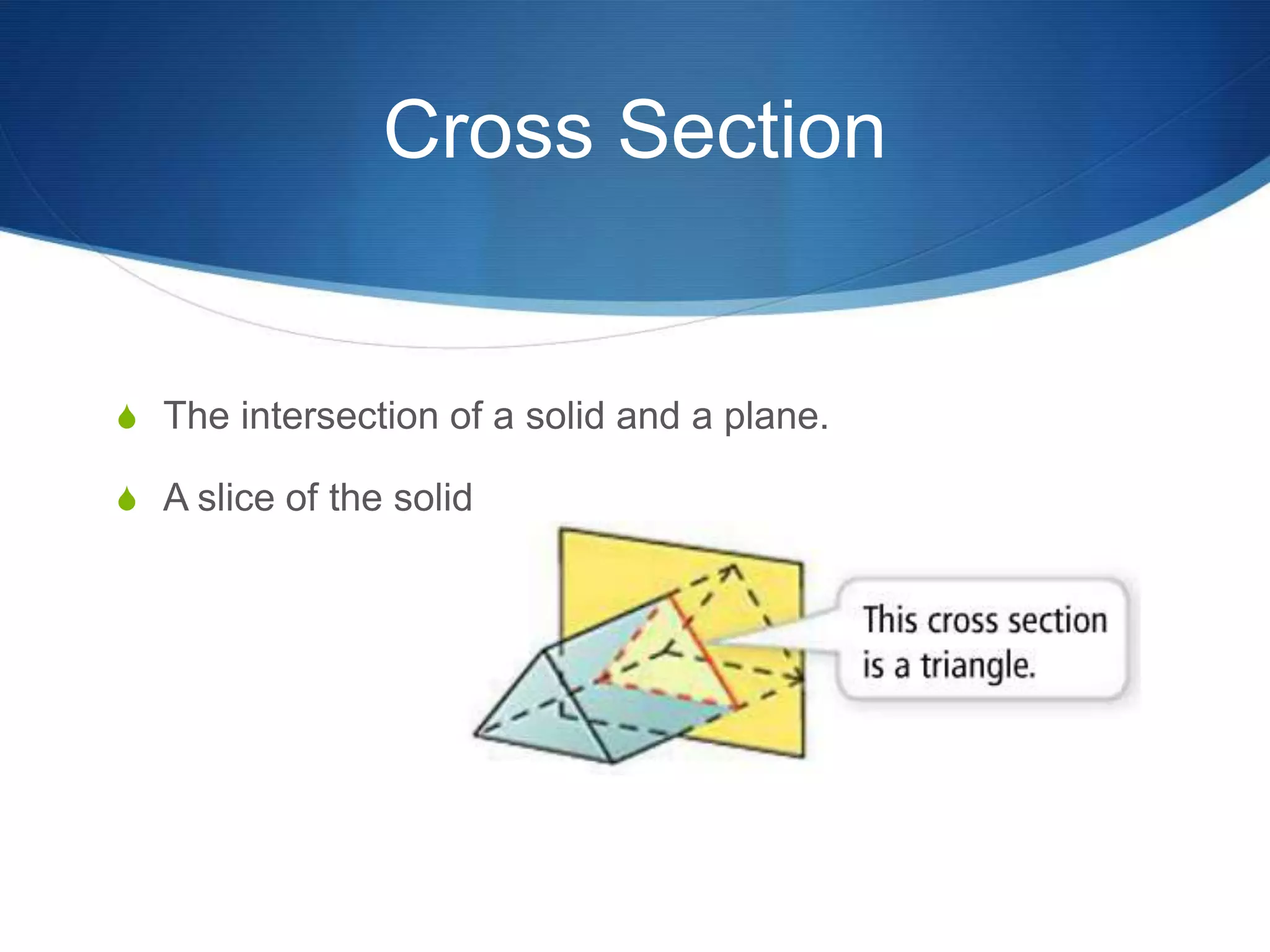
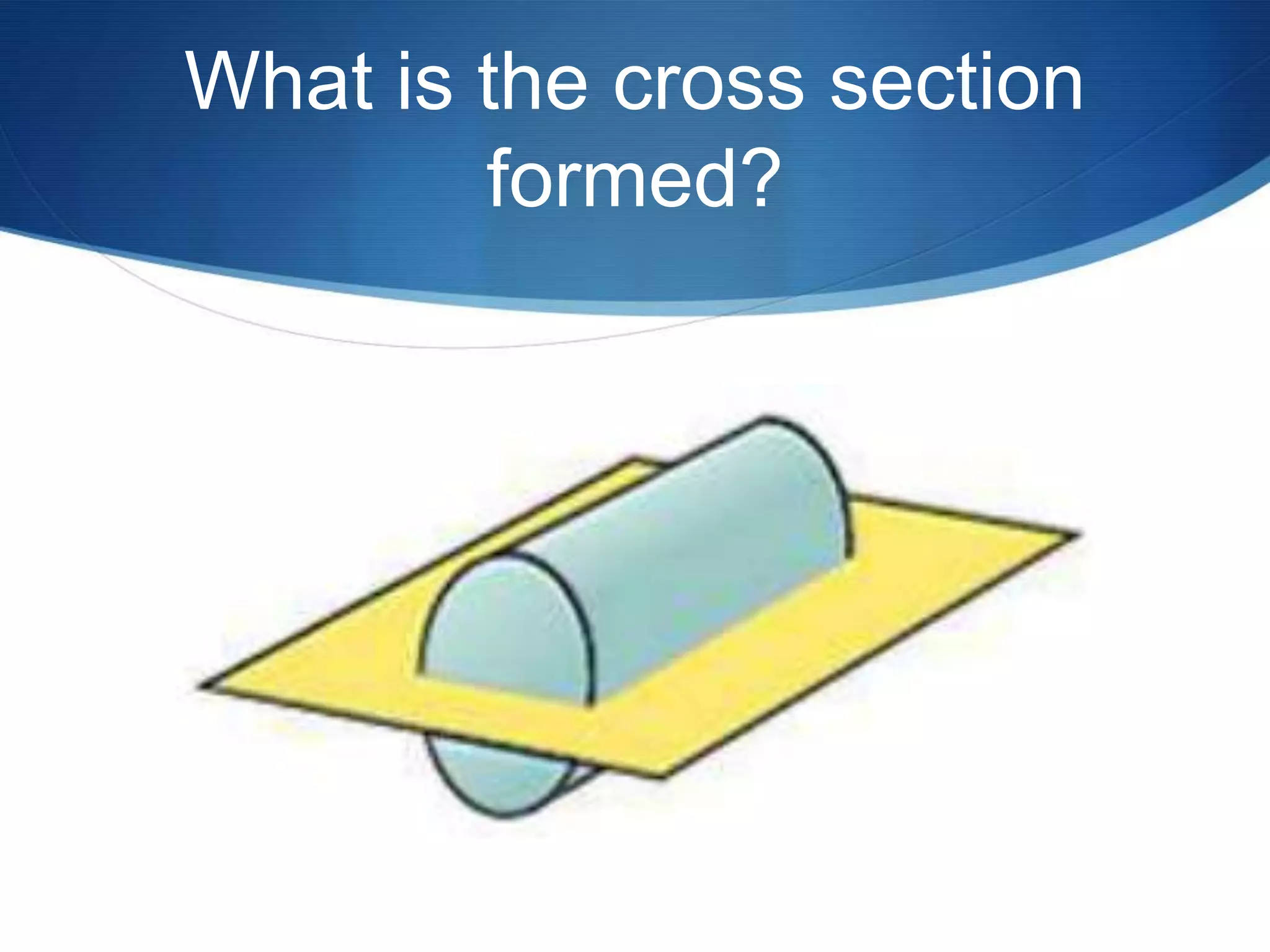
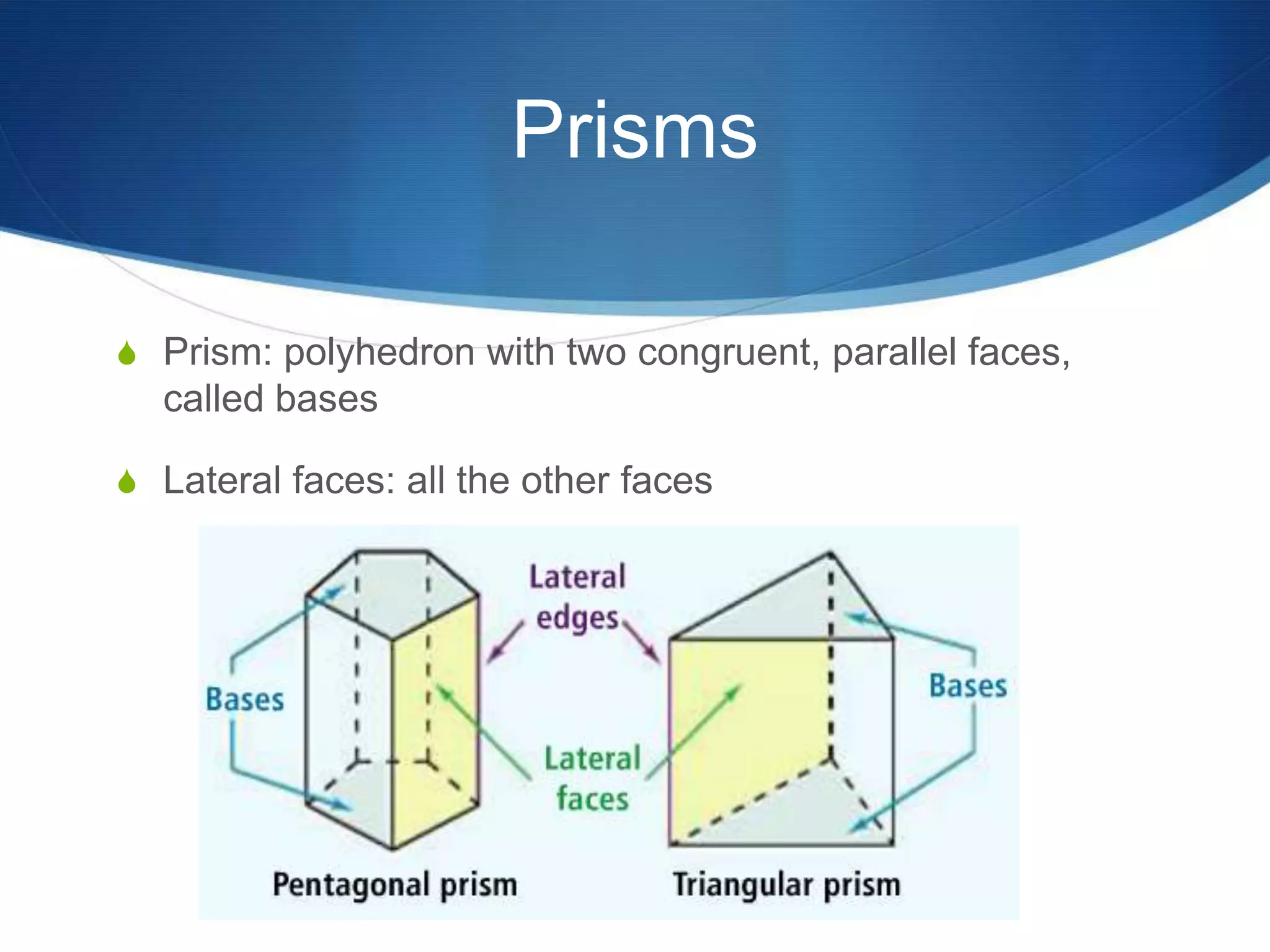
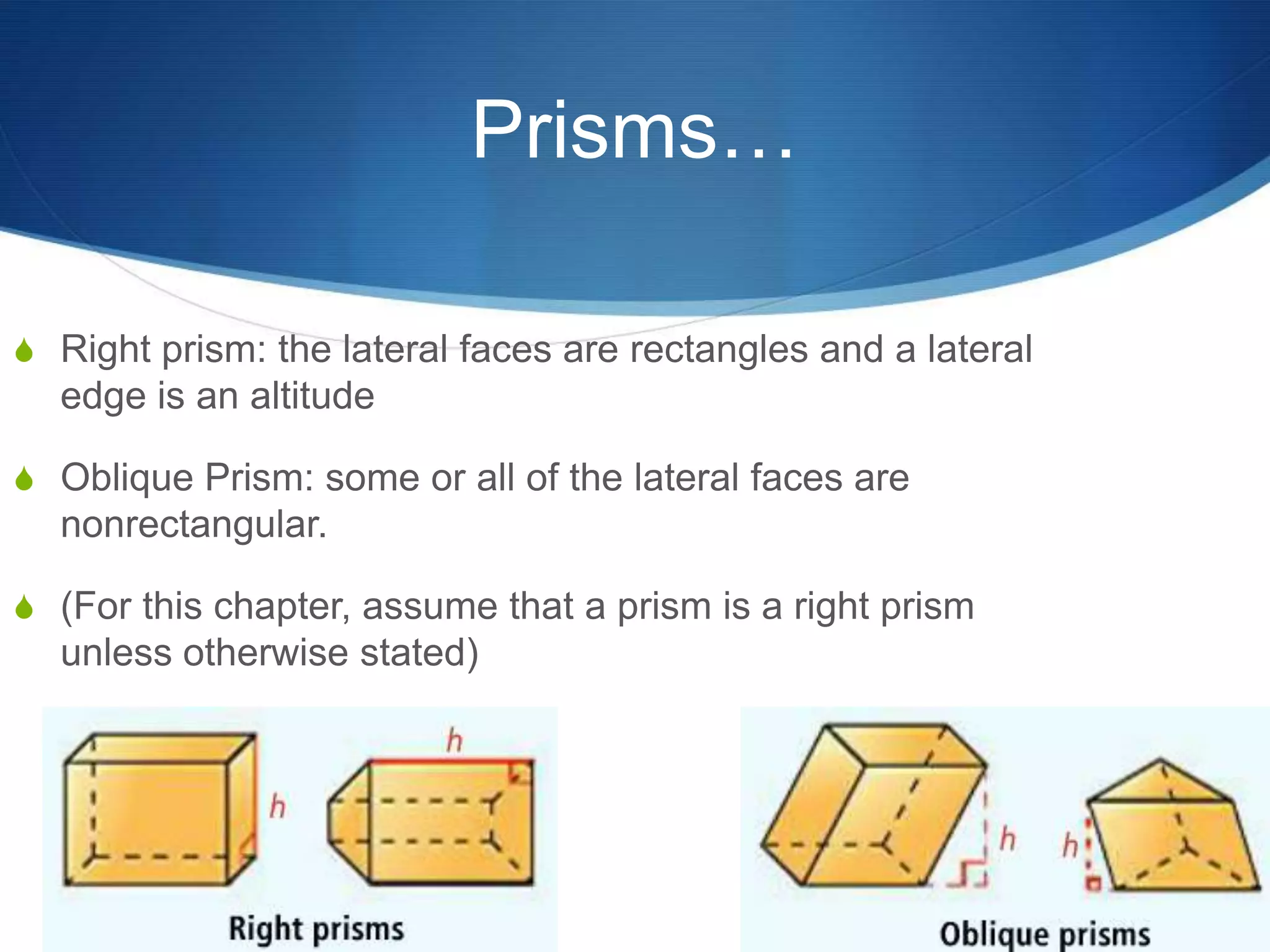
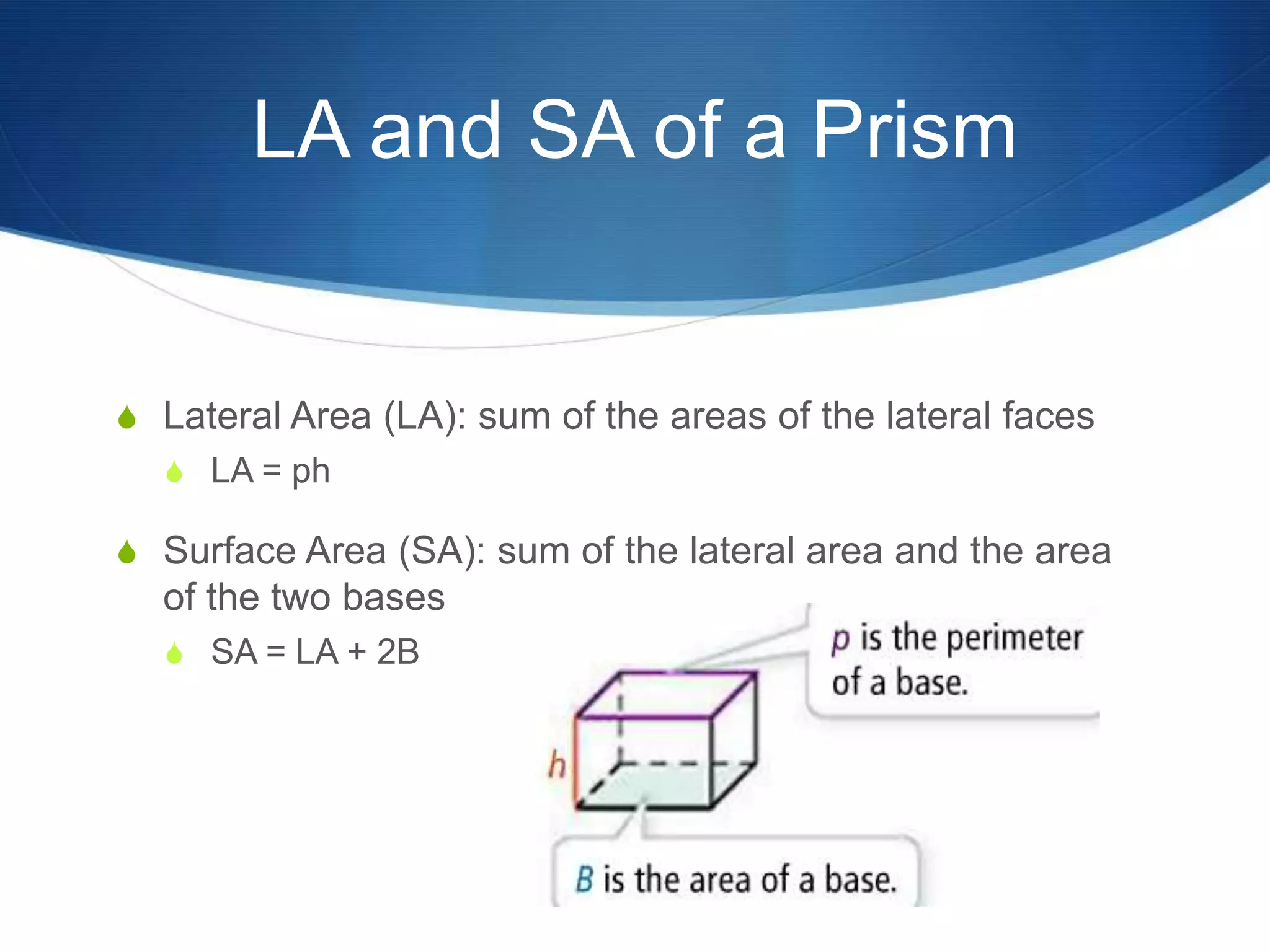
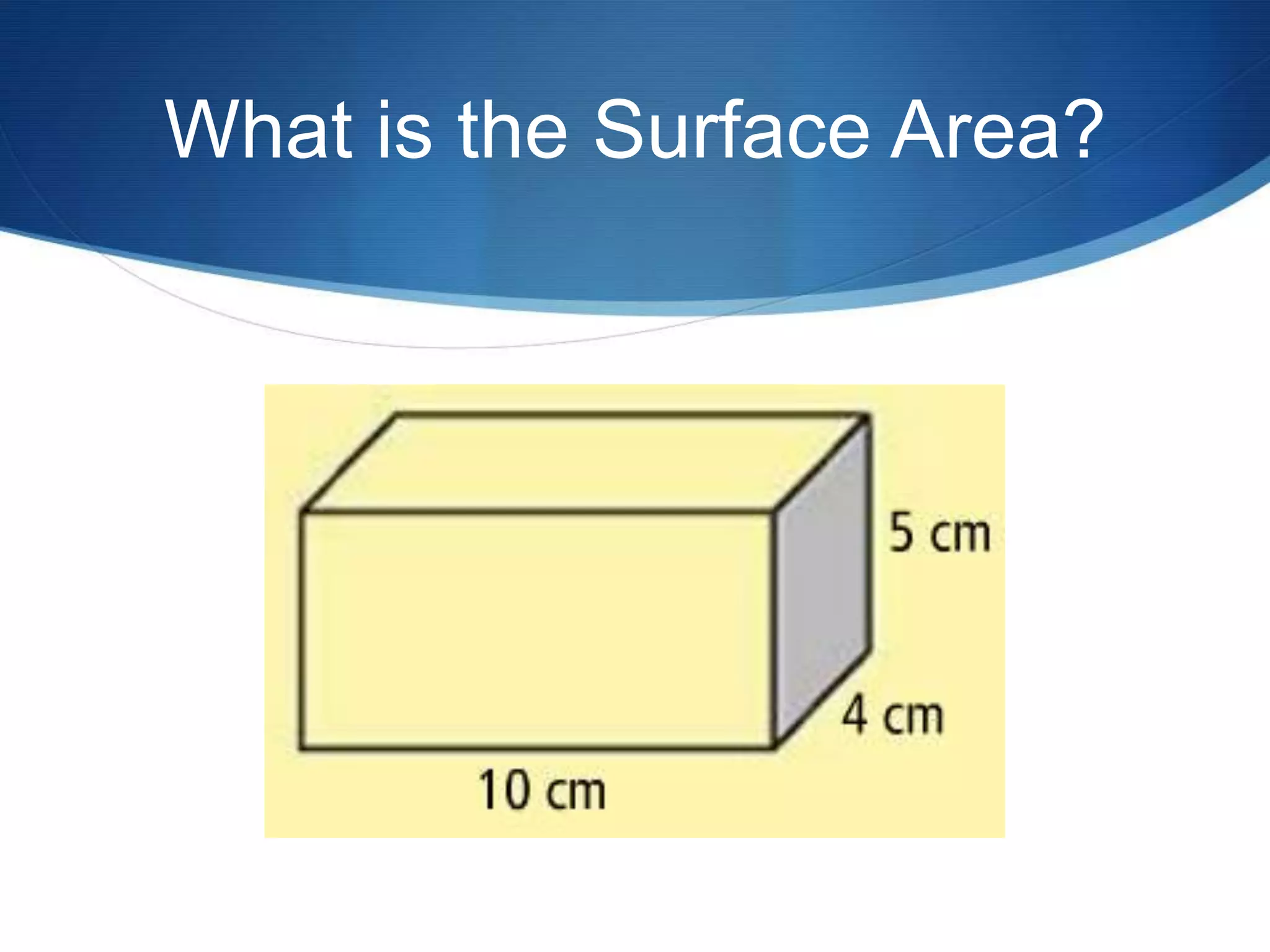
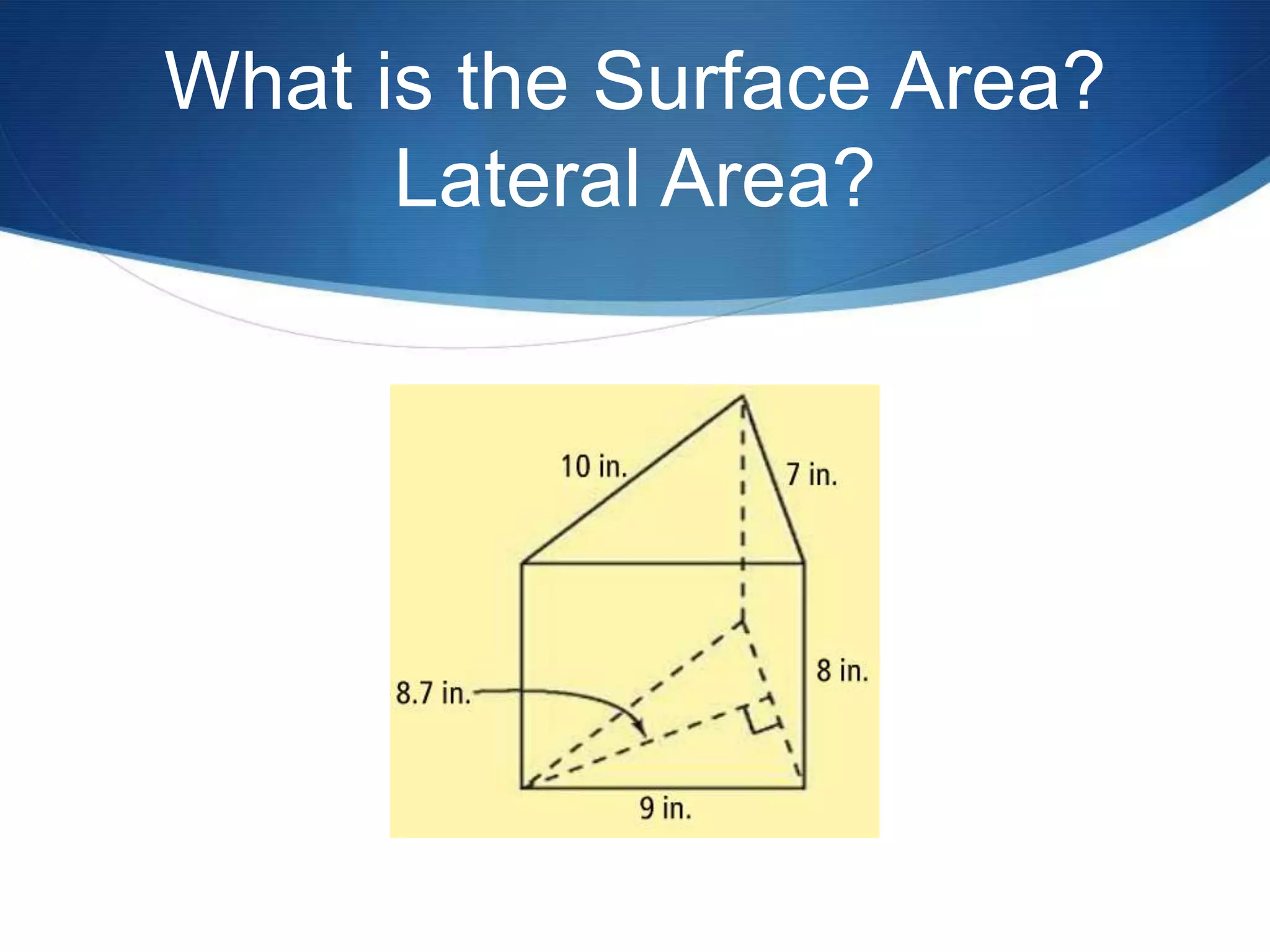
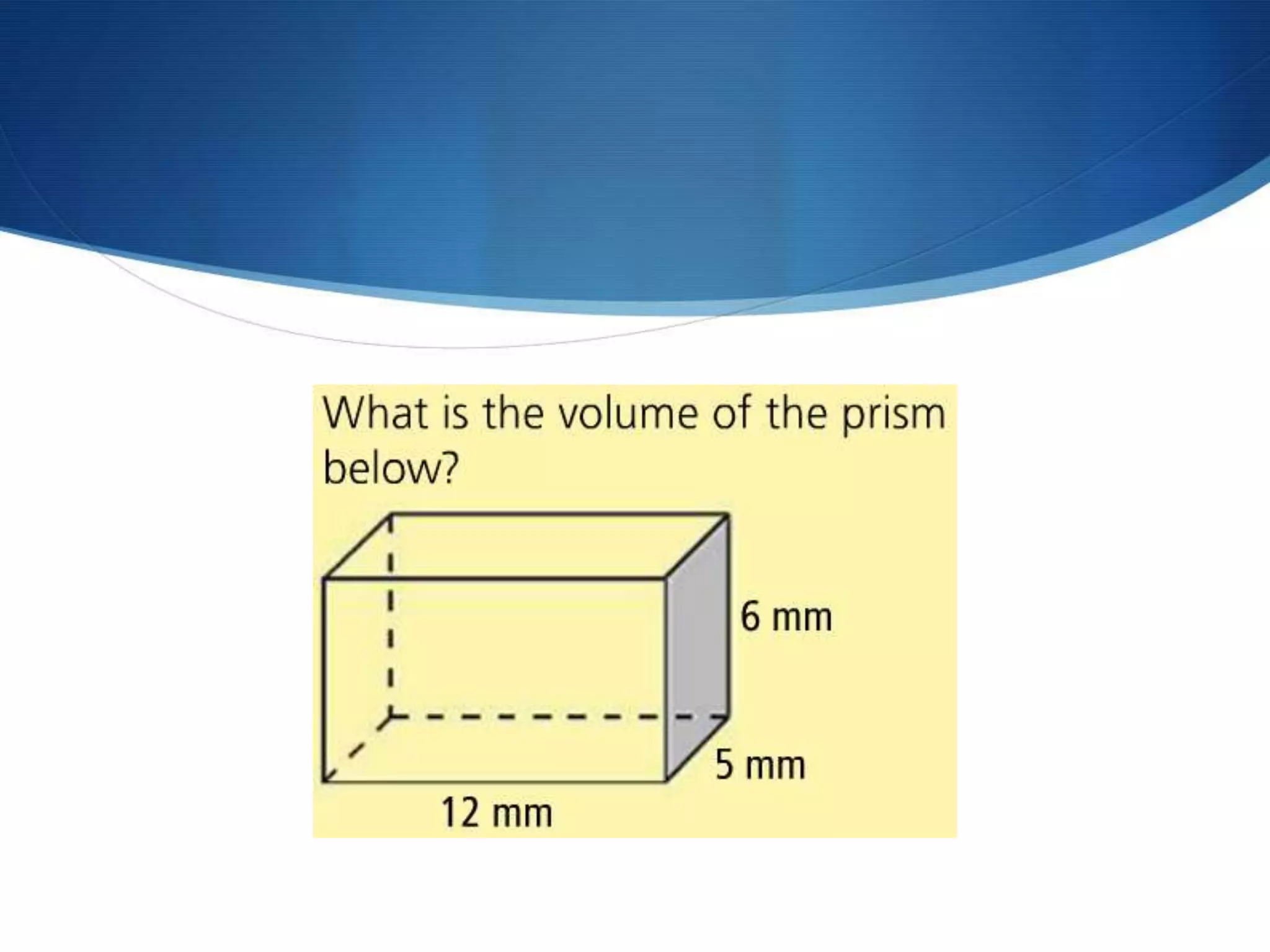
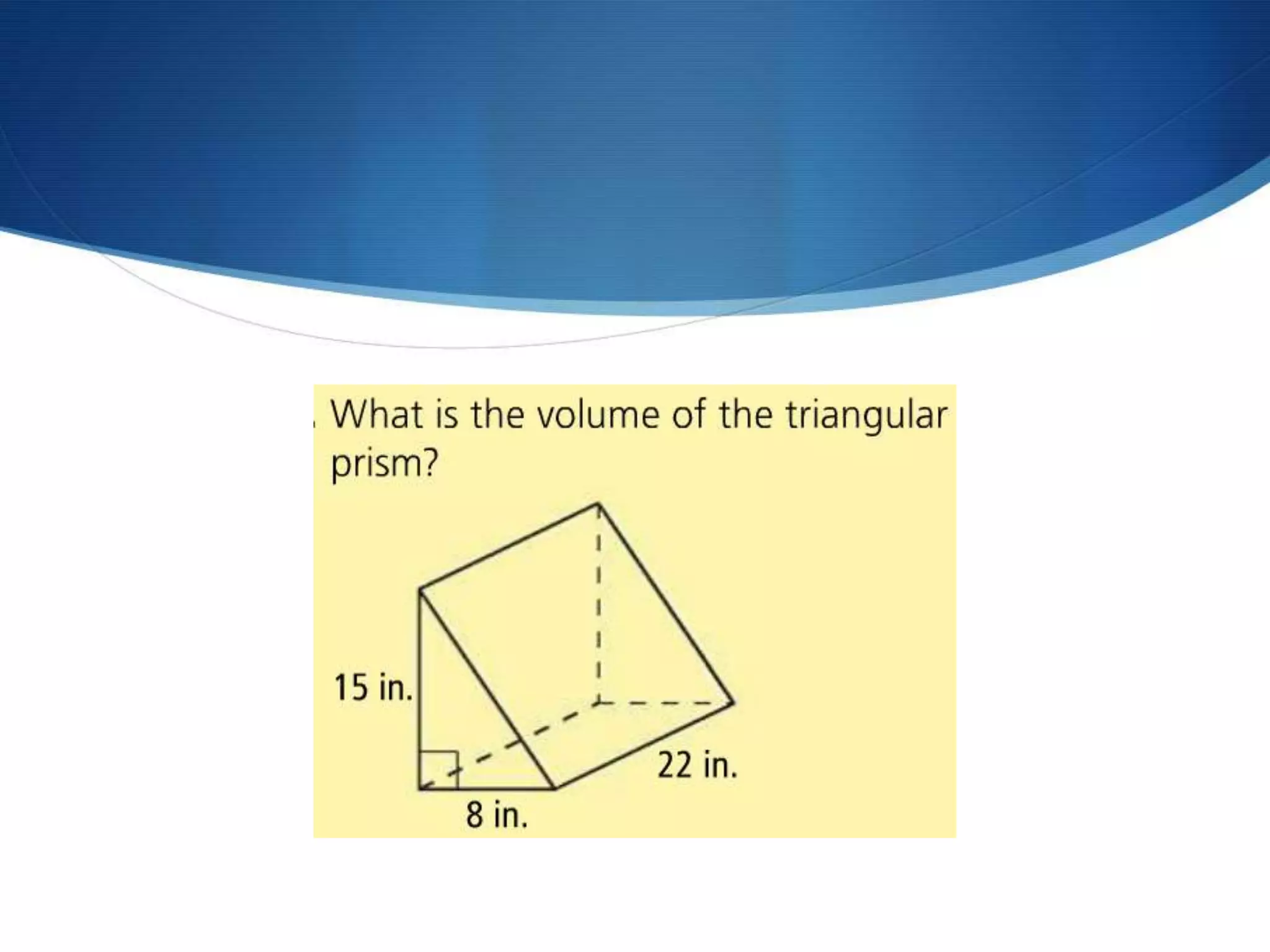
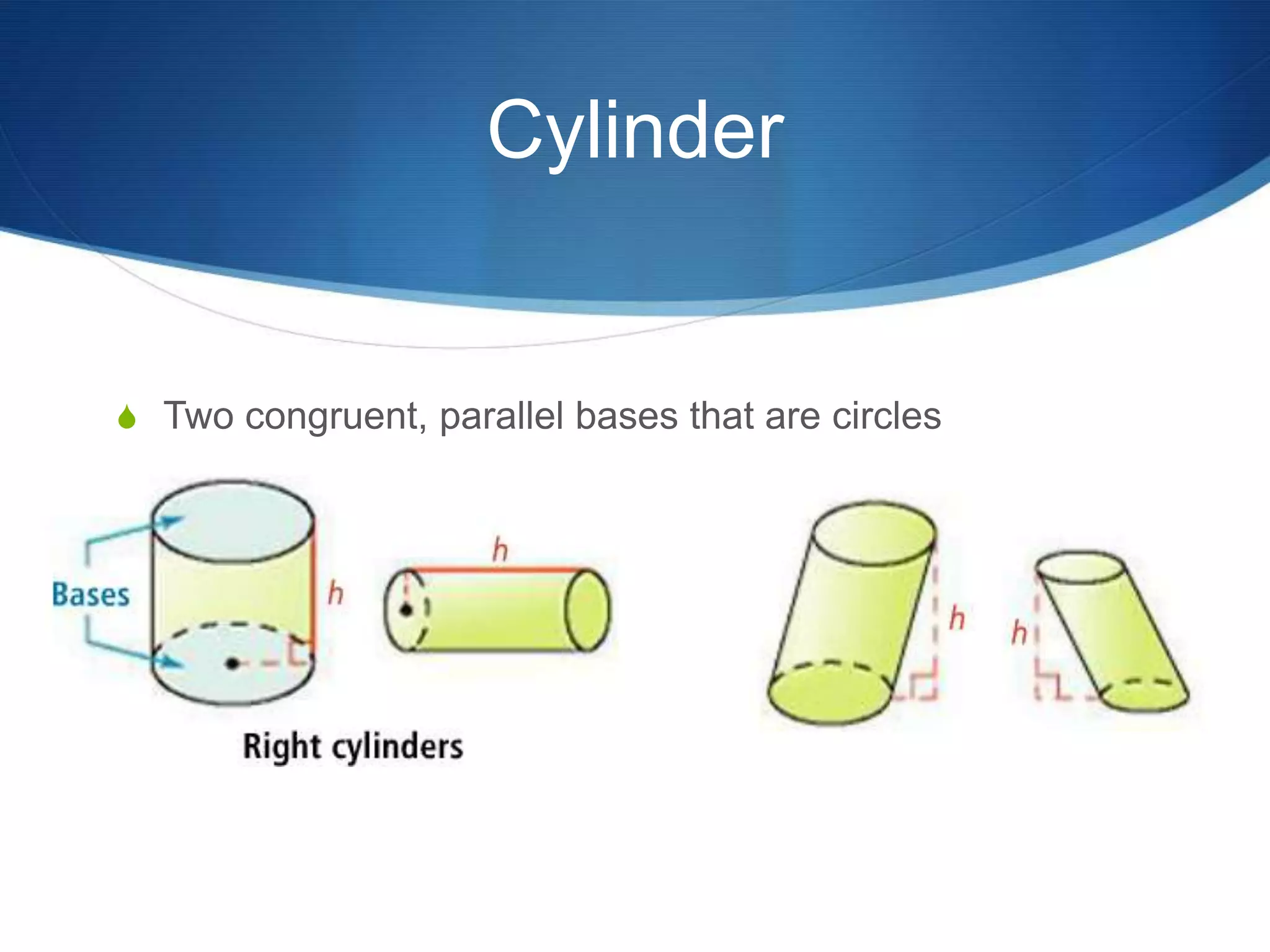
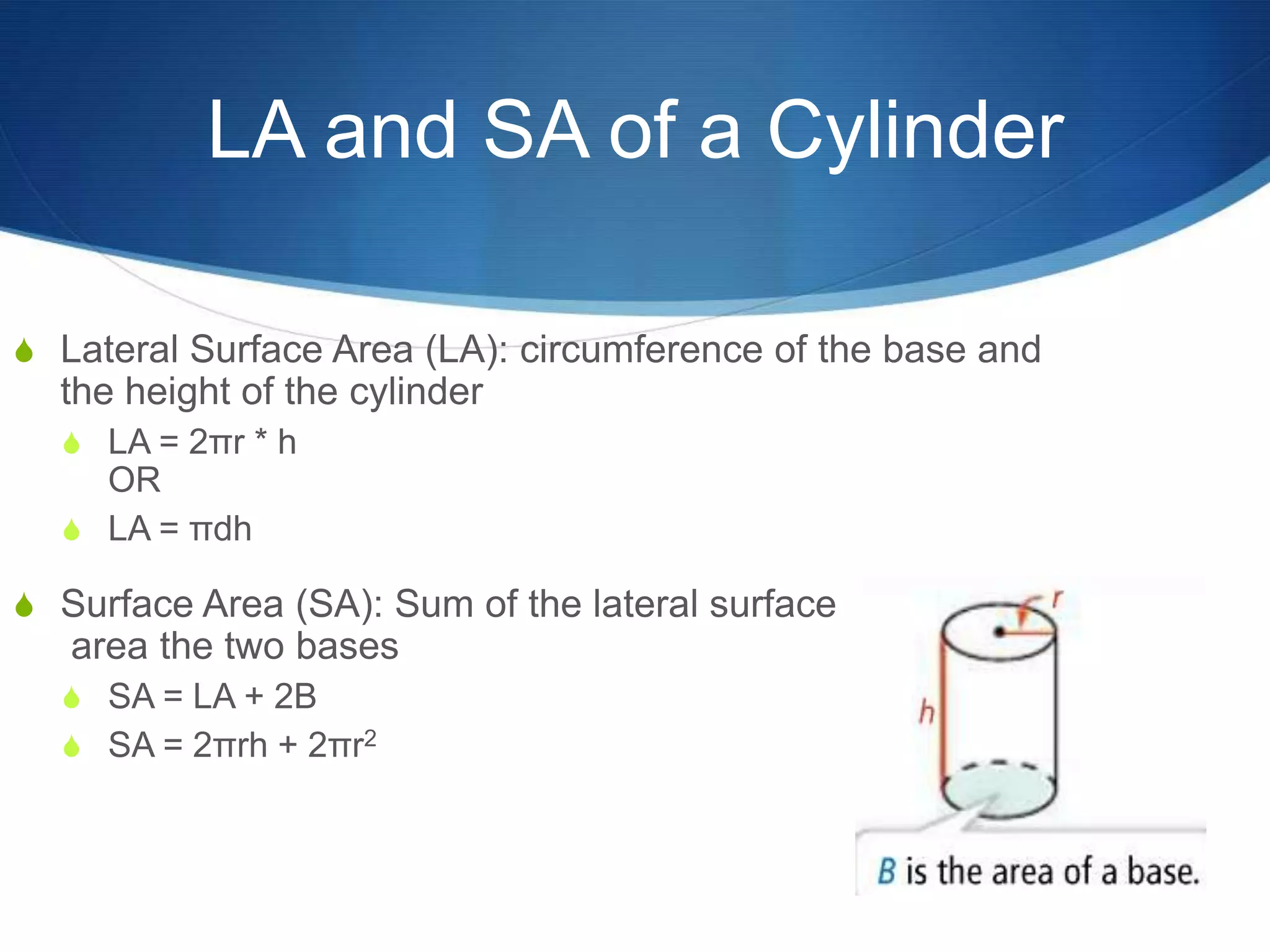
The document provides information about surface area and volume of 3D shapes. It defines polyhedrons, prisms, cylinders, and their key components. It explains how to calculate the surface area of prisms and cylinders by finding the sum of the lateral area and base areas. It also explains how to calculate the volume of prisms and cylinders by multiplying the area of the base by the height. Students are assigned 17 homework problems calculating surface areas and volumes of various prisms and cylinders.