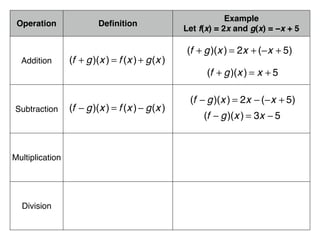
The document discusses operations that can be performed on functions, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Definitions of each operation are provided, along with examples of applying the operations to specific functions. Addition of functions involves adding the outputs of each function, subtraction involves subtracting the outputs, multiplication involves multiplying the outputs, and division involves dividing the outputs given the denominator function is not equal to 0. Several examples are worked through applying the different operations to functions like f(x)=2x and g(x)=-x+5. The examples also demonstrate evaluating composite functions and restricting domains as needed.