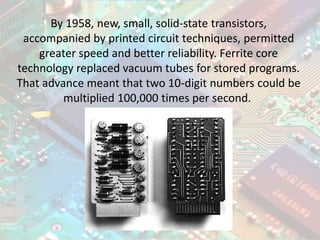
Electronics deals with electrical circuits involving active components like transistors and diodes. Vacuum tubes were early electronic components and drove technological advances in the early 20th century. By the 1950s, transistors replaced vacuum tubes and allowed for smaller, faster, and more reliable electronics. Key branches of electronics include digital, analog, microelectronics, and optoelectronics. Electronics is widely used today for entertainment, communication, defense applications, industrial control, medical devices, and instrumentation.