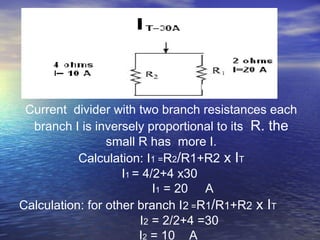
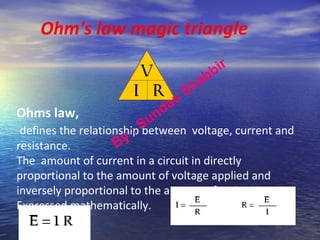
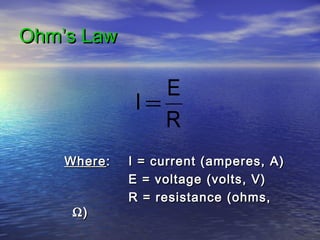
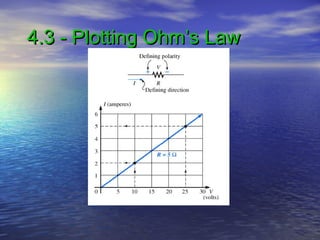
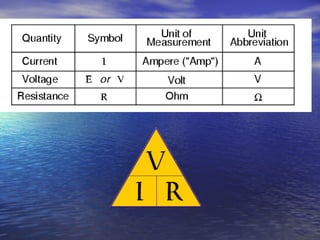
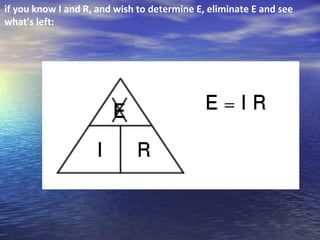
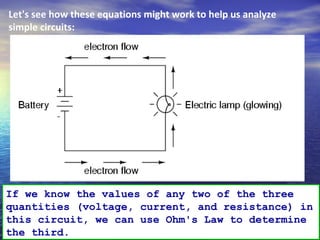
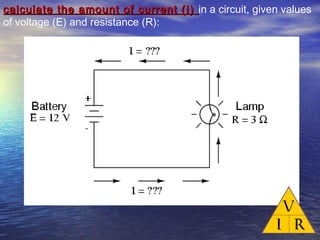
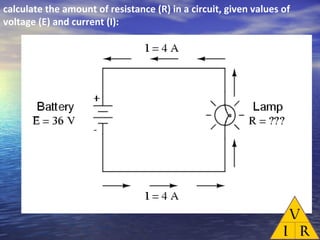
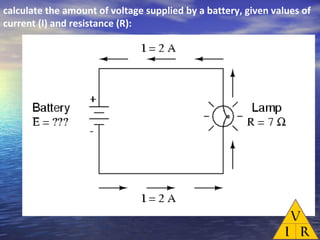
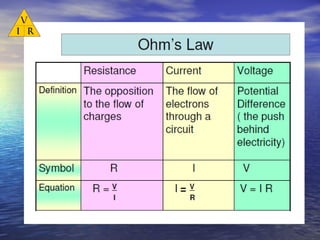
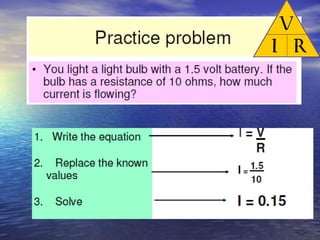
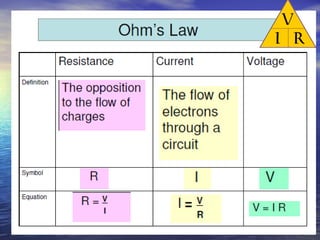
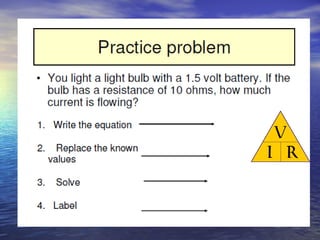
Ohm's law defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. It states that current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance. The amount of current, voltage, or resistance in a circuit can be calculated if two of the three values are known using the equation: I = V/R
Some key points about Ohm's law include:
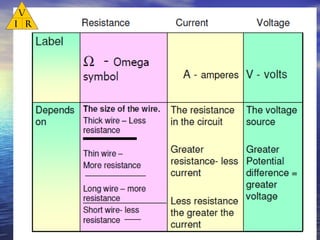
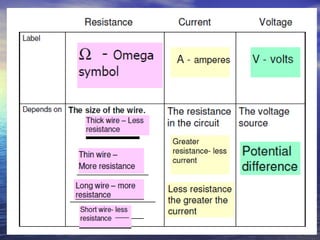
- Voltage is measured in volts (V), current in amps (A), and resistance in ohms (Ω)
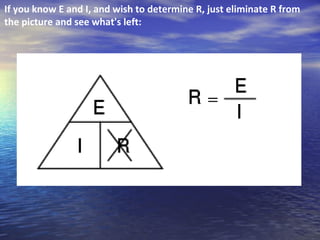
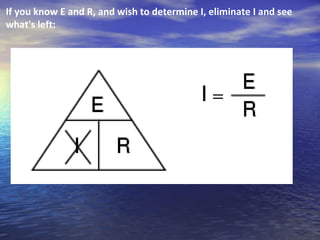
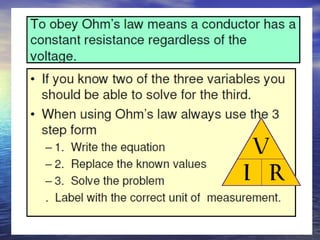
- Ohm's law can be rearranged to solve for any of the three circuit variables
- Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating unknown values given two known values
















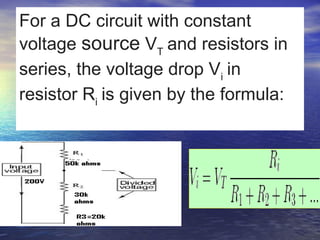
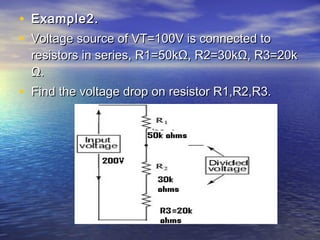
![• VVi - voltage drop in resistor Ri in volts [V].i - voltage drop in resistor Ri in volts [V].
• VTVT - the equivalent voltage source or - the equivalent voltage source or
voltage drop in volts [V].voltage drop in volts [V].
• RRi - resistance of resistor i - resistance of resistor RRi in ohms [Ω].i in ohms [Ω].
• RR1 - resistance of resistor 1 - resistance of resistor RR1 in ohms [Ω].1 in ohms [Ω].
• RR2 - resistance of resistor 2 - resistance of resistor RR2 in ohms [Ω].2 in ohms [Ω].
• RR3 - resistance of resistor 3 - resistance of resistor RR3 in ohms [Ω].3 in ohms [Ω].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sssa-140312143914-phpapp01/85/Ohms-Law-36-320.jpg)