Embed presentation
Downloaded 353 times




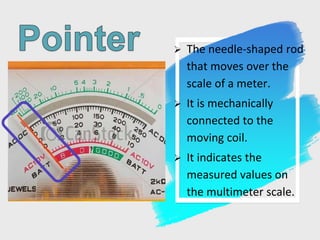







The multimeter, also known as a VOM, can measure voltage, resistance, and current. It exists in two forms, analog and digital. The analog multimeter uses a needle that moves across a scale to indicate measured values. The digital multimeter uses buttons to select functions and ranges and displays numeric readings. Both types are zeroed before measurements and have probes to connect to circuits under test.










