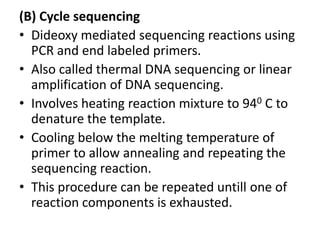
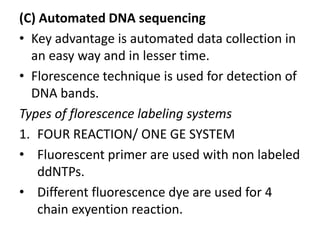
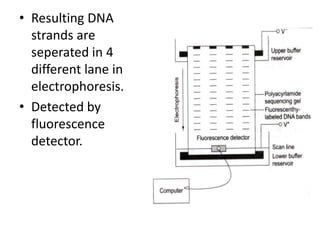
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the order of nucleotides in DNA. There are several methods of DNA sequencing including conventional, cycle sequencing, automated sequencing, and pyrosequencing. Conventional methods include chemical degradation and chain termination. Chemical degradation uses base-specific chemical reactions to cleave DNA fragments for sequencing. Chain termination uses DNA polymerase and dideoxynucleotides to terminate DNA strand extension for sequencing. Cycle sequencing applies the chain termination method to PCR for linear amplification of sequencing products. Automated sequencing uses fluorescence labeling for high-throughput sequencing. Pyrosequencing sequences DNA by detecting pyrophosphate release during polymerase nucleotide incorporation without electrophoresis.




![(A)Conventional DNA sequencing methods:
1. Chemical degradation method
[ Maxam and Gilbert’s method]
• This method involves the base specific
chemical cleavage of an end labeled DNA
segment to generates a set of labeled
molecules.
PRINCIPLE:
• The partially cleaved DNA fragment is
subjected to five separate chemical reactions.
• Each of which is specific for a particular base.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnasequencing-130416001849-phpapp02/85/Dna-sequencing-6-320.jpg)




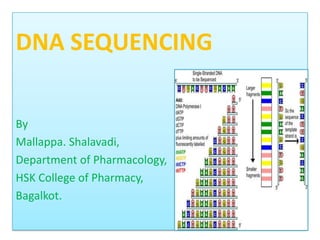
![2. Chain Termination Method
[Sanger’s Dideoxy method]
• Developed by Frederic’s Sanger.
• Common method.
• Involves controlled synthesis of DNA to
generate fragments terminating at specific
point.
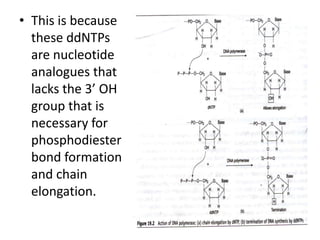
PRINCIPLE
• Replacement of dNTPs with 2’, 3’ dideoxy
NTPs in the DNA chain terminates DNA
synthesis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnasequencing-130416001849-phpapp02/85/Dna-sequencing-11-320.jpg)