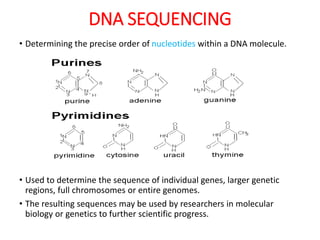
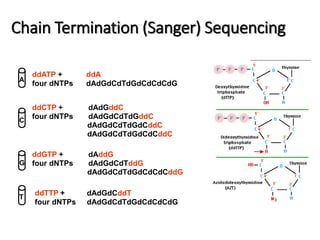
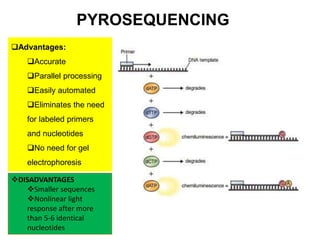
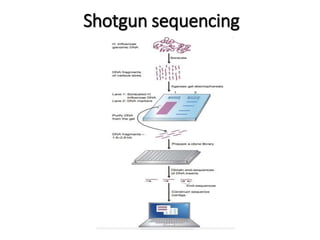
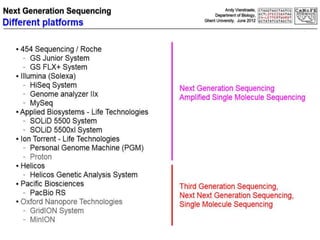
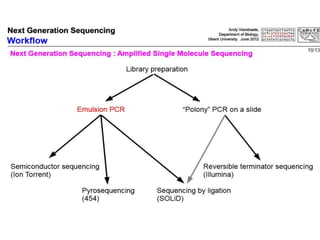
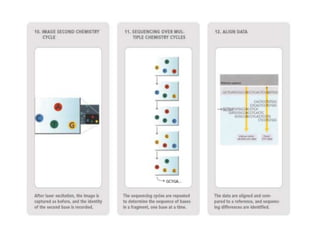
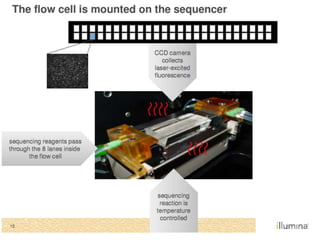
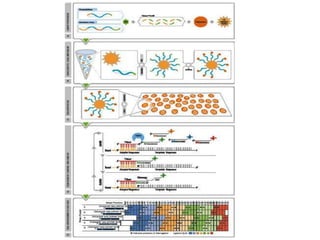
This document discusses the history and various methods of DNA sequencing. It begins with a brief overview of DNA sequencing and its uses. It then outlines some of the major developments in DNA sequencing techniques, including the earliest RNA sequencing in 1972, Sanger sequencing in 1977, and the first complete genome of Haemophilus influenzae in 1995. The document proceeds to provide more detailed explanations of several DNA sequencing methods, such as Sanger sequencing, pyrosequencing, shotgun sequencing, Illumina sequencing, and SOLiD sequencing.