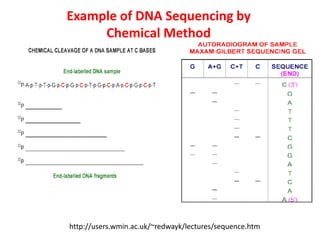
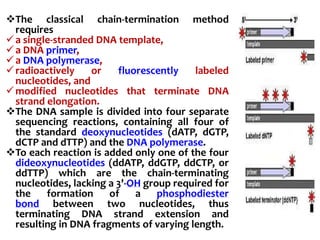
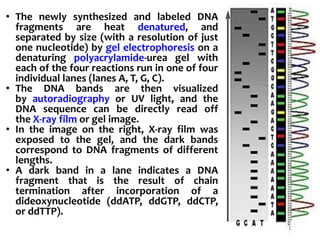
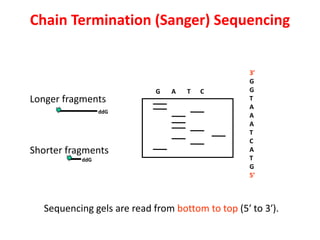
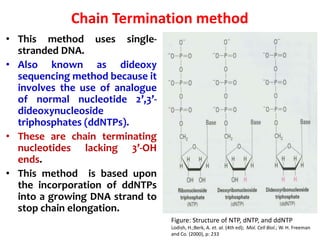
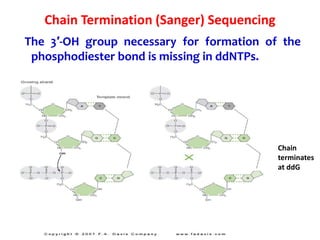
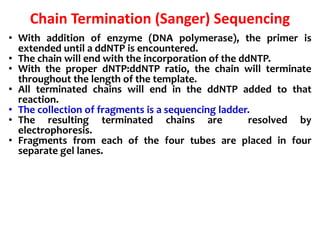
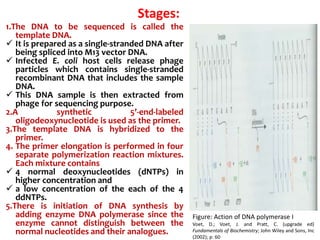
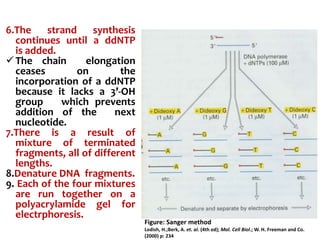
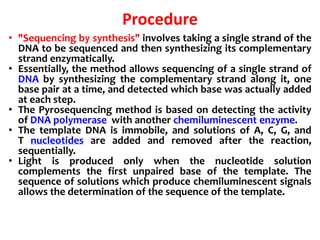
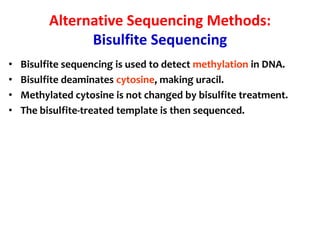
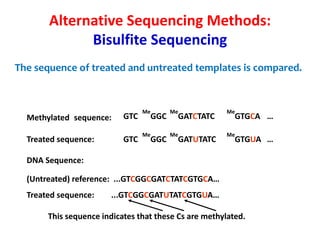
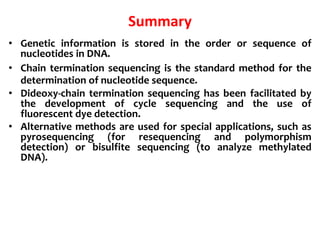
1) DNA sequencing refers to determining the order of nucleotide bases (A, G, C, T) in a DNA molecule. This provides essential genetic information for growth and development.
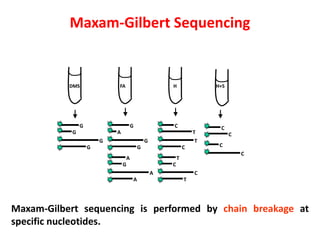
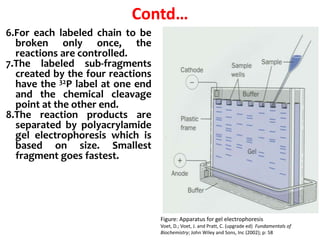
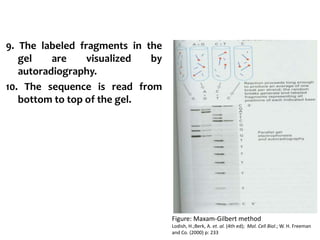
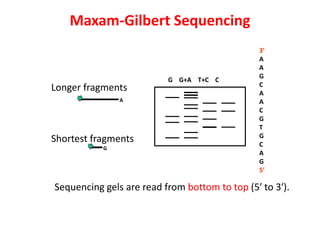
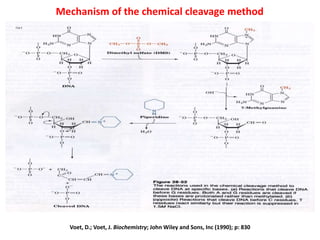
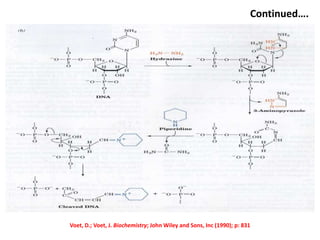
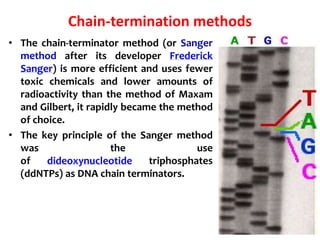
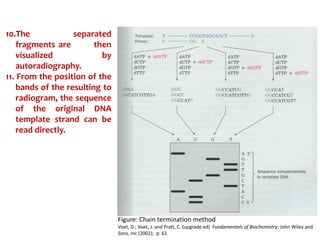
2) Two major early methods for DNA sequencing were the chemical cleavage method developed by Maxam and Gilbert in 1977 and the chain termination method developed by Sanger. Sanger's method became more popular due to fewer toxic chemicals.
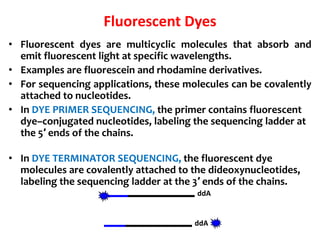
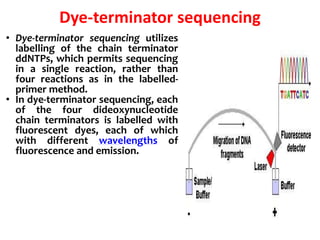
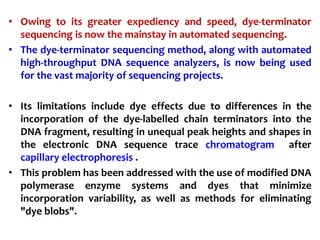
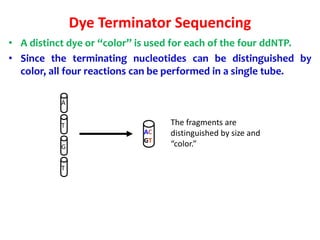
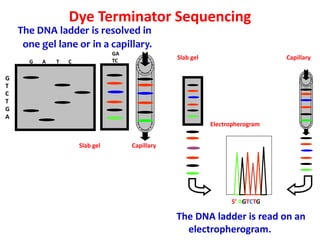
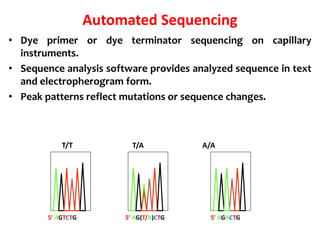
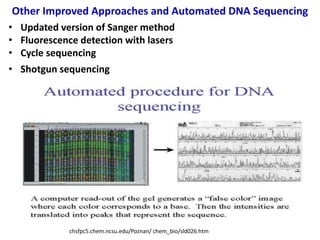
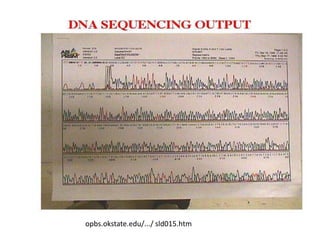
3) Modern DNA sequencing often uses fluorescent dye-labeled chain terminators and capillary electrophoresis. Each dye fluoresces at a different wavelength, allowing all four reactions to occur in one tube. This high-throughput automated approach has accelerated genomic research.