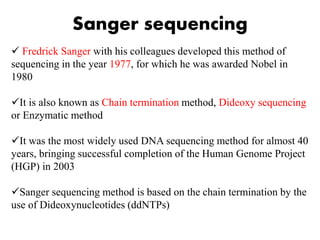
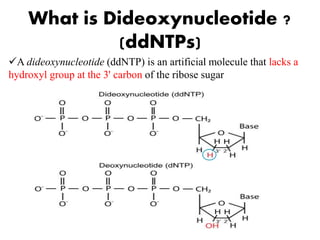
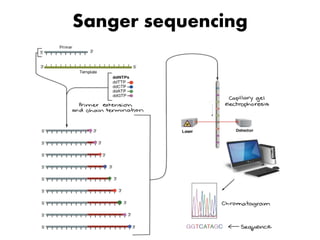
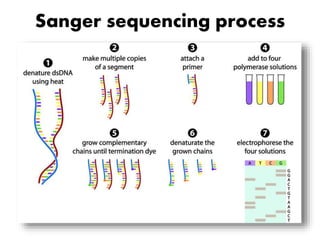
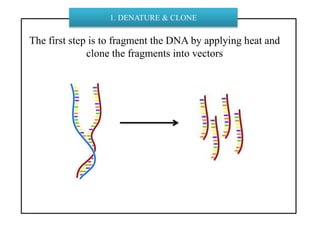
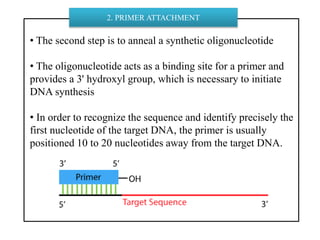
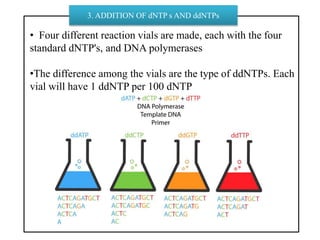
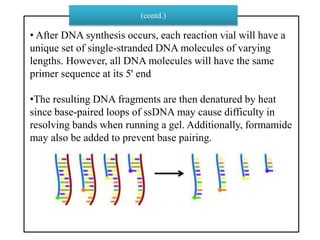
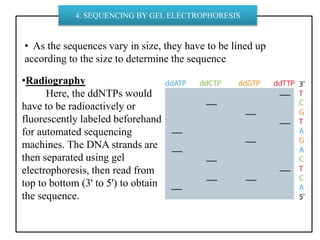
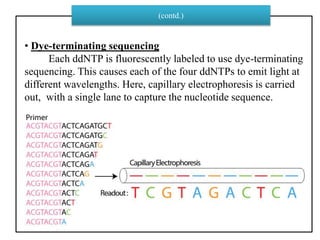
DNA sequencing determines nucleotide sequences in DNA, with Sanger sequencing being a prominent method developed in 1977. This method involves steps including denaturing DNA, annealing primers, adding nucleotides, and sequencing via gel electrophoresis or dye-terminating techniques. While Sanger sequencing is accurate and easier to automate, it has limitations such as generating short reads and requiring electrophoretic separation, leading to time consumption.