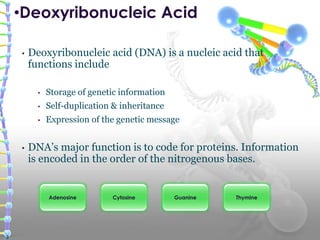
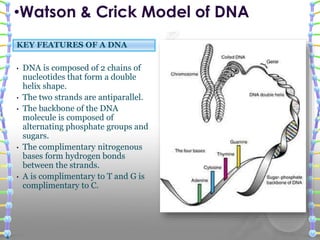
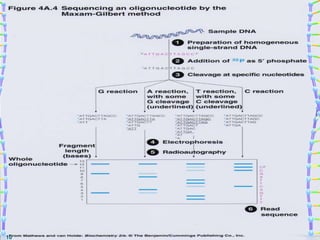
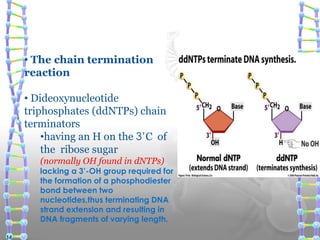
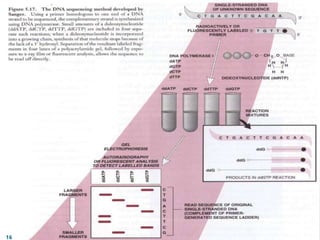
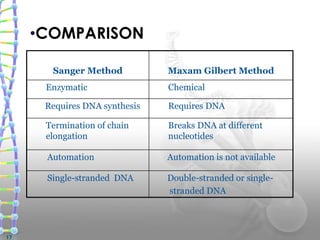
DNA sequencing methods determine the order of nucleotide bases in a DNA sample. The first methods were developed in the 1970s by Maxam and Gilbert (chemical method) and Sanger (chain termination method). The Sanger method is now most commonly used. It involves DNA synthesis with chain terminating nucleotides to generate fragments of different lengths that can be separated and read to determine the DNA sequence. DNA sequencing has revolutionized biological sciences by allowing for gene mapping and identification of genetic variations linked to disease.