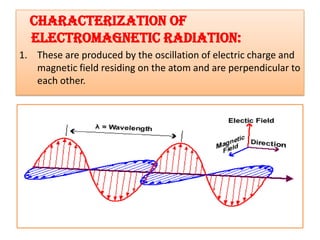
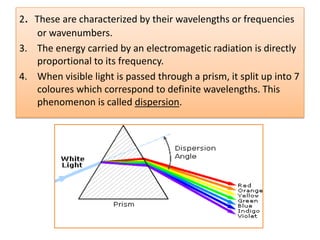
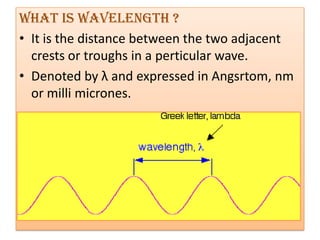
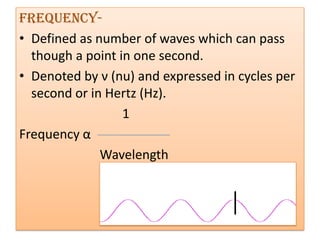
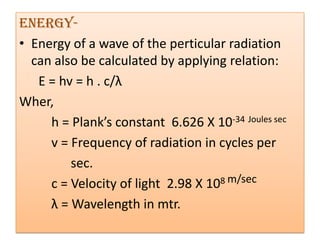
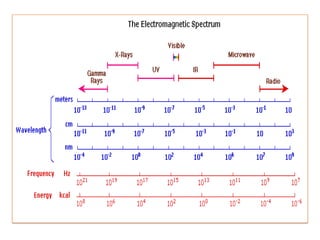
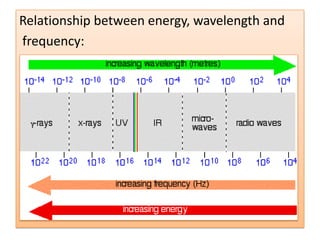
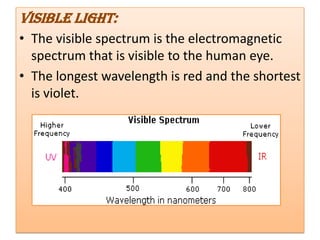
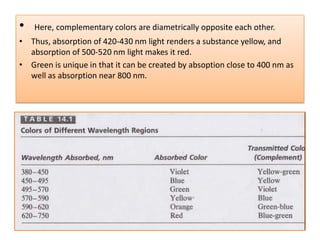
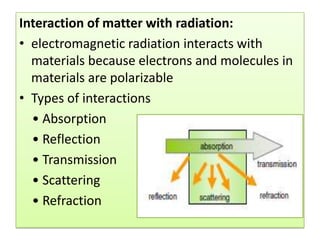
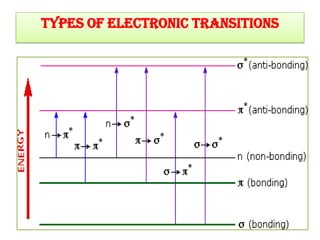
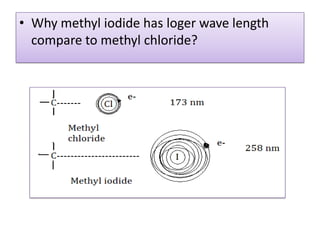
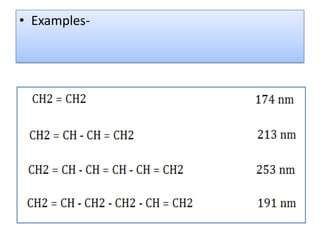
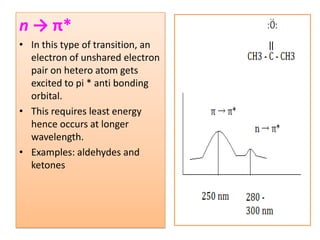
UV-Visible spectroscopy involves using electromagnetic radiation in the UV-Visible range to analyze molecules based on their absorption characteristics, which are determined by electronic transitions between molecular orbitals. Different types of transitions like σ→σ*, n→π*, and π→π* occur at different wavelengths and can be used to identify functional groups in compounds. This technique provides information about the structure and bonding of molecules based on their absorption spectra.