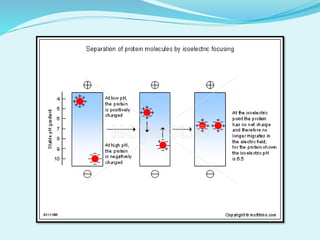
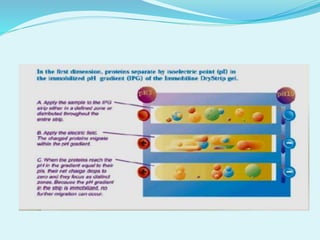
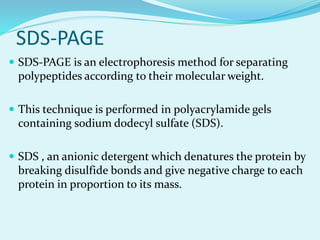
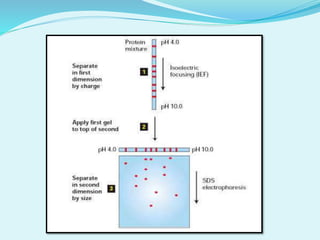
2D-PAGE is a technique used to separate complex protein mixtures based on isoelectric point and molecular weight. It involves two sequential steps - isoelectric focusing and SDS-PAGE. In isoelectric focusing, proteins are separated based on their isoelectric point in an immobilized pH gradient. They are then separated by SDS-PAGE based on their molecular weight. The separated proteins can then be visualized through staining and identified through mass spectrometry. While useful for proteomic analysis, 2D-PAGE has limitations such as low reproducibility and dynamic range.