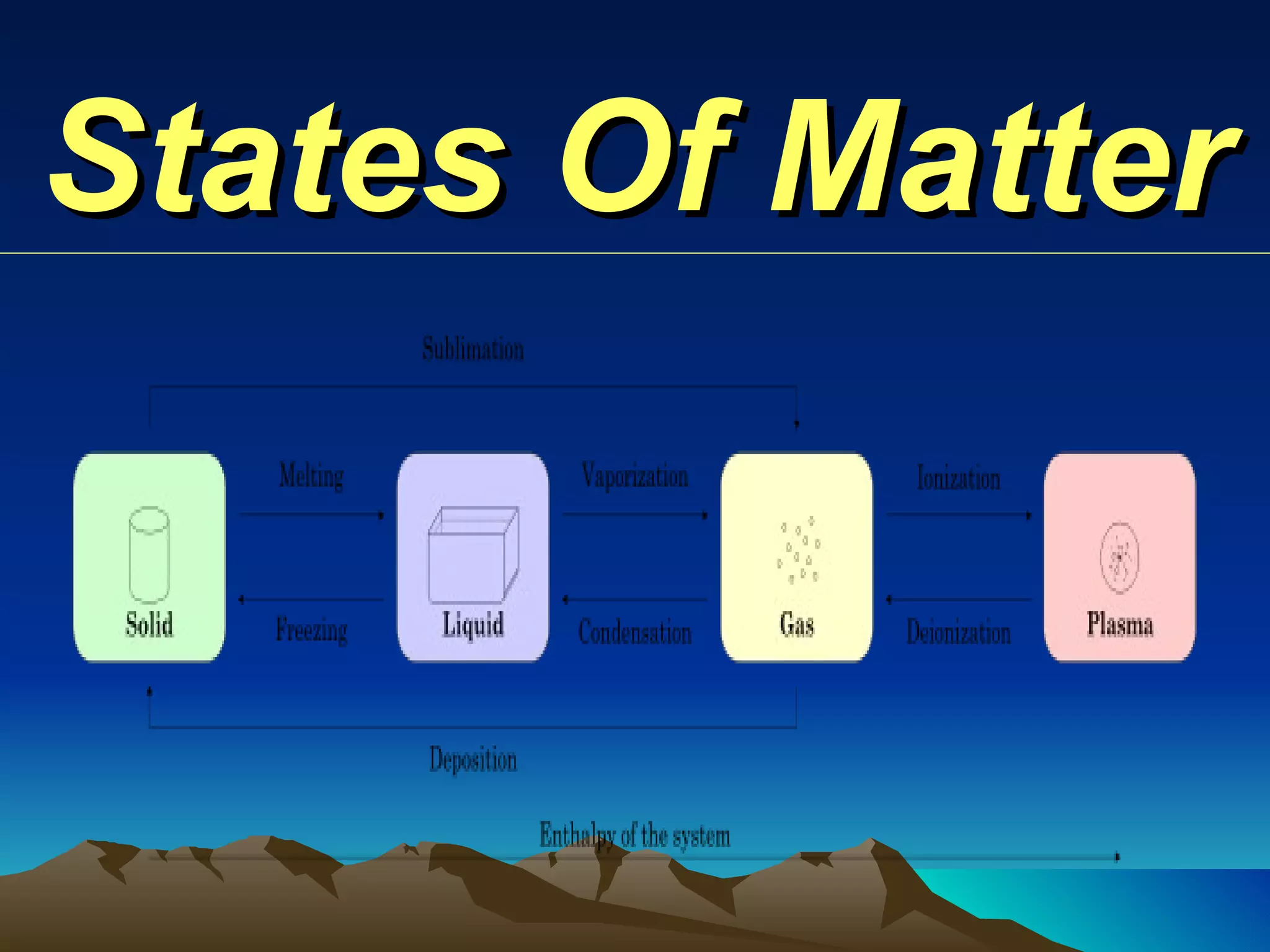
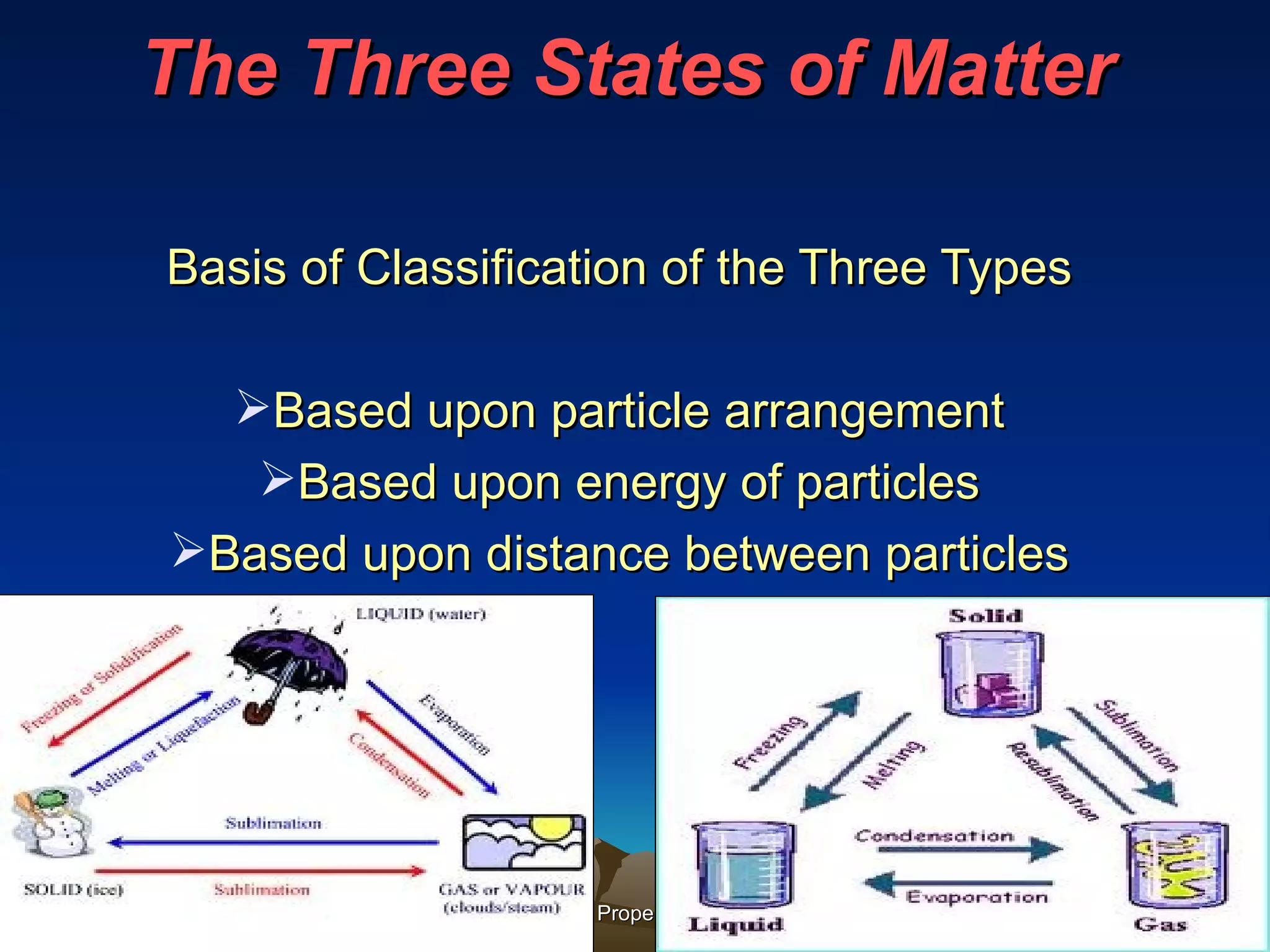
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. It exists in three main states: solid, liquid, and gas. The state depends on how tightly or loosely the particles are packed. Solids have a fixed shape and volume as particles are tightly packed and vibrate in place. Liquids take the shape of their container but maintain a fixed volume as particles can move past one another. Gases have no definite shape or volume as particles are very far apart and move freely. Water can change states by adding or removing heat, going from solid ice to liquid to gas vapor.