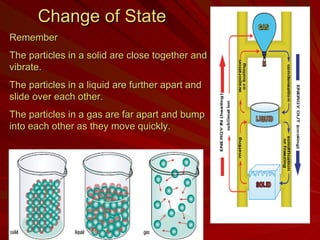
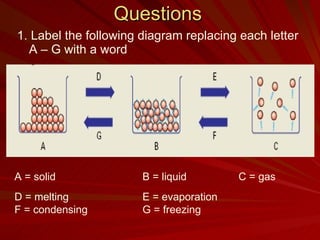
The document discusses physical and chemical changes. Physical changes alter the state of a substance but do not create a new substance, such as melting, freezing, or breaking something into smaller pieces. Chemical changes form an entirely new substance, evidenced by a change in color, gas release, or new solid forming. Examples of physical changes include shattering a plate or melting wax, while examples of chemical changes include burning wood or rusting metal.