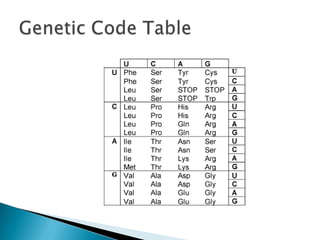
The document discusses the genetic code, which is the set of rules by which DNA and mRNA sequences are translated into amino acid sequences in proteins. Some key points are:
- The genetic code is made up of 3 nucleotide sequences called codons that each encode for a specific amino acid.
- The code is degenerate, meaning most amino acids are encoded by more than one codon.
- Experiments in the 1960s were the first to demonstrate that the genetic code consists of codons that are three nucleotides long and elucidated the nature of the codon-amino acid relationship.