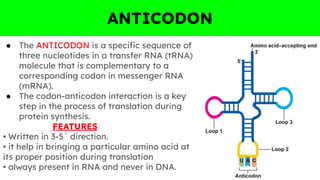
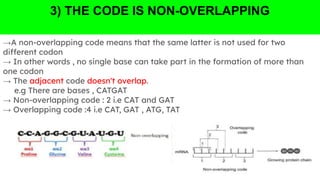
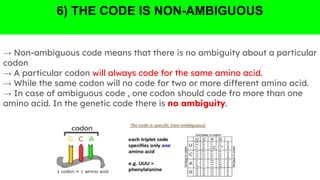
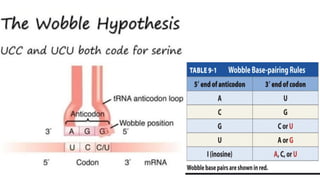
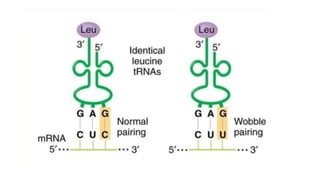
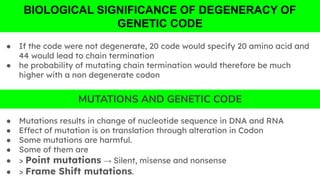
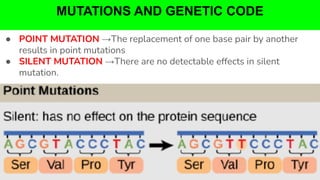
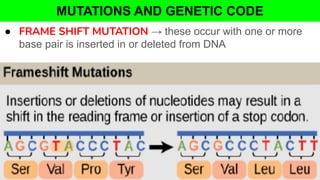
The document outlines the genetic code and the central dogma, detailing how DNA information is transcribed to mRNA and translated into proteins. It discusses codon and anticodon interactions, the characteristics of the genetic code, and the significance of its degeneracy, including the wobble hypothesis. Furthermore, it addresses mutations and their impact on genetic coding and protein synthesis.