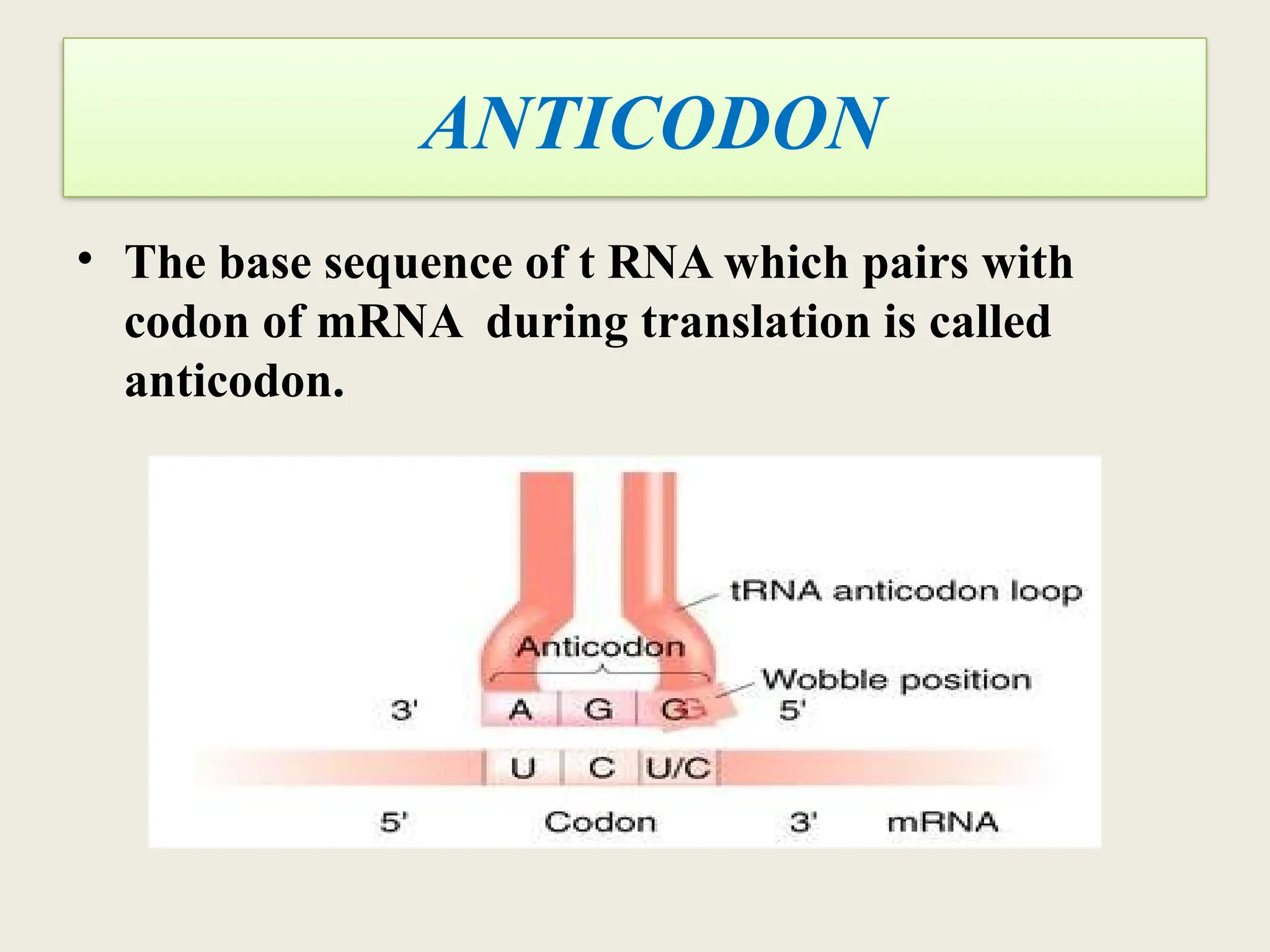
The genetic code is a set of rules that translates nucleotide sequences into proteins, consisting of 64 codons that correspond to 20 amino acids. It features characteristics like being triplet-based, degenerate, and universal, facilitating processes like gene expression and protein synthesis. Applications of the genetic code span various fields, including biotechnology, agriculture, medicine, and forensic science, highlighting its significance in understanding life and advancing human health.