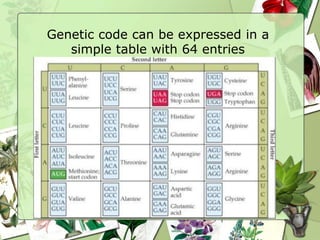
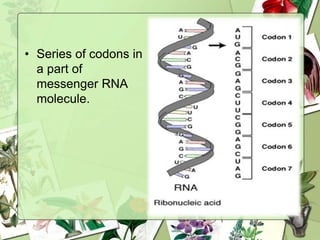
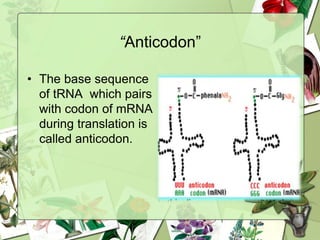
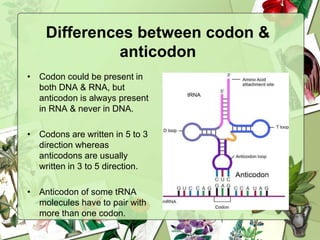
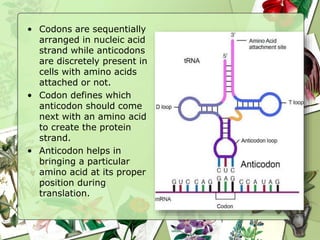
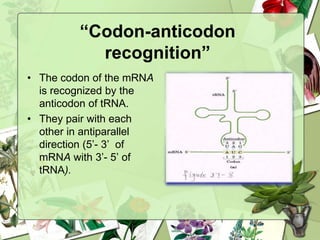
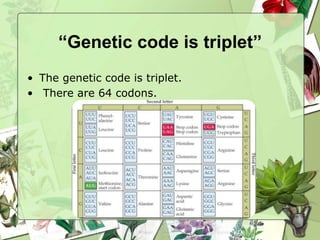
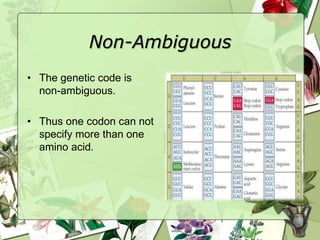
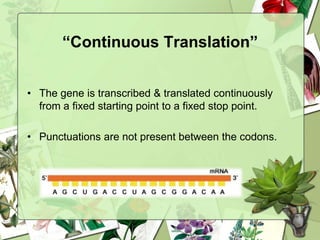
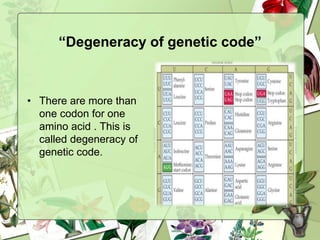
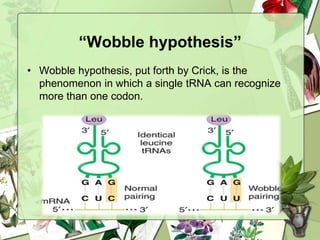
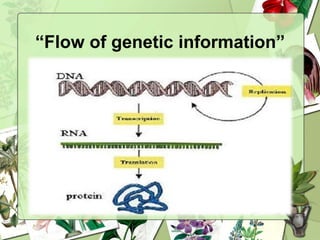
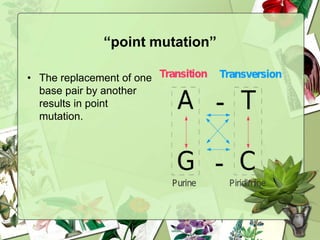
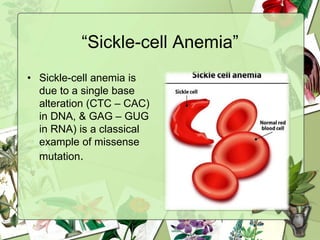
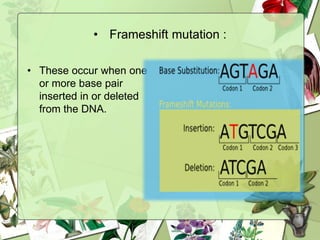
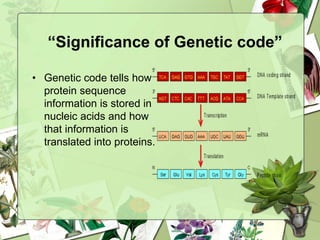
The document summarizes a presentation on the genetic code. It defines the genetic code as the set of rules by which information in DNA and RNA is translated into proteins. It discusses key topics like the discovery of the genetic code, codons and anticodons, characteristics like degeneracy and universality, and how mutations can affect the genetic code. While the genetic code differs slightly between mitochondria and cytoplasm, it is largely universal across living organisms using the same coding mechanism of three-base codons, tRNA, and ribosomes to translate DNA into amino acid sequences.