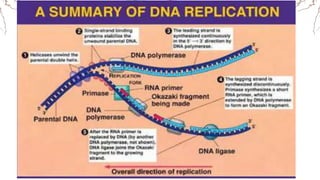
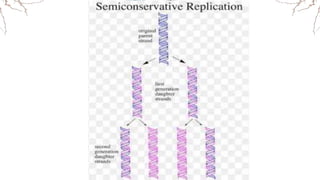
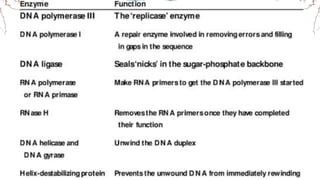
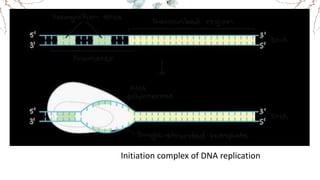
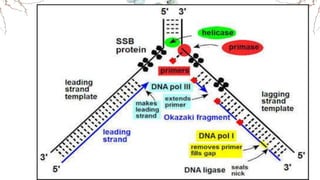
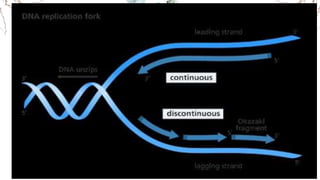
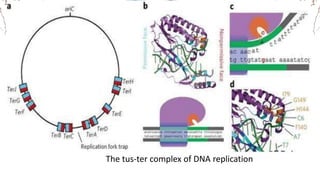
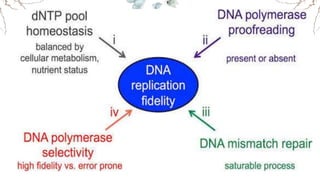
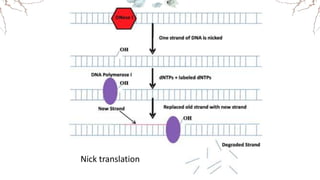
DNA replication involves the synthesis of new DNA strands through a semi-conservative process whereby each new molecule contains one old strand and one new strand synthesized using the old strand as a template. Key enzymes involved include helicase, which unwinds the DNA double helix, primase, which initiates DNA synthesis, and DNA polymerase, which catalyzes phosphodiester bond formation to elongate the new strands. Fidelity is maintained through proofreading mechanisms that remove incorrectly incorporated nucleotides and DNA repair pathways that correct errors made during replication.